Design of Half-Through Cable-Arch Bridge with 700 m Main Span
-
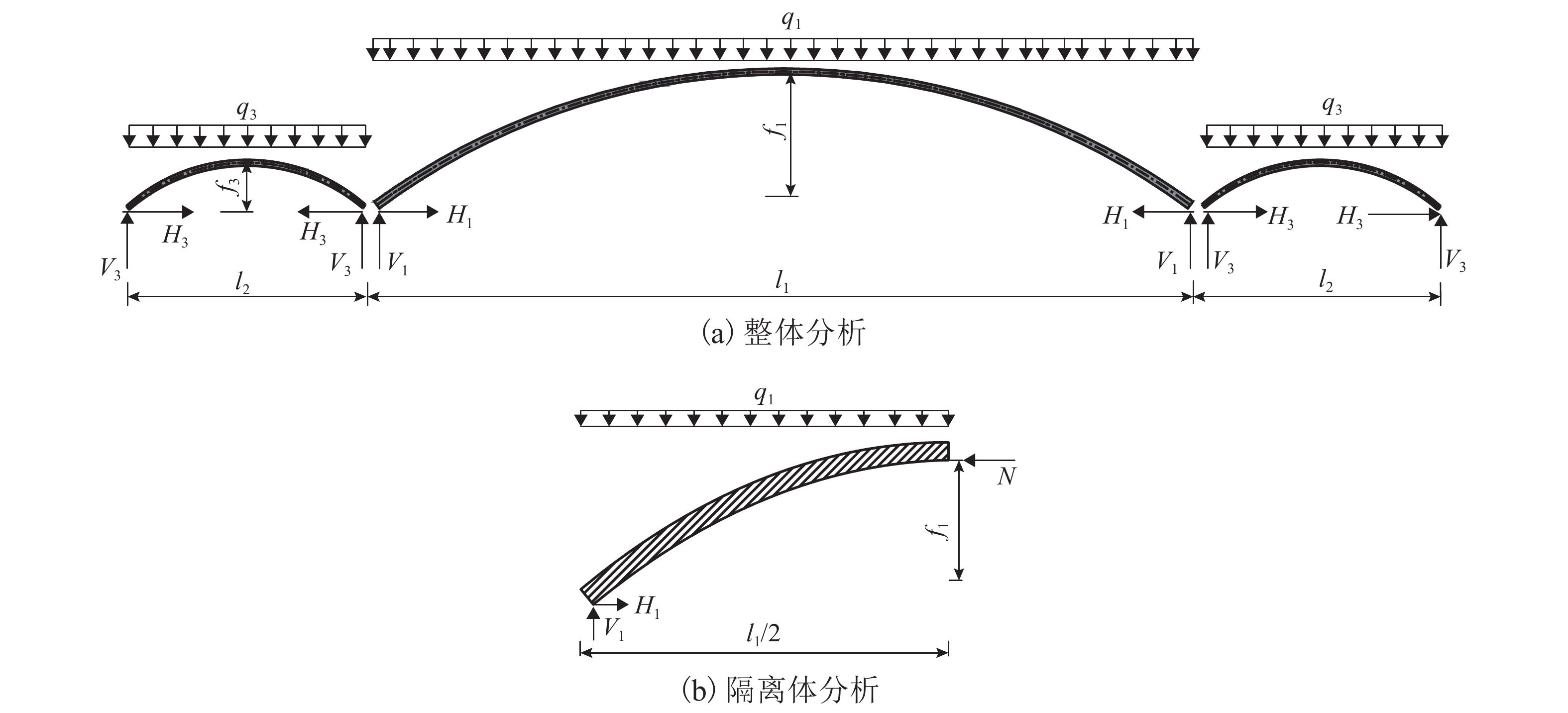
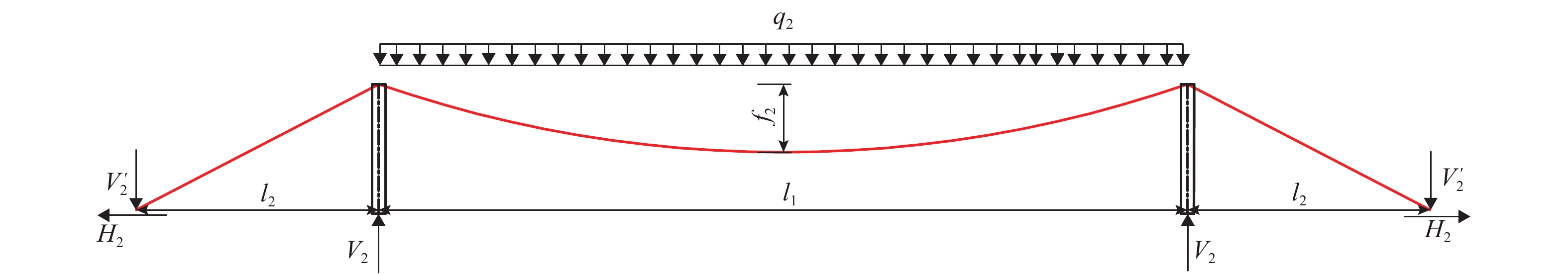
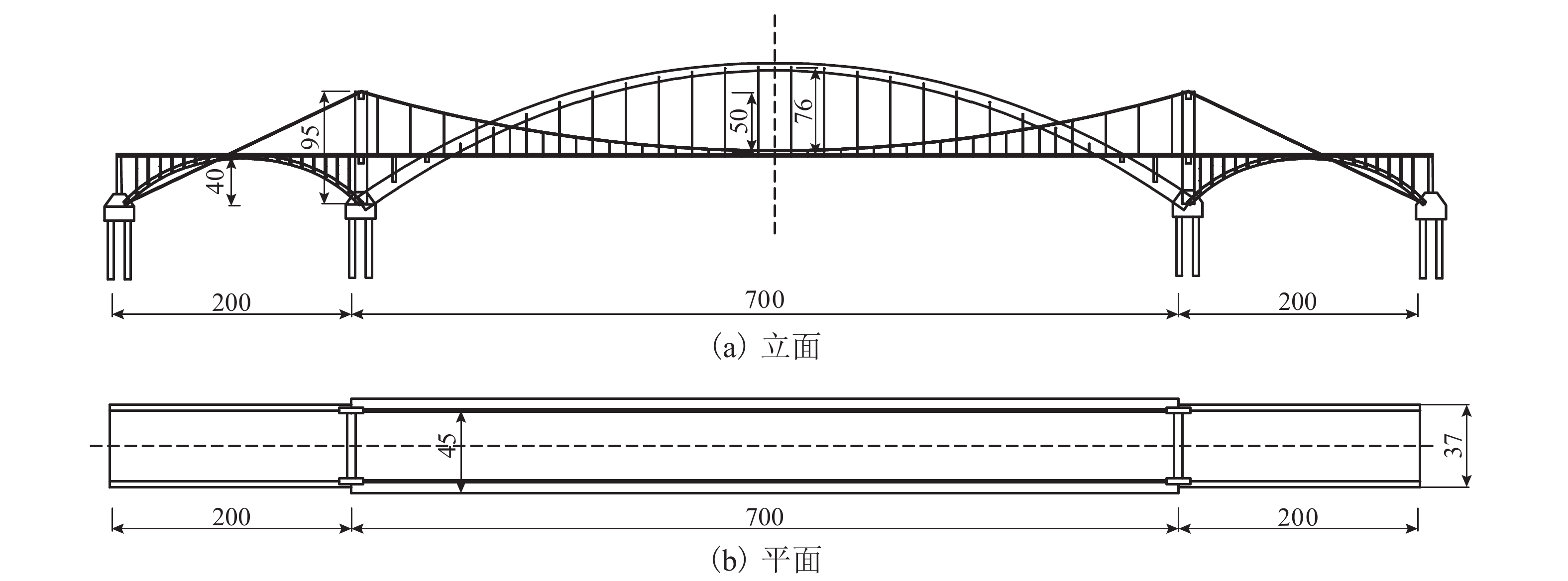
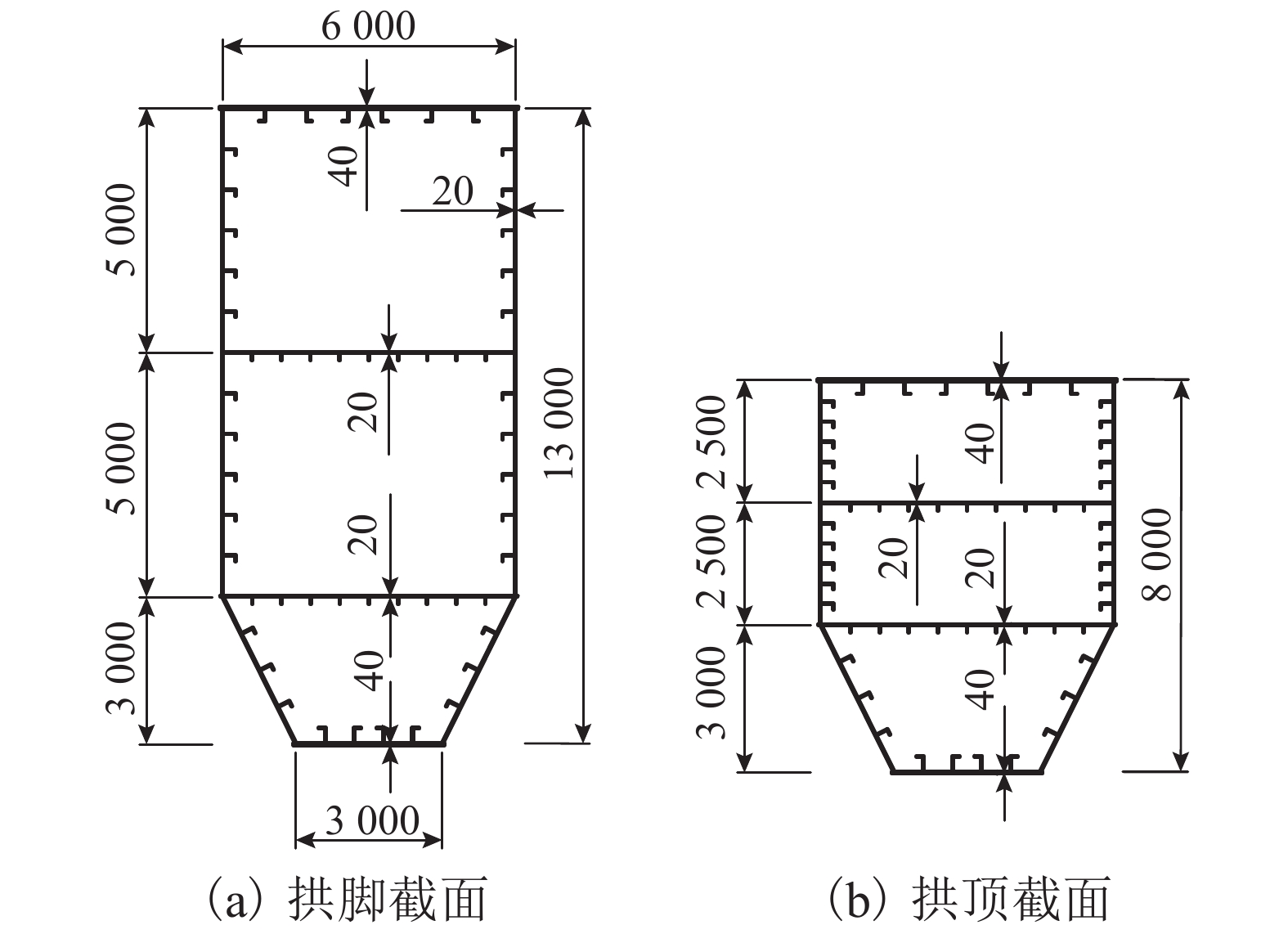
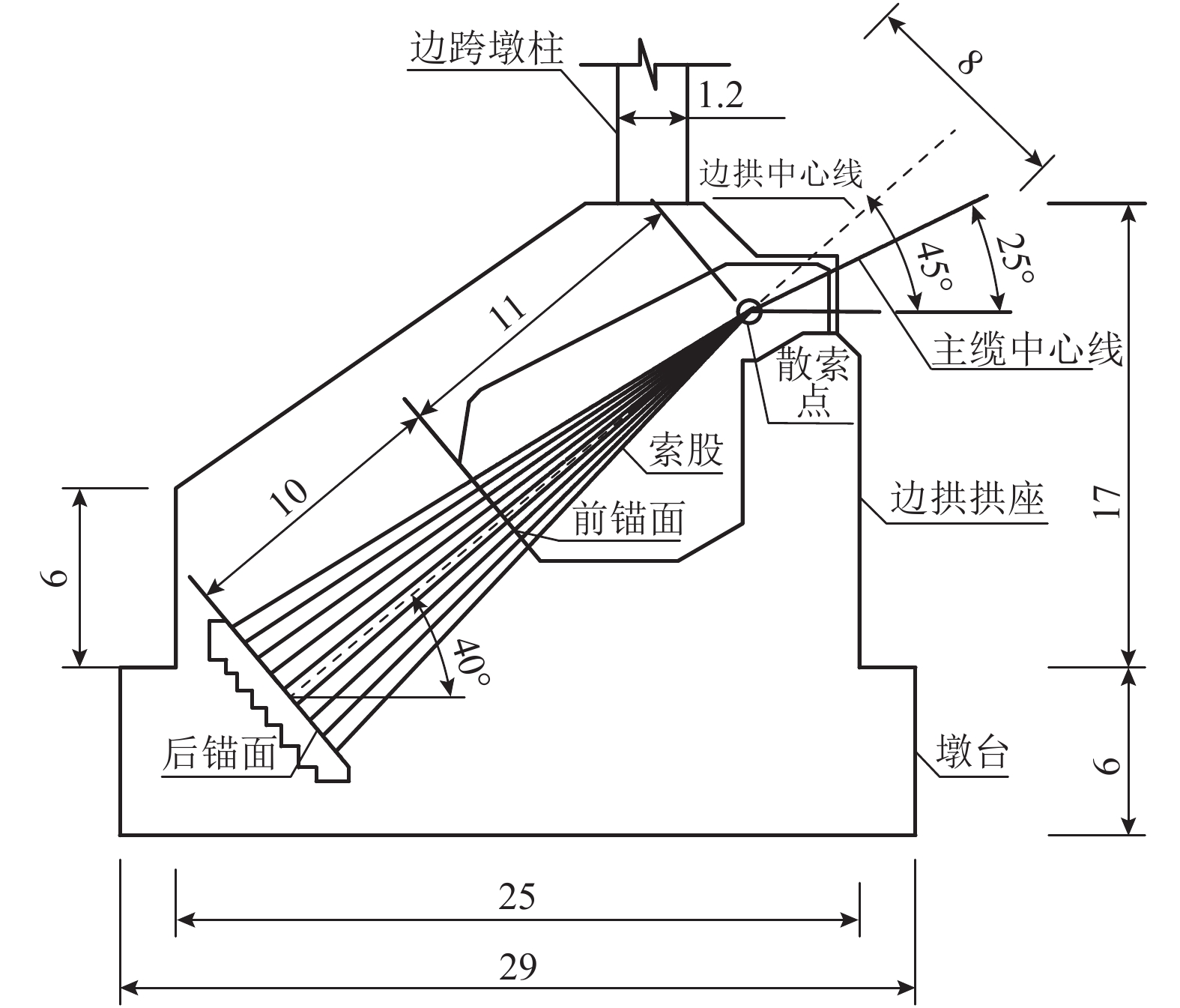
摘要: 随着拱桥跨径的增加,拱肋稳定性问题突出,且巨大的推力需通过系杆或基础平衡,大跨度悬索桥的庞大锚碇耗资巨大. 针对这两个问题,结合拱和缆索的受力特点,提出一种新的桥梁结构体系——中承式缆拱桥. 首先,在主跨和边跨均加入拱圈;其次,去掉悬索桥锚碇,将主缆锚固于边拱拱脚;最后,通过选取适宜的垂跨比、矢跨比及拱轴系数,保证结构在恒载作用下主缆张力、主拱推力、边拱推力在数值上基本相等,从而使结构处于无推力状态并达到改善结构力学性能的目的. 给出了新型桥的具体结构形式和受力机理,并以700 m跨径为例对其进行设计研究,对其施工过程提出了设想. 有限元计算分析表明:中承式缆拱桥的拱与缆索共同承担桥面荷载,与同条件下的连续拱桥相比,其强度承载力提高约25%,稳定承载力提高约70%,同时恒载作用下结构产生的水平力基本为0,为突破拱桥跨径奠定了坚实的基础.Abstract: As the span of arch bridges increases, the stability problem of the arch rib is becoming severe and the huge horizontal thrust needs to be balanced with tie rods or foundation; meanwhile, large anchors of a long-span suspension bridge costs a lot. Aiming at the two problems above, a new type of bridge structure, half-through cable-arch bridge, was proposed based on mechanical properties of arches and cables. The specific structure and force mechanism of this new type bridge are elaborated. First, arch rings are added to both the main span and side span of a suspension bridge. Then, its anchors are removed and main cables are anchored to the side arch feet. Finally, by choosing appropriate parameters such as sag-to-span ratio, rise-to-span ratio and arch-axis coefficient, the tension of main cable, the thrust of main arch and the thrust of side arch can be basically equal in value under dead load, so that the structure is in a state of no thrust and thus structural mechanical properties can be improved. Taking a half-through cable-arch bridge with a 700 m main span as an example, the design of its structural layout and components are described in details and a sequence of construction steps is suggested. Finite element analysis shows that the arch and cable of half-through cable-arch bridge share the load of bridge deck; compared with the continuous arch bridge under the same conditions, the half-through cable-arch bridge can increase the strength bearing by nearly 25% and increase the stable bearing capacity nearly by 70%. In addition, the horizontal force generated by the structure is nearly zero under dead load, which lays a solid foundation for breaking through the span limit of arch bridges.
-
Key words:
- half-through /
- cable-arch bridge /
- arch bridge /
- suspension bridge /
- hybrid bridge
-
表 1 组合一主拱应力
Table 1. Stress of main arch under the first load combination
类型 主缆承担
荷载比例/%主拱拱脚
最大应力/MPa主拱拱顶
最大应力/MPa连续拱桥 100 149.98 149.90 700 m 中承
式缆拱桥47 112.17 111.07 变化率/% 25.2 25.9 表 2 组合二主拱应力
Table 2. Stress of main arch under the second load combination
类型 主缆承担
荷载比例/%主拱拱脚
最大应力/MPa主拱拱顶
最大应力/MPa连续拱桥 100 173.20 174.39 700 m 中承
式缆拱桥45 108.74 133.20 变化率/% 37.3 23.6 表 3 结构位移
Table 3. Structural displacement
类型 塔顶水平
位移/mm主拱竖向
位移/mm主跨最大
挠度/mm连续拱桥 8.24 122.29 237.91 700 m 中承
式缆拱桥108.68 273.27 变化率/% 11.1 14.9 表 4 组合三及组合四主拱应力
Table 4. Stress of main arch under the third and fourth load combination
类型 升温 25 ℃ 降温 25 ℃ 不均匀沉降 拱脚最大应力/MPa 拱顶最大应力/MPa 拱脚最大应力/MPa 拱顶最大应力/MPa 拱脚最大应力/MPa 拱顶最大应力/MPa 连续拱桥 134.82 139.78 170.78 160.02 181.80 162.10 700 m 中承
式缆拱桥103.71 106.12 126.28 115.43 145.10 127.60 变化率/% 23.1 24.1 26.1 27.9 20.2 21.3 表 5 组合五主拱应力
Table 5. Stress of main arch under the fifth load combination
升温 25 ℃ 降温 25 ℃ 拱脚最大应力/MPa 拱顶最大应力/MPa 拱脚最大应力/MPa 拱顶最大应力/MPa 连续拱桥 179.17 184.92 198.79 132.12 中承式缆拱桥 118.93 146.66 192.79 152.47 变化率/% 33.6 20.7 33.5 20.9 表 6 屈曲分析结果
Table 6. Results of buckling analysis
类型 连续拱桥 中承式缆拱桥 稳定系数变化率/% 临界荷载系数 稳定系数 临界荷载系数 稳定系数 第1模态 58 4.20 81 7.45 77.38 表 7 不同垂跨比的计算结果
Table 7. Calculation results for different sag-span ratios
矢跨比 垂跨比 主缆承担
荷载比例/%主拱最大
应力/MPa稳定系数 1/6 1/14 45.00 133.00 7.45 1/12 50.88 128.14 10.30 1/10 58.43 122.19 13.50 -
项海帆. 桥梁概念设计[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2011: 238-240 GALVÍN P, DOMÍNGUEZ J. Dynamic analysis of a cable-stayed deck steel arch bridge[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2007, 63(8): 1024-1035. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2006.11.001 陈宝春,陈康明,赵秋. 中国钢拱桥发展现状调查与分析[J]. 中外公路,2011,31(2): 121-127. 陈宝春. 拱桥技术的回顾与展望[J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版),2009,37(1): 94-106.CHEN Baochun. View and review of arch bridge technology[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(1): 94-106. 肖汝诚.桥梁结构体系[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2013: 104-105 马明,钱永久,徐佰顺. 新月型钢管混凝土拱桥极限承载能力分析[J]. 桥梁工程,2017,52(4): 678-684,714.MA Ming, QIAN Yongjiu, XU Baishun. Analysis of ultimate load-carrying capacity of crescent-shaped concrete-filled steel tube arch bridge[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(4): 678-684,714. 邵旭东, 顾安邦. 桥梁工程[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2007: 254-255. 张双洋,赵人达,贾毅,等. 大跨度高速铁路劲性骨架混凝土拱桥模型试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(6): 1088-1096.ZHANG Shuangyang, ZHAO Renda, JIA Yi, et al. Model test study on long-span railway concrete arch bridge with rigid skeleton[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(6): 1088-1096. 穆祥纯. 中外城市桥梁[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2015: 27-28 郑皆连,王建军,牟廷敏,等. 700 m 级钢管混凝土拱桥设计与建造可行性研究[J]. 中国工程科学,2014,16(8): 33-37.ZHENG Jielia, WANG Jianjun, MOU Yanmin, et al. Feasibility study on design and construction of concrete filled steel tubular arch bridge with a span of 700 m[J]. Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014, 16(8): 33-37. 项海帆, 范立础. 高等桥梁结构理论[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2013: 373-374 HANS D B, AMELIE O, PHILIPPE V B. Buckling design of steel tied-arch bridges[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2014, 103: 159-167. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2014.09.004 ARIE R, CHARALAMPOS B. Investigation of the arch in-plane buckling behaviour in arch bridges[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2008, 64(12): 1349-1356. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2008.01.035 颜东煌,刘雪锋,田仲初,等. 组合体系拱桥的发展与应用综述[J]. 世界桥梁,2007(2): 65-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7767.2007.02.020 李光凤. 自锚式悬索桥与上承式拱桥组合体系桥梁的稳定性分析[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2011 陈礼榕. 大跨刚构拱桥的组合有限元计算分析研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2005 汪剑,陆伟. 斜拉拱桥面内弹性稳定性研究[J]. 城市道桥与防洪,2016(3): 158-161. 孙全胜,韩宏光. 无背索斜拉拱桥受力性能研究[J]. 中外公路,2015,35(1): 204-208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2579.2015.01.046 KANG H J, ZHAO Y Y, ZHU H P, et al. Static behavior of a new type of cable-arch bridge[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2013, 81: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2012.10.010 -




 下载:
下载: