Time-History Analysis of Temperature Field of Medium-Low Maglev Guideway Girder
-
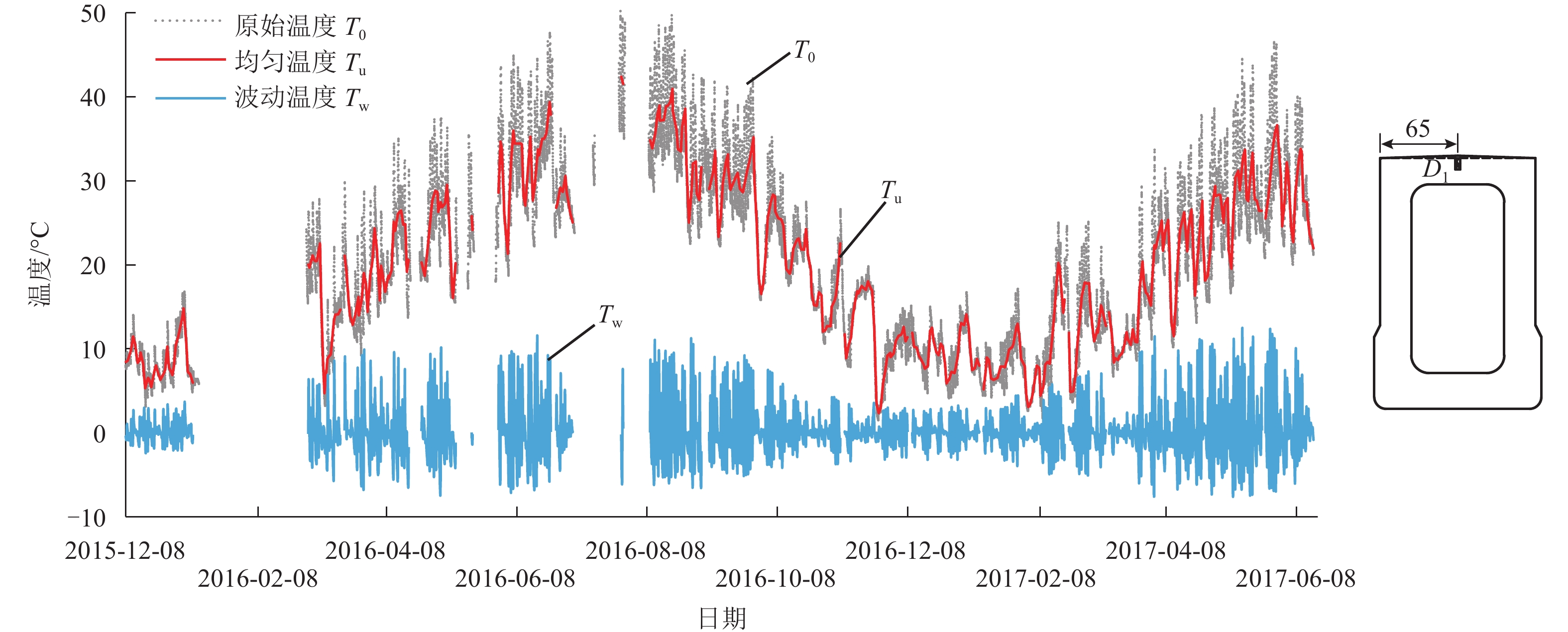
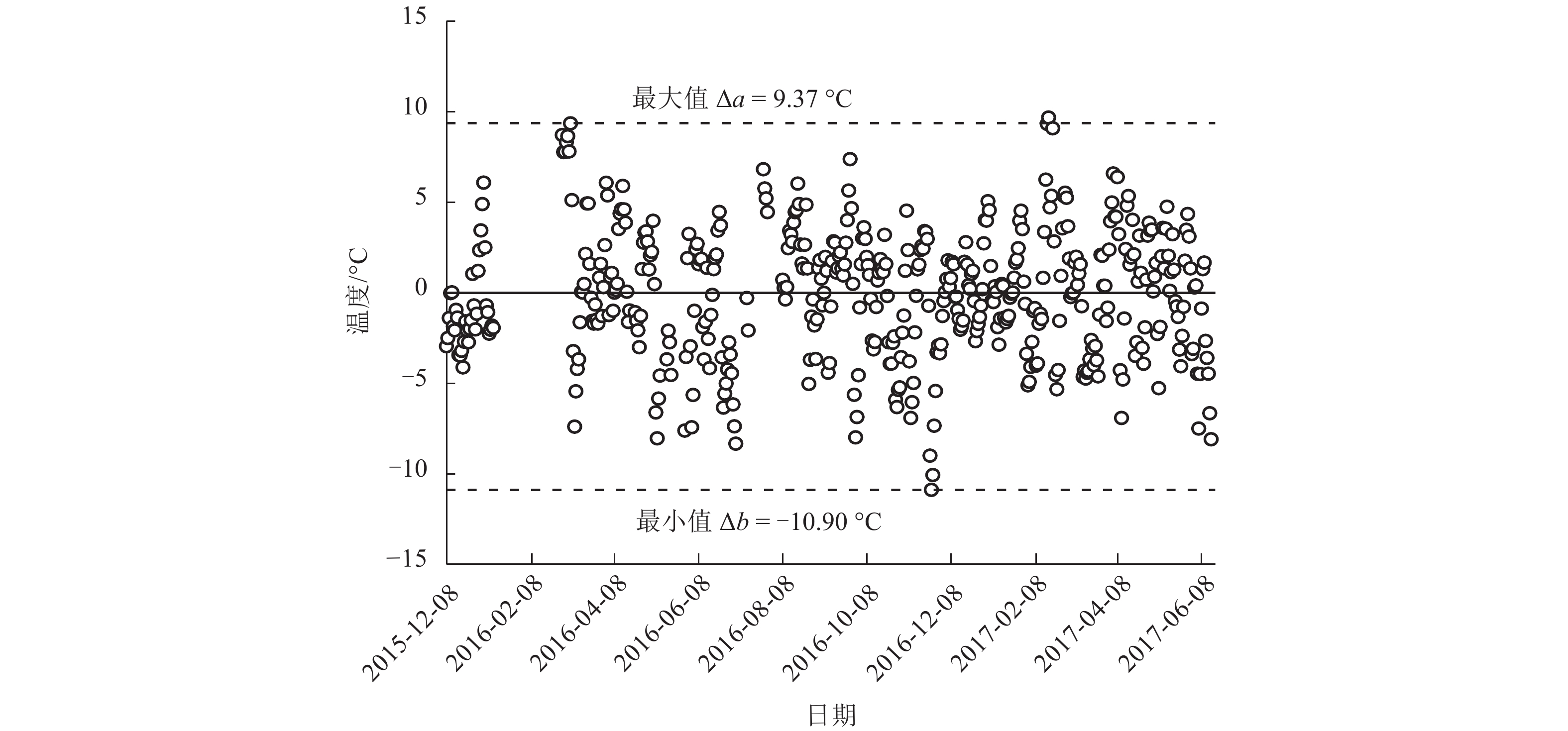
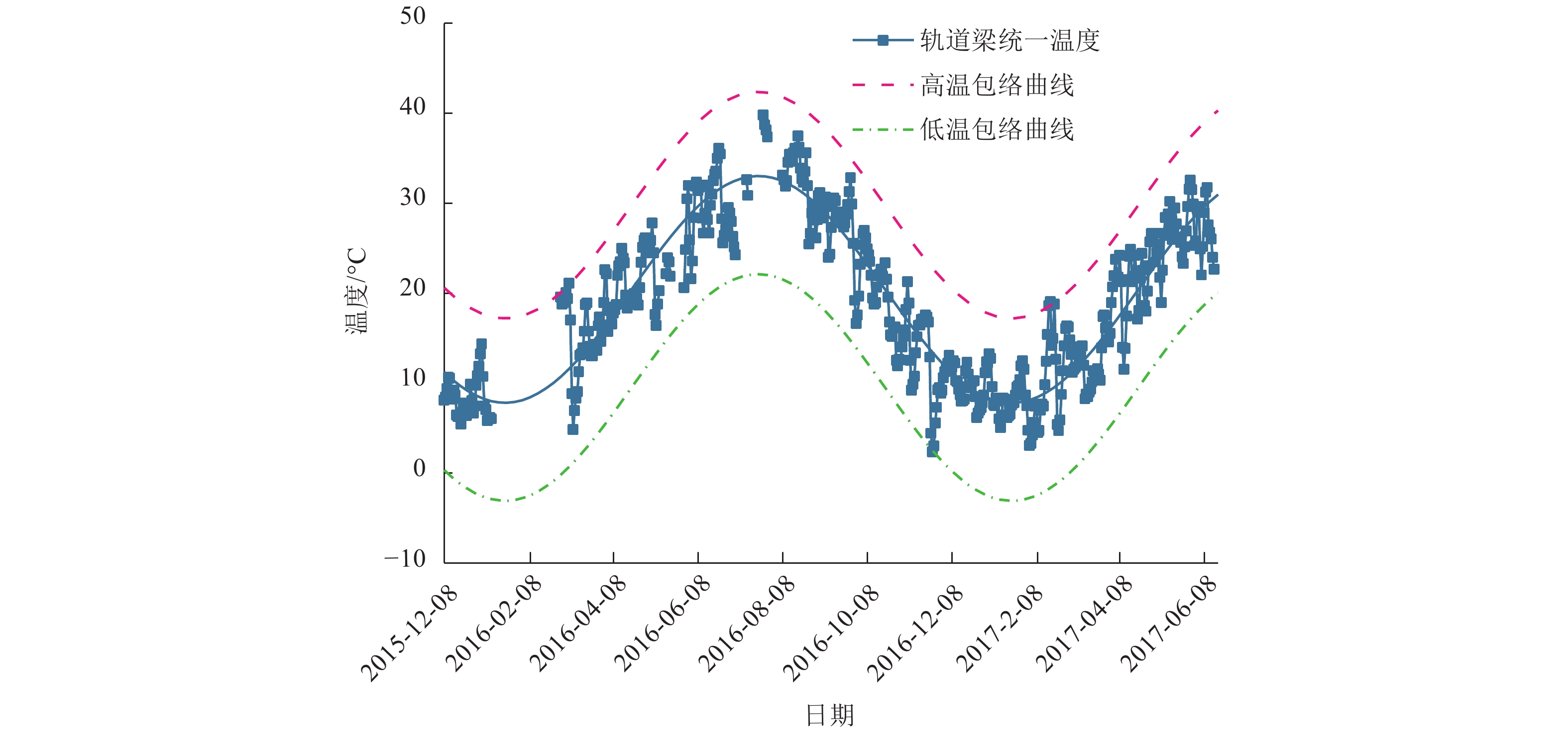
摘要: 为掌握磁浮轨道梁在长期外界环境作用下产生的复杂的温度场时变规律,在长沙磁浮运营线的轨道梁内埋设温度传感器,通过1.5 a的现场温度监测,获得测点温度时程曲线,并提出了基于时间序列加法模型求解的方法. 该方法将测点温度分解成均匀温度与波动温度,并利用傅立叶曲线拟合方法研究二者的时程曲线,得到轨道梁温度场时变规律. 研究结果表明:均匀温度与当地气候变化相关,各测点均温基本相同,结构温度时变趋势可用中位值为20.41 ℃、变化幅值为12.61 ℃、初相位为20 d、周期为365 d的余弦函数表示长沙磁浮轨道梁均温时程曲线;波动温度与日照作用相关,以日为周期在0线上下波动,可用两个正弦函数分段拟合升降温时程曲线.Abstract: To master the laws of time-varying temperature fields of maglev girders generated by long-term environmental loading, thermal sensors were installed on a concrete guideway girder in the Changsha Maglev Express. By performing up to 1.5 a of site monitoring, the time-history curve of points was obtained. A method based on the time-series addition model is presented. With this method, the original temperature is decomposed into uniform temperature and fluctuating temperature, and the time-history curves of both temperatures are analysed using the Fourier curve fitting method. Then, the time-varying temperature field of the guideway girder is determined. The results show that uniform temperature is relevant to the climate, and each point is basically the same, reflecting the trend of the original temperature. The overall time-history curve of the girder can be expressed as a cosine function with a median value of 20.41 ℃, amplitude of 12.61 ℃, initial phase of 20 d, and cycle of 365 d. The fluctuating temperature is mainly because of solar radiation, and the curves fluctuate near the zero line. Two sine functions can be used to fit the rising and falling time-history curves.
-
Key words:
- medium-low maglev transit /
- guideway girder /
- temperature field /
- time history analysis /
- site test
-
表 1 特定测点拟合结果
Table 1. Fitting results of specific points
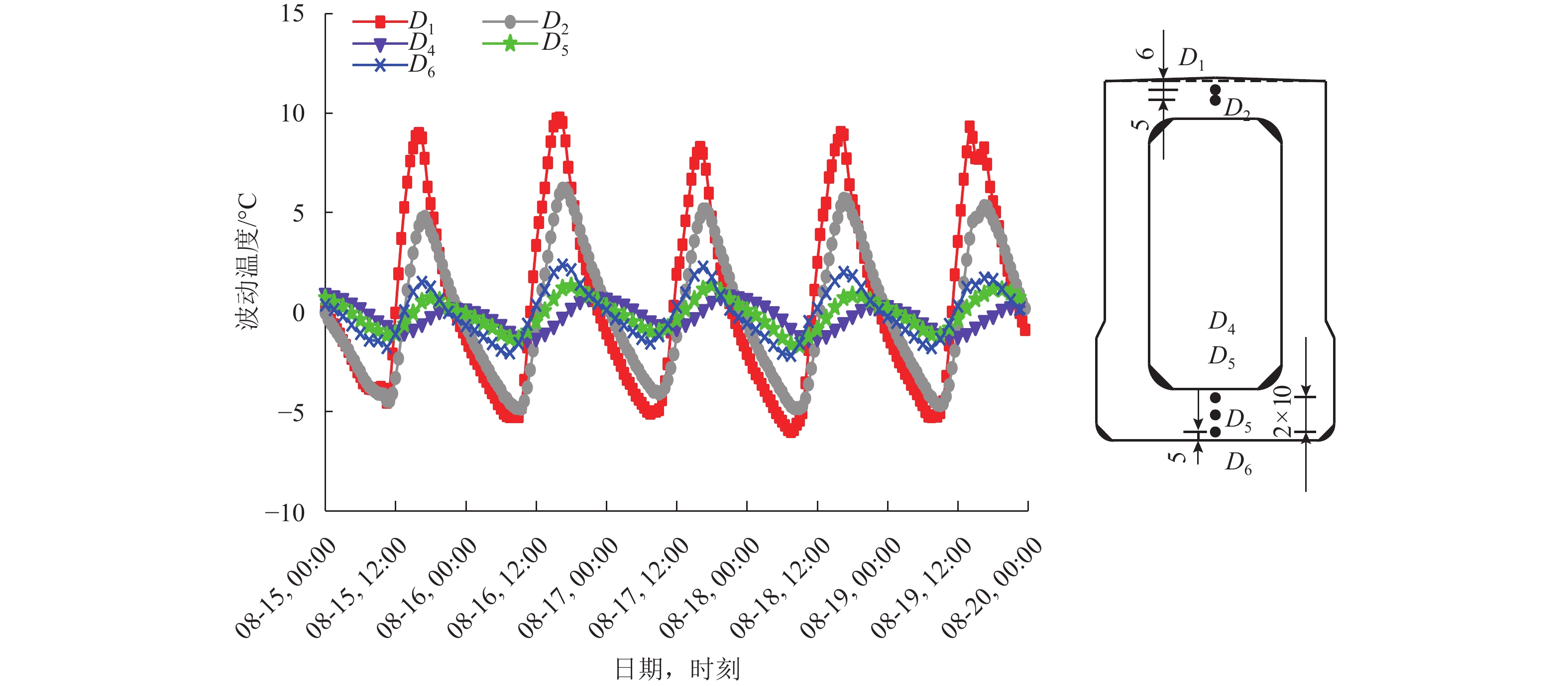
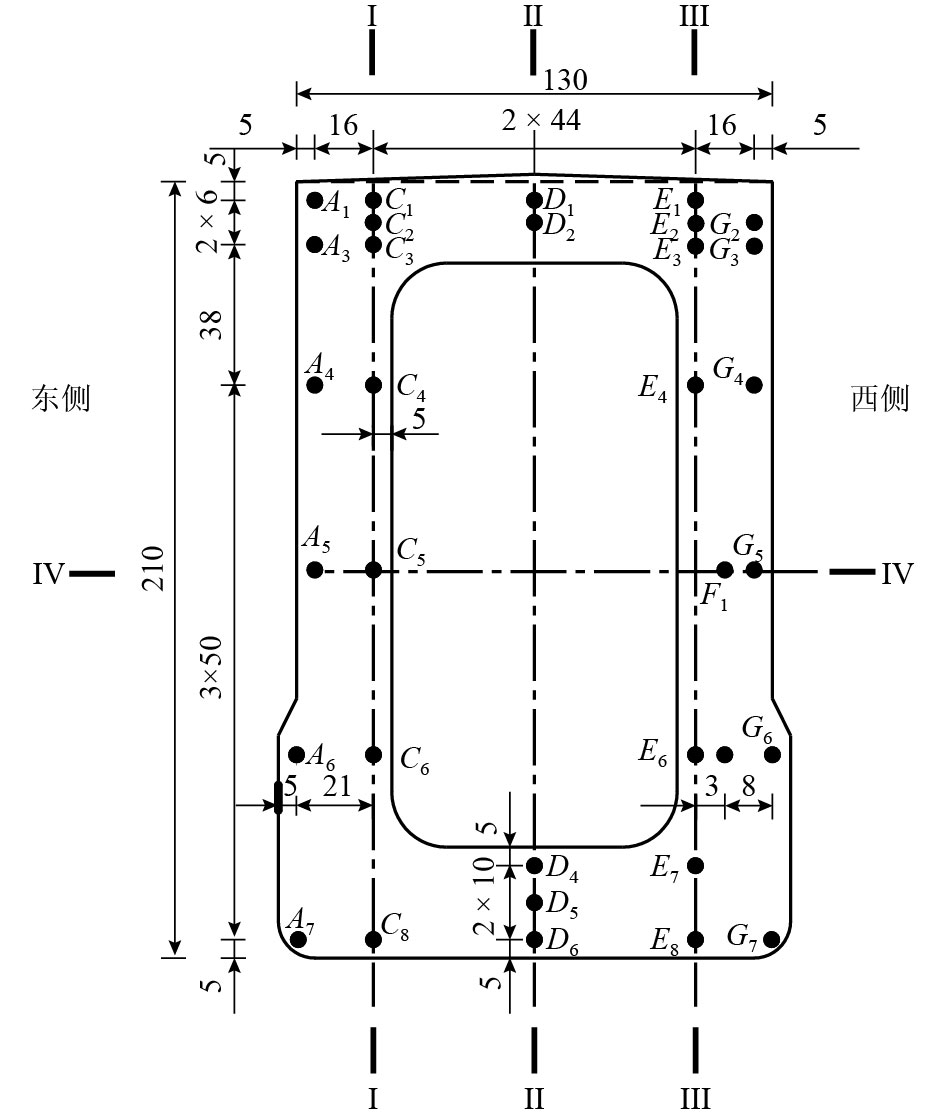
测点组 测点号 距表面距离/m Tum/℃ ΔTu/℃ φd/d R2 截面Ⅱ D1 0.05 21.55 13.21 18 0.940 1 D2 0.11 21.39 13.15 19 0.937 3 D4 1.85 20.01 11.89 21 0.950 6 D5 1.95 20.07 11.73 21 0.949 6 D6 2.05 20.02 11.74 21 0.947 0 截面IV A5 0.05 19.92 11.74 20 0.943 2 C5 0.16 20.08 11.76 21 0.946 4 F1 0.65 20.45 12.38 20 0.947 6 G5 1.09 21.34 13.59 22 0.947 8 注:截面Ⅱ,距表面距离表示测点距上表面距离;截面IV,距表面距离表示距左侧表面距离. 表 2 各结构的统一温度曲线拟合结果
Table 2. Fitting results of overall temperature of structures
结构类型 Tum/℃ ΔTu/℃ φd/d R2 西侧轨道梁 20.41 12.61 20 0.944 6 东侧轨道梁 20.52 12.19 22 0.915 3 端横梁 19.51 11.95 19 0.911 3 中横梁 18.37 11.77 20 0.915 4 桥墩 18.96 11.34 21 0.901 7 表 3 波动温度幅值竖向分布拟合结果
Table 3. Fitting results of vertical dispersion of amplitudes
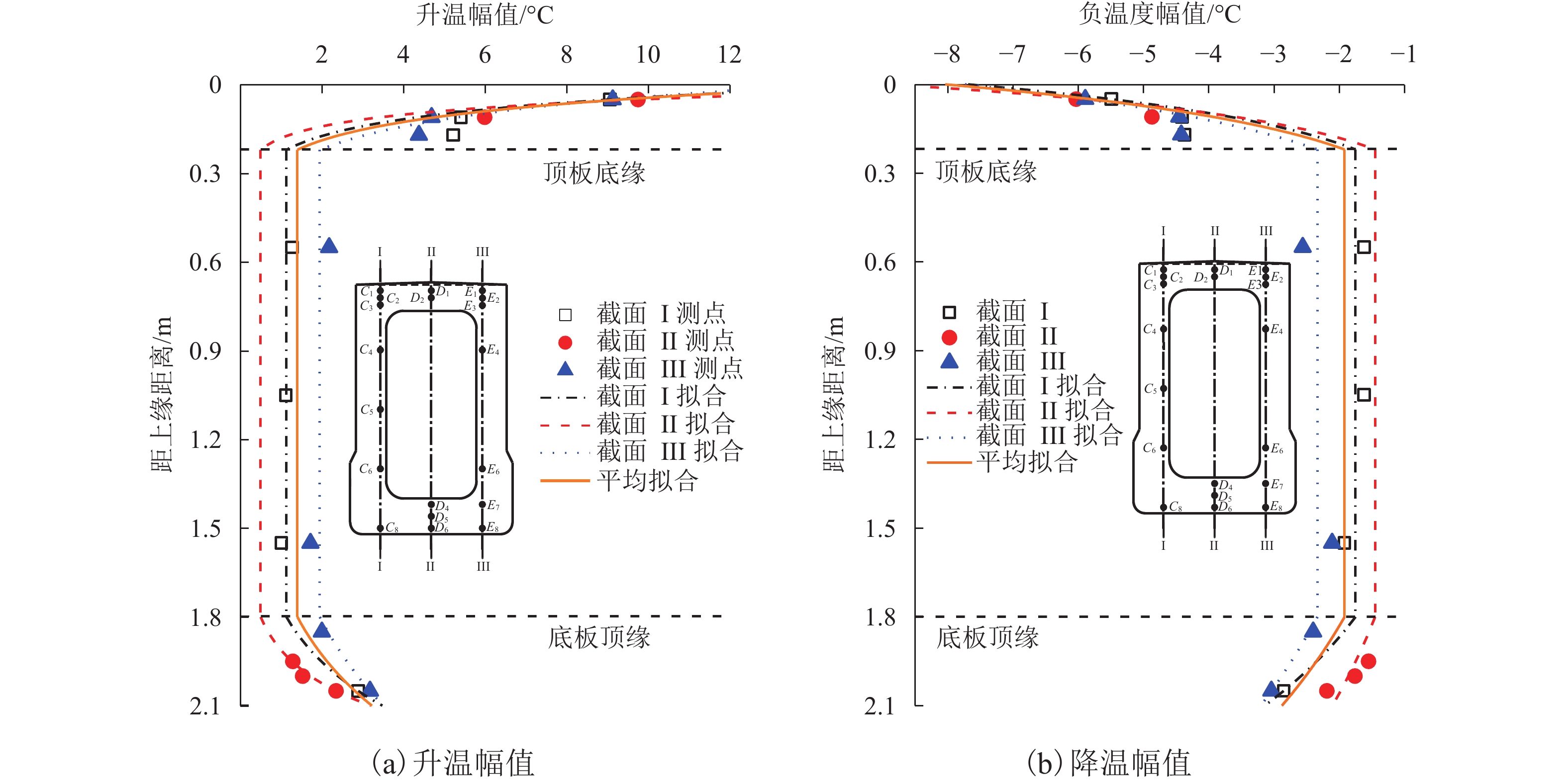
拟合参数 顶板A(y) = aeby 腹板A = T0 底板A(y) = aeby 升温 降温 升温 降温 升温 降温 a/℃ b/m–1 a/℃ b/m–1 c/℃ b/℃ a/℃ b/m–1 a/℃ b/m–1 截面I 16.71 –12.25 –7.68 –6.73 1.13 –1.75 3.49 –3.76 –3.14 –1.95 截面II 17.11 –11.25 –8.9 –8.25 0.5 –1.45 2.59 –1.96 –2.11 –1.25 截面III 14.38 –9.08 –7.73 –5.44 1.95 –2.34 3.51 –1.96 –3.21 –1.06 平均 16.26 –11.15 –7.73 –6.51 1.4 –1.92 3.23 –2.78 –2.88 –1.35 注:为表现传热随箱梁结构深度的变化,规定顶板、底板均以外表面到内表面为正方向. 表 4 升降温时刻及时长规律
Table 4. Moment and duration of riging and falling stage
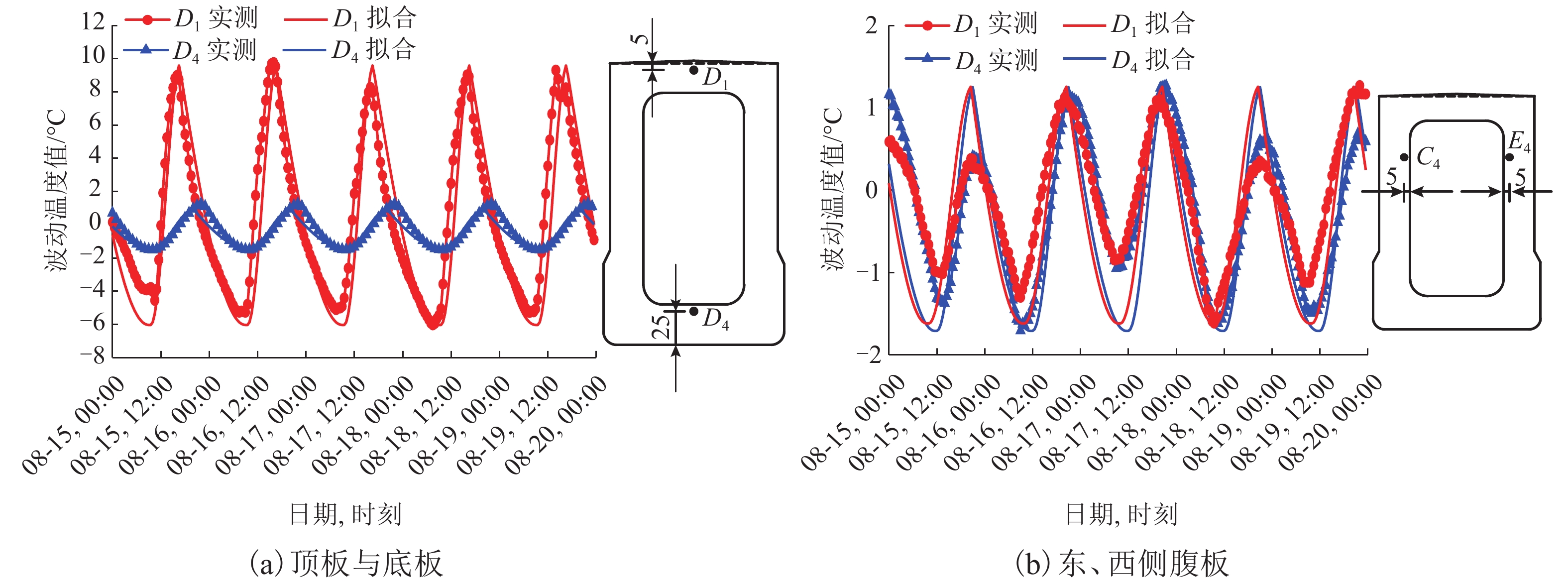
位置 tr tf Lr Lf 顶板 9.0 16.5 7.5 16.5 底板 10.0 20.0 10.0 14.0 东侧腹板 9.5 20.5 11.0 13.0 西侧腹板 11.5 21.0 9.5 14.5 -
陈波,孙玉周,郭伟华. 钢筋混凝土板动力特性的时变温度效应实验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(1): 66-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.01.011CHEN Bo, SUN Yuzhou, GUO Weihua. Experimental investigation of temperature effects on dynamic characteristics of reinforced concrete slab[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(1): 66-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.01.011 乔柏平. 磁浮单跨轨道梁温度变形及对振动的影响[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2008 张庆福. 磁浮连续轨道梁温度变形及对振动的影响[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2009 中国土木工程学会. 中低速磁浮交通设计规范: CJJ/T262—2017[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社出版, 2017 刘华波. 异形截面预应力混凝土箱梁温度场及温度效应研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2002 徐钢. 箱梁温度场及其效应分析[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2008 张智晖. 预应力混凝土箱梁时变温度场及其效应研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2010 LEE J H, KALKAN I. Analysis of thermal environmental effects on precast,prestressed concrete bridge girders:temperature differentials and thermal deformations[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2012, 15(3): 447-459. doi: 10.1260/1369-4332.15.3.447 SALLAL R A, NILDEM T, MUSTAFA O. Experimental analysis of temperature gradients in concrete box-girders[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 106: 523-532. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.12.144 徐庆元,孟亚军,李斌,等. 温度梯度作用下纵连板式无砟轨道疲劳应力谱[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版,2015,46(2): 736-741.XU Qingyuan, MENG Yajun, LI Bin, et al. Fatigue stress spectrum of longitudinally connected ballastless track under temperature gradient[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2015, 46(2): 736-741. PETER J B, RICHARD A D. Time series: theory and methods[M]. Second Edition. New York: Springeze-Verlag, 1991: 14-25 刘兴法. 混凝土结构的温度应力分析[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1991: 10-13 卢理. 时间序列加法模型的分解预测研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2007 廖春花,刘甜甜,林海,等. 长沙近57年气温变化特征分析[J]. 气象与环境科学,2008,31(4): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7148.2008.04.005LIAO Chunhua, LIU Tiantian, LIN Hai, et al. Analysis of the characteristics of temperature variation in recent 57 years in Changsha[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 2008, 31(4): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7148.2008.04.005 Standards Policy and Strategy Committee. Eurocode Ⅰ, actions on structures – part 1-5: general actions-thermal actions: BS EN 1991-1-5—2003[S]. London: BSI Group, 2003 戴公连,杨凌皓,朱俊樸,等. 桥上CRTS II型板式无砟轨道均匀温度研究[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版,2017,44(7): 136-142.DAI Gonglian, YANG Linghao, ZHU Junpu, et al. Research on uniform temperature of CRTS II slab-type ballastless track on bridge[J]. Journal of Hunan University:Natural Sciences, 2017, 44(7): 136-142. -




 下载:
下载: