High-Speed Ballasted Railway Track Lateral Resistance Characteristics and Reinforcements
-
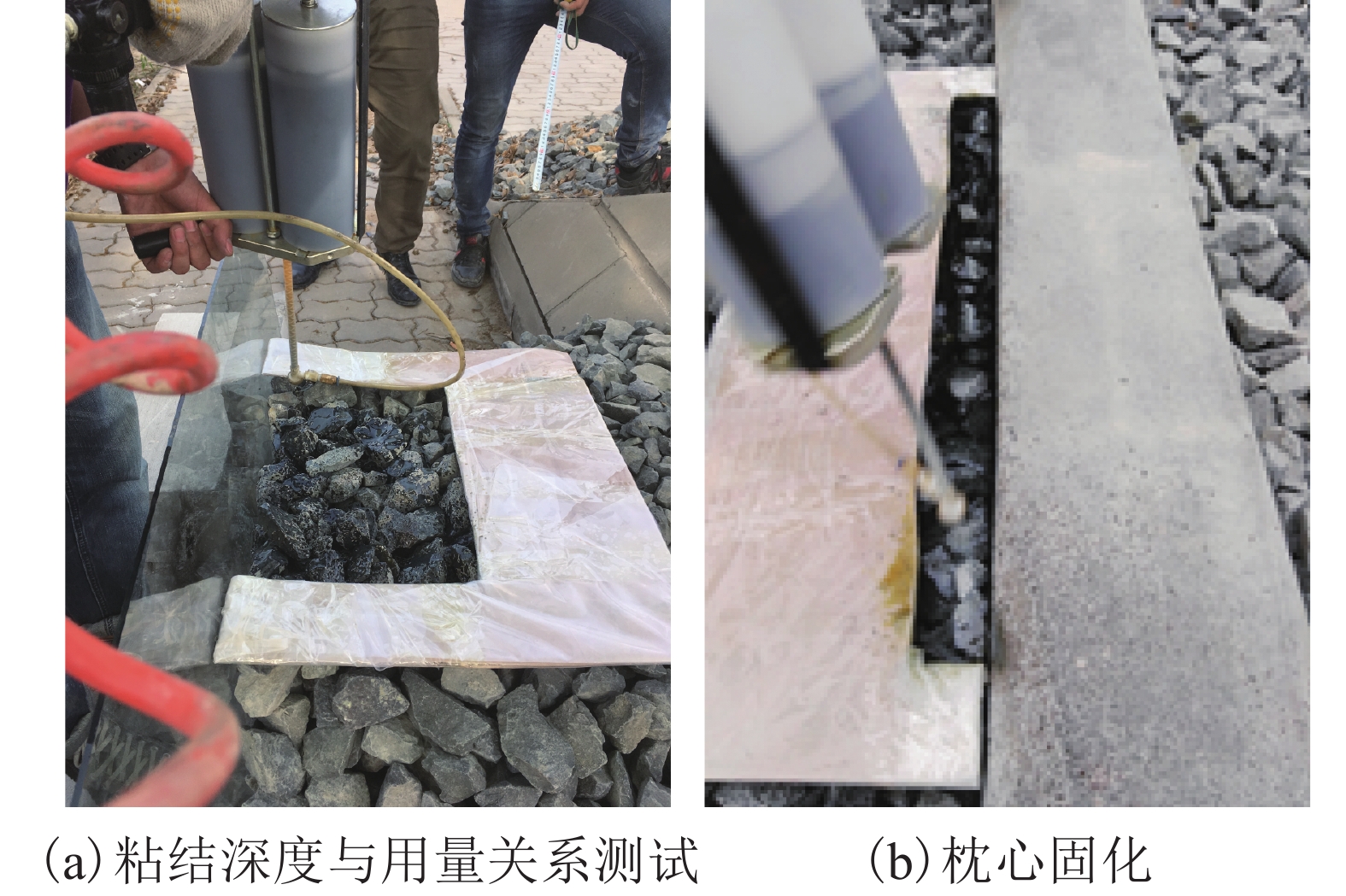
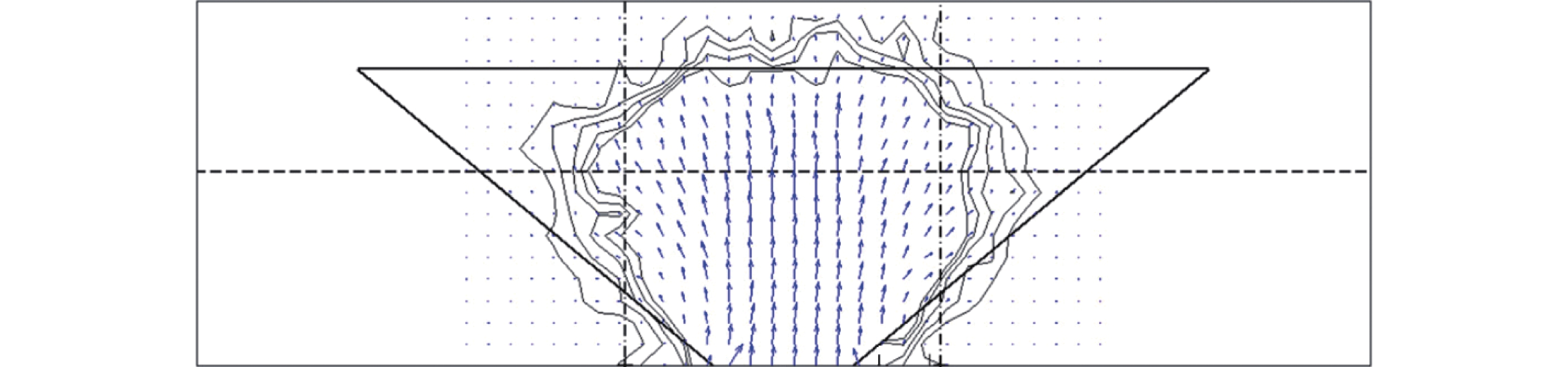
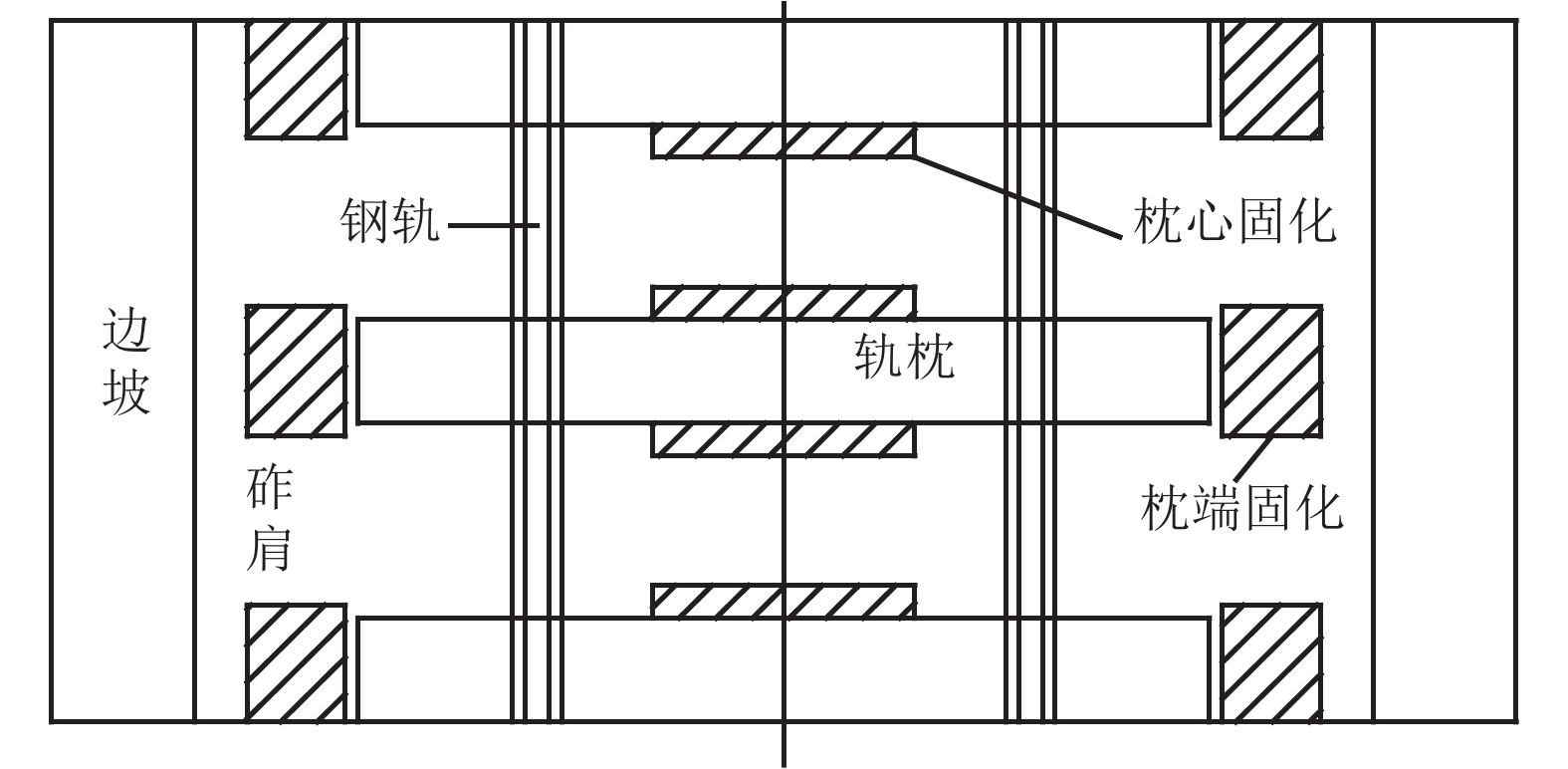
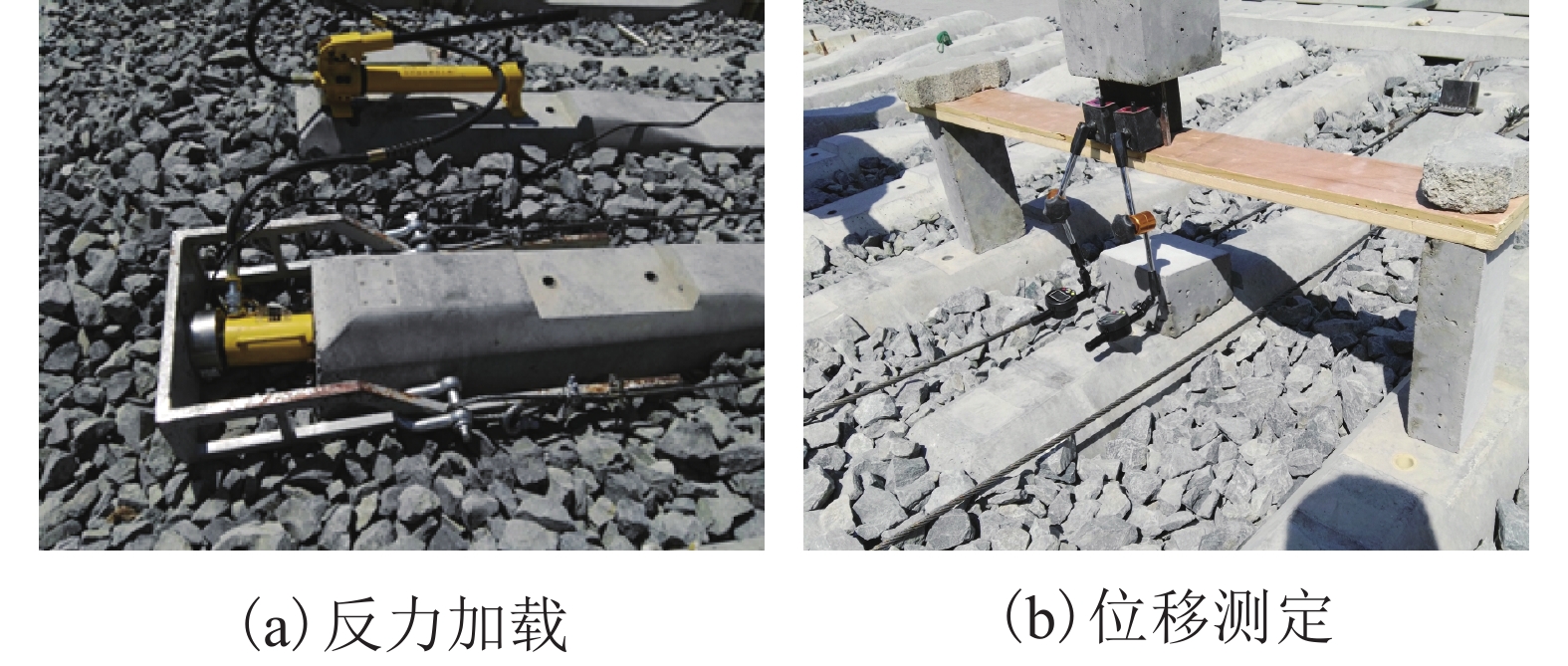
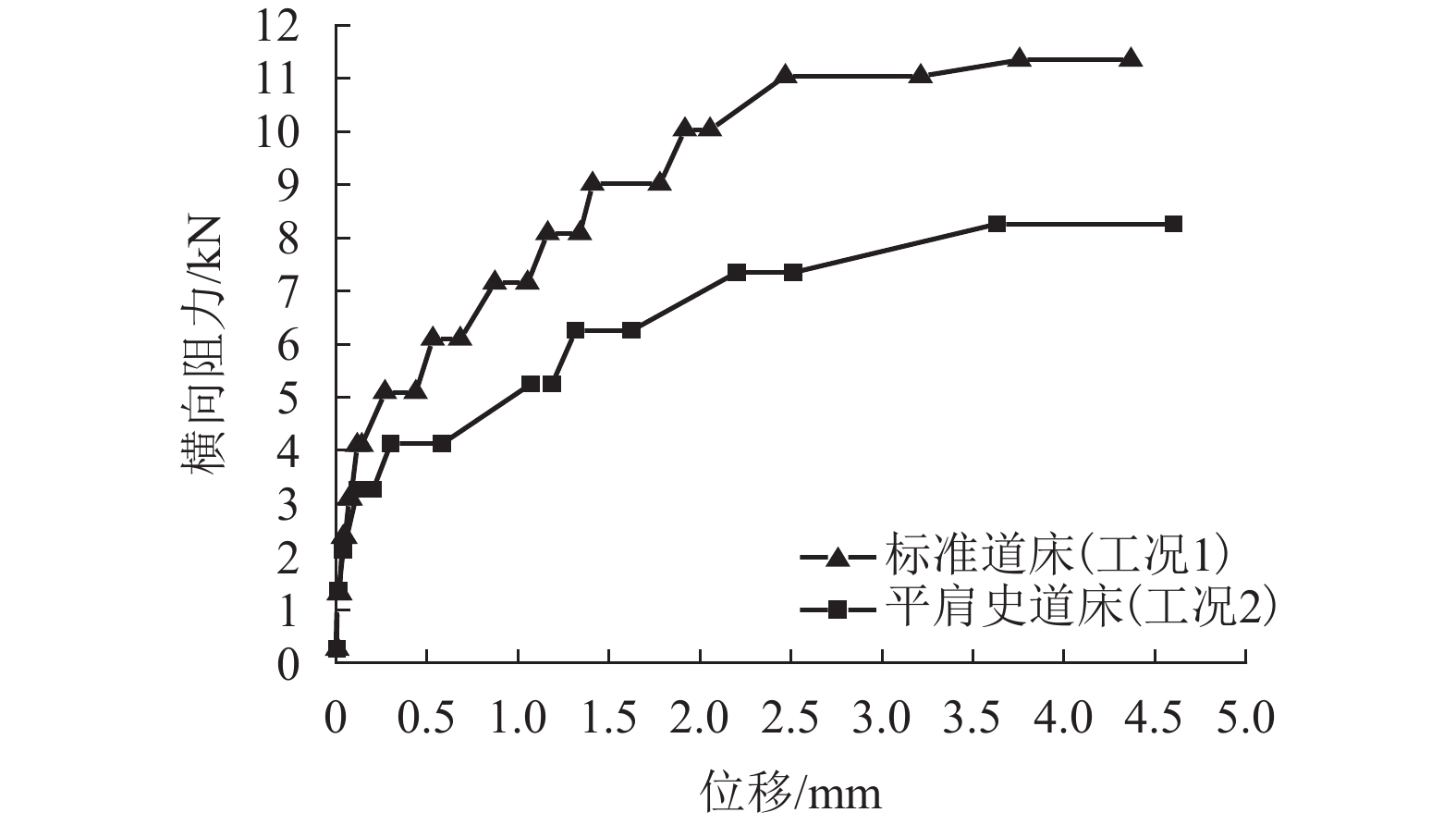
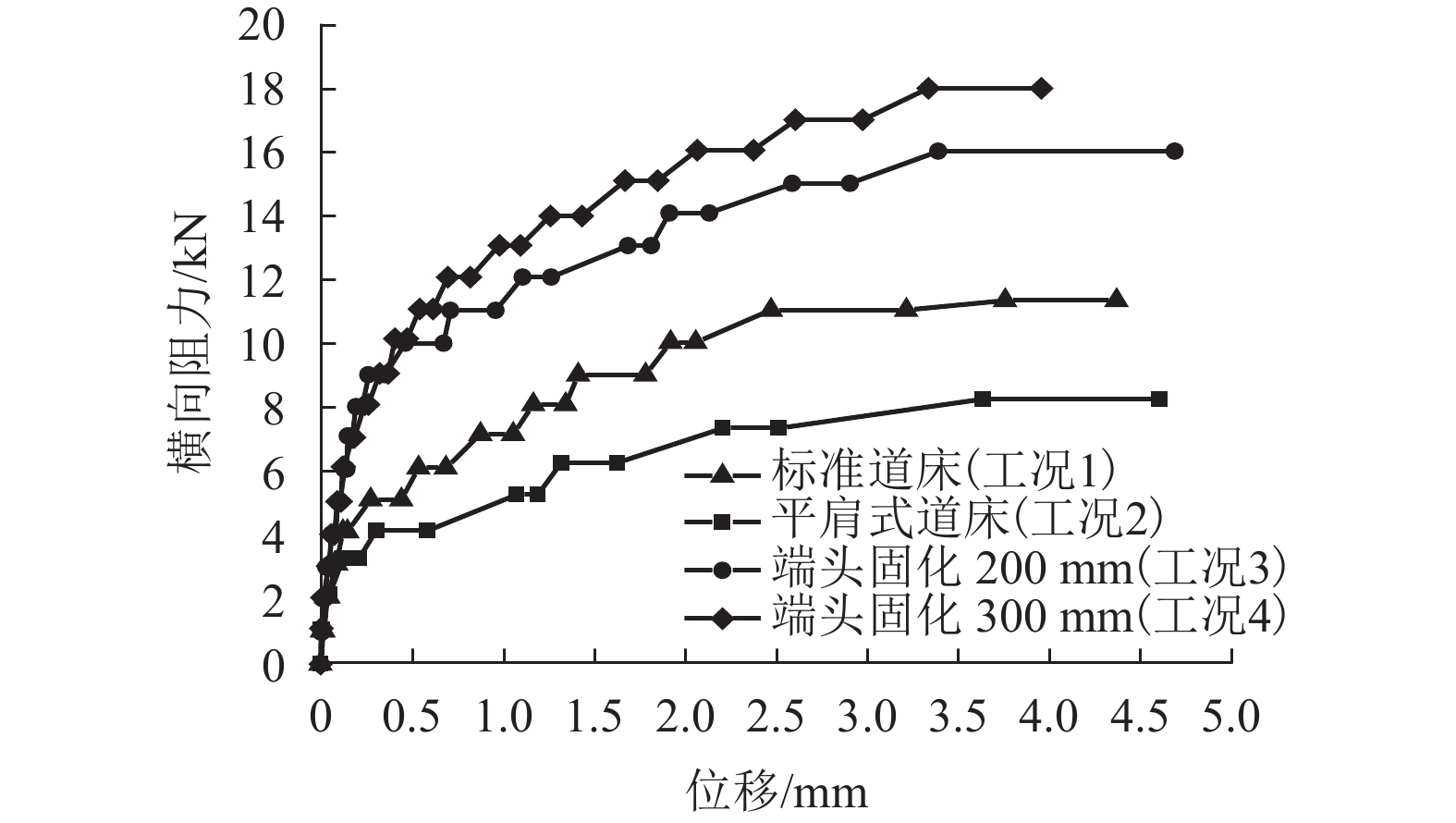
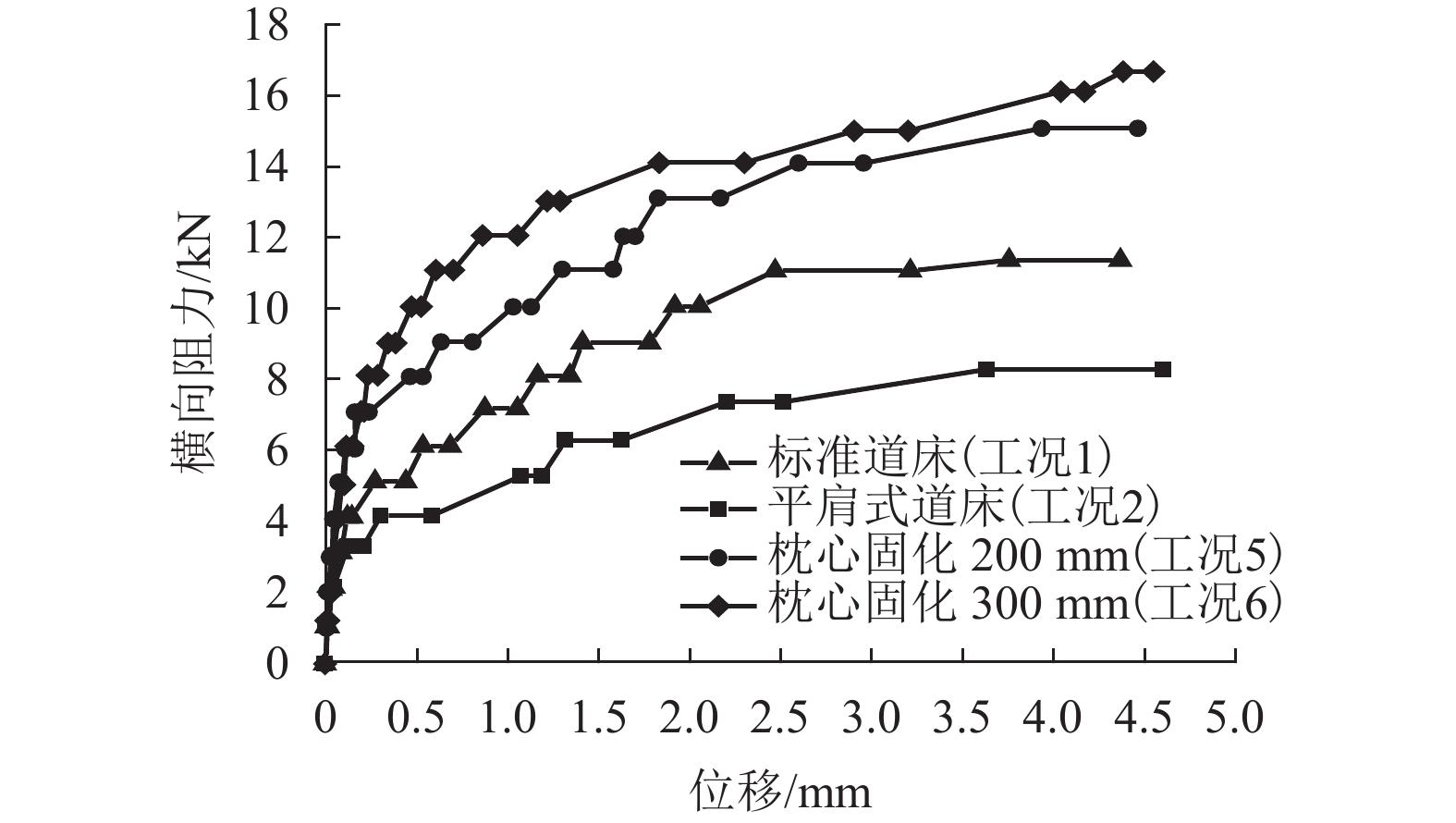
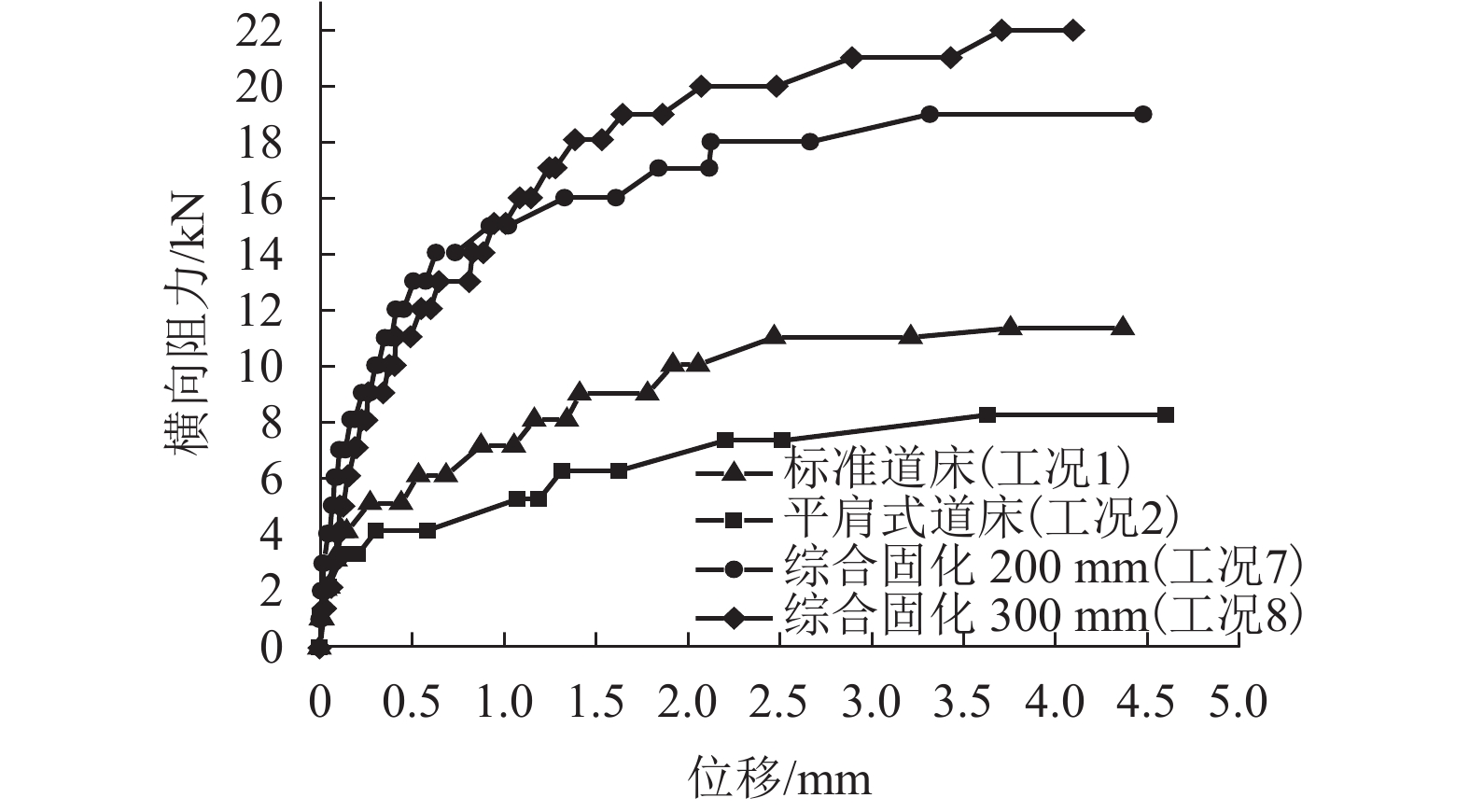
摘要: 高速铁路有砟道床存在发生飞砟的可能性,且飞砟概率随着砟肩堆高增加而增加,因此部分国家降低砟肩堆高,甚至采用平肩结构,但随之会引起道床阻力降低. 通过研究砟肩堆高对道床阻力的影响,同时在此基础上,提出了聚氨酯局部固化方案,包含枕心固化和枕端固化,均在增加平肩式道床横向阻力的同时不影响捣固维修作业. 道床横向阻力试验结果表明:与砟肩堆高150 mm相比,采用平肩式道床横向阻力降低30%;喷涂200 mm和300 mm聚氨酯的情况下,采用枕端固化的道床横向阻力分别可提高阻力约41%、60%,枕心固化可分别提高约31%、40%,综合固化(枕心和枕端固化同时采用)可提高阻力约70%、100%.Abstract: Ballast flight commonly occurs in high speed ballasted railway tracks, and the probability of ballast flight increases with the decrease of shoulder height; thus, reduced shoulder heights or flat shoulders are used in some countries, which result in lateral resistance reduction. The influence of shoulder height on lateral resistance was analysed in this study. Further, two polyurethane reinforcement methods were proposed, including crib-ballast reinforcement and shoulder reinforcement, which increased the lateral resistances of flat shoulder ballasted tracks and met the demands of tamping. A series of in-situ lateral resistance tests were carried out in this research. The results show that compared to a shoulder height of 150 mm, a 30% reduction in lateral resistance occurs in flat shoulders. For polyurethane spraying depths of 200 mm and 300 mm, the corresponding changes observed were 31% and 41% increase in crib-ballast reinforcement, 41% and 60% increase in shoulder reinforcement, and 70% and 100% increase in synthetic reinforcement (both crib-ballast and shoulder).
-
Key words:
- shoulder ballast /
- lateral resistance /
- ballast flight /
- polyurethane
-
表 1 聚氨酯参数
Table 1. Parameters of polyurethane
参数 数值 密度/(g•cm–3) 1.13 拉伸强度/MPa 14.2 断裂伸长率/% 20 撕裂强度/(N•mm–1) 60 硬度(邵D) 46 表 2 试验工况
Table 2. Testing condition
工况 砟肩堆高
/mm枕心高度
/mm固化
方式喷涂深度
/mm1 150 0 2 0 – 40 3 0 – 40 枕端固化 200 4 0 – 40 枕端固化 300 5 0 – 40 枕心固化 200 6 0 – 40 枕心固化 300 7 0 – 40 综合固化 200 8 0 – 40 综合固化 300 表 3 聚氨酯用量
Table 3. Quantity of polyurethane
固化方式 粘结深度/mm 聚氨酯用量/kg 枕端固化 200 0.26 300 0.82 枕心固化 200 0.10 300 0.32 综合固化 200 0.36 300 1.14 -
TUTUMLUER E, HUANG H, HASHASH Y. Aggregate shape effects on ballast tamping and railroad track lateral stability[C]// AREMA Annual Conference.Loisville: AREMA, 2006: 17-20 井国庆. 铁路有砟道床[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2012: 15-70 ESVELD C. Modern railway track[M]. Delft: MRT-Production, 2001: 52-58 高亮,罗奇,徐旸,等. 道床断面尺寸对道床横向阻力的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(6): 954-960. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.06.004GAO Liang, LUO Qi, XU Yang. Effects of ballast bed section dimension on its lateral resistance[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(6): 954-960. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.06.004 刘浩,谢铠泽,王平,等. 道床阻力区域分布及退化对钢轨纵向力的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(1): 98-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.014LIU Hao, XIE Kaize, WANG Ping, et al. Effect of regional distribution and degradation of ballast resistance on longitudinal force of rail[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(1): 98-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.014 国家铁路局. 高速铁路设计规范: TB 10621—2014[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2014 井国庆,王子杰,林建. 基于力学平衡原理飞砟机理与防治研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2014(6): 96-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2014.06.017JING Guoqing, WANG Zijie, LIN Jian. Mechanical equilibriu m analysis of ballast flight mechanis m and counteracting measures[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2014(6): 96-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2014.06.017 SAAT M R, BEDINIJACOBINI F, TUTUMLUER E, et al. Identification of high-speed rail ballast flight risk factors and risk mitigation strategies[R]. Sydeny: 10th World Congress on Railway Research, 2013 QUINN A D. A full-scale experimental and modelling study of ballast flight under high-speed trains[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part f Journal of Rail & Rapid Transit, 2010, 224(2): 61-74. LE P L, POWRIE W. Contribution of base,crib,and shoulder ballast to the lateral sliding resistance of railway track:a geotechnical perspective[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part F Journal of Rail & Rapid Transit, 2011, 225(2): 113-129. WANG Z J, JING G Q, LIU G X. Analysis on railway ballast-glue micro-characteristics[J]. Applied Mechanics & Materials, 2013(477/478): 535-538. STJEPAN L. Track stability using ballast bonding method[J]. Slovenski Kongres O Cestah In Prometu, 2010, 10: 333-340. WOODWARD P K, KENNEDY J, MEDERO G M, et al. Maintaining absolute clearances in ballasted railway tracks using in situ three-dimensional polyurethane GeoComposites[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part F Journal of Rail & Rapid Transit, 2012, 226(3): 257-271. THOMAS S, WOODWARD P, LAGHROUCHE O. Influence of stiffening ballasted track bed overlying a masonry arch bridge using a polyurethane polymer material[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2015, 92: 111-117. KRUGLIKOV A A, YAVNA V A, ERMOLOV Y M. Strengthening of the railway ballast section shoulder with two-component polymeric binders[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2017, 11: 133-143. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2017.05.004 DERSCH M, TUTUMLUER E, BOWER C P. Polyurethane coating of railroad ballast aggregate for improved performance[C]// Joint Rail Conference. Urbana: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2010: 337-342 郄录朝,王红,许永贤. 聚氨酯固化道床的力学性能试验研究[J]. 铁道建筑,2015(1): 107-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2015.01.24QIE Luchao, WANG Hong, XU Yongxian. Experimental study on mechanical performance of polyurethane solidified ballast bed[J]. Railway Engineering, 2015(1): 107-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2015.01.24 PLOOY R F D. Characterisation of rigid polyurethane foam reinforced ballast through cyclic loading box tests[D]. Pretoria: University of Pretoria, 2016 铁道部运输局. 2012 高速铁路有砟轨道线路维修规则(试行)[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2012 LICHTBERGER B. the lateral resistance of the track[J]. European Railway Review, 2007, 3: 1-7. PEN L L, BHANDARI A R, POWRIE W. Sleeper end resistance of ballasted railway tracks[J]. Journal of Geotechnical & Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2014, 140(5): 04014004-1-04014004-14. -




 下载:
下载: