Review of Bridge Foundation Scour
-
摘要: 冲刷是导致桥梁结构破坏的关键因素之一,从机理、计算、模型、探测及防护、承载及变形等5个方面较为系统地对桥梁基础冲刷的研究和实践进行了综述. 首先,在总结现有桥梁基础冲刷机理的基础上,对比分析了已有冲刷计算公式,阐明不同公式的局限性;随后,通过综述桥梁基础冲刷在试验和数值方面的研究,指出模型试验及数值模拟方法存在的不足和问题;此外,讨论了桥梁基础冲刷探测方法及主要的冲刷防护措施,比较了各种探测方法的优缺点及各种防护措施的作用原理,概述了冲刷对桥墩承载及变形特性的影响;最后,指出了桥梁基础冲刷方面值得进一步研究的问题和发展方向.Abstract: Scour is one of the key causes of bridge failures. This paper presents a comprehensive review of the current research on scour at bridge foundations from five aspects: mechanism, calculation, modelling, monitoring and countermeasures, load and deformation. Based on the mechanism of scour around bridge foundations, different formulae developed for calculating scour depth are compared and analysed, and the limitations of the existing formulae are summarized. The results of numerical and laboratory models established for the scour studies are presented, along with a summary of the experimental and simulation limits. Moreover, a summary of monitoring methods with their advantages and disadvantages, as well as the countermeasures with their mechanisms and the effects on lateral load and deformation of bridge pillars is given. Finally, the future research trends of bridge foundation scour are presented, which provides some reference for research, design, and construction.
-
Key words:
- bridge foundation /
- scour /
- review /
- research status
-
表 1 中美桥梁基础冲刷计算公式的优缺点对比
Table 1. Advantages and disadvantages of calculation formulae of China and US
计算公式 优点 缺点 中国规范 清水冲刷和动床冲刷采用不同的计算公式,两者区分更加明显;修正式65-1和式65-2选择两者估算值中
最不利的一种;与现场实测数据结果的拟合较好.参数较多,且大部分参数的取值存在较大的不确定性;同一公式两边的量纲不一致,不同公式右侧的量纲也不相同,公式经验性极强;未考虑漂流物墩前聚集对桥墩局部冲刷的影响;复杂群桩桥墩冲刷的计算结果对设计和工程实际的参考价值有限. 美国规范 参数较少,简化,便于理解和应用;公式两边量纲一致,引入弗劳德数,使水力学方面的物理意义更明确;对于复杂群桩桥墩冲刷的叠加法,概念明确,实现了与简单桥墩冲刷的统一计算;能考虑漂浮物聚集对桥墩局部冲刷的影响. 未涉及河床泥沙颗粒对局部冲刷深度的影响,仅仅通过系数考虑河床地貌的影响;计算结果偏于保守;与现场实测数据的拟合误差较大. 表 2 桥梁基础冲刷现有测量仪器对比
Table 2. Comparison of existing instruments for monitoring bridge foundation scour
探测仪器 优点 缺点或局限性 相对成本 雷达 持续探测 操作耗时;需要专业培训 高 声纳 持续精确探测 平缓的河流 (河口) 中 声学多普勒电流分析仪 便携能测量速度分布和水深 不适用于泥沙浓度含量高的条件 高 FBG传感器 河床连续监测 现场测试成功率有限 高 编号的砖 易于获得;适用于高度湍流和快速流动 要求开挖河床;适用于临时河流 低 SMC 易于操作 要求开挖河床;高维护和修理费用 低 钢棒 易于操作 要求开挖河床;高维护和修理费用 低 表 3 两种不同原理的冲刷措施对比
Table 3. Comparison between two different scour countermeasures
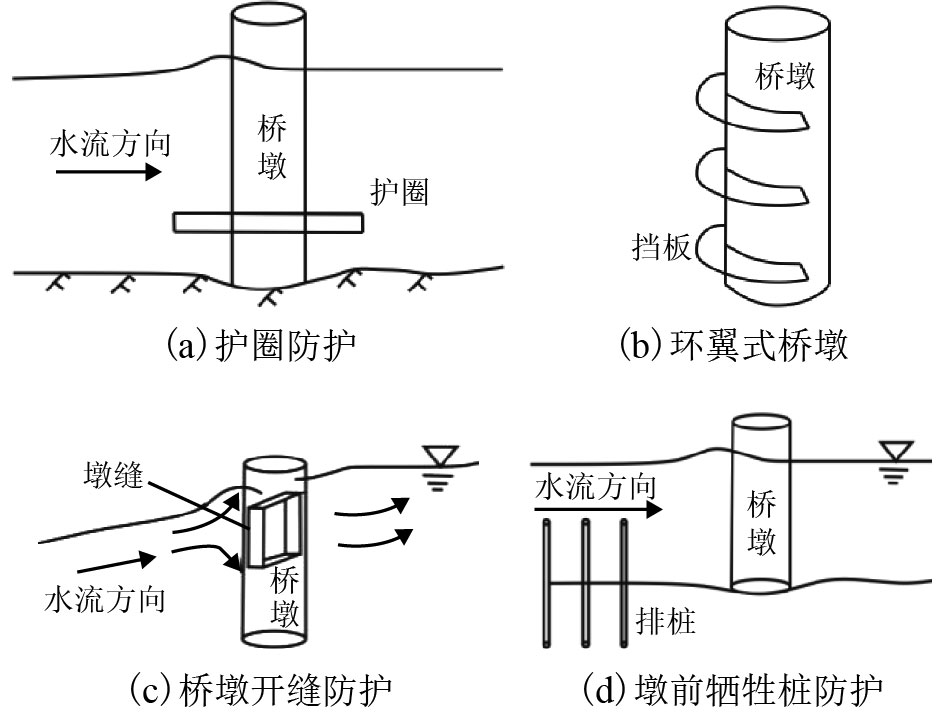
项目 主动防护 被动防护 原理 改变水流特性、破坏涡流,减少冲刷效应 铺设保护层,保护下层免受冲刷 工程措施 护圈、挡板、桥墩开缝、墩前排桩等 铺设防护层、抛石防护、扩大基础等 优点 可以为不同位置条件选择不同的设计以获得满意的结果 最常用;使用方便;在多数情况下效果好 缺点 特定的条件下需要特殊设计;成本增加和新结构的建设 难以保持保护层位置;引起额外的束缩冲刷 -
DENG L, CAI C S. Applications of fiber optic sensors in civil engineering[J]. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 2007, 25(5): 577-596. doi: 10.12989/sem.2007.25.5.577 HUNT E B. Monitoring scour critical bridge[R], Washington D. C.: Transportation Research Board, National Research Council, 2009 XIONG W, CAI C S, KONG X. Instrumentation design for bridge scour monitoring using fiber bragg grating sensors[J]. Applied Optics, 2012, 51(5): 547-557. doi: 10.1364/AO.51.000547 LIANG F Y, BENNETT C, PARSONS R, et al. A literature review on behavior of scoured piles under bridges[C]//Proceadings of the 2009 International foundation Congress and Equipment Expo. Orlando: the International Foundation Congress & Equipment Expo, 2009: 482-489 DENG L, CAI C S. Bridge scour:prediction,modeling,monitoring and countermeasures-review[J]. Practice Periodical on Structural Design and Construction, 2009, 15(2): 125-134. 詹磊,董耀华,惠晓晓. 桥墩局部冲刷研究综述[J]. 水利电力科技,2007(3): 1-13. 易仁彦. 桥梁坍塌事故的原因和风险分析[J]. 养护与管理,2016(4): 22-26. 高冬光, 王亚玲. 桥涵水文[M]. 4版. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2009 MELVILLE B W, COLEMAN S E. Bridge scour[M]. Highlands Ranch: Water Resources Publications, 2000 COLEMAN S E. Clearwater local scour at complex piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2005, 131(4): 330-334. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2005)131:4(330) WANG C, YU X, LIANG F Y. A review of bridge scour:mechanism,estimation,monitoring and countermeasures[J]. Natural Hazaids, 2017, 87(3): 1-26. BABU M R, RAO S N, SUNDAR V. Current-induced scour around a vertical pile in cohesive soil[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2003, 30(7): 893-920. doi: 10.1016/S0029-8018(02)00063-X WANG C, YU X, LIANG F Y. Erosion mechanism of local scour around cushioned caisson on reinforced ground[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2017, 35(7): 1028-1036. MELVILLE B M. Local scour at bridge sites[D]. New Zealand: University of Auckland, 1975 ETTEMA R. Scour at bridge piers[D]. New Zealand: University of Auckland, 1980 VEERAPPADEVARU G, RAMASWAMYIYENGER T, JAGADEESH T R. Temporal variation of vortex scour process around caisson piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 2012, 50(2): 200-207. doi: 10.1080/00221686.2012.666832 尹学良. 清水冲刷河床粗化研究[J]. 水利学报,1963(1): 17-27. 秦荣昱,胡春宏. 河床冲刷粗化研究进展[J]. 泥沙研究,1997(2): 79-82. 韩其为, 向熙瑰, 王玉成. 床沙粗化[C]//第二次河流泥沙国际学术讨论会论文集. 北京: 水利电力出版社, 1983: 356-367 BRIAUD J L, TING F C K, CHEN H C, et al. Erosion function apparatus for scour rate predictions[J]. Journal of Geotechnical & Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2001, 127(2): 105-113. 中华人民共和国行业标准. 铁路工程水文勘测设计规范: TB10017—99[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1999 中华人民共和国行业标准. 公路工程水文勘测设计规范: JTG C30—2002[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2002 RICHARDSON E V, DAVIS S R. Evaluating scour at bridges: 4th editon[M]. Washington D. C.: Federal Highway Administration, 2001 MELVILLE B W, SUTHERLAND A J. Design method for local scour at bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1988, 114(10): 1210-1226. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1988)114:10(1210) MELVILLE B W. Pier and abutment scour:integrated approach[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1997, 123(2): 125-136. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1997)123:2(125) 张佰战,李付军. 桥墩局部冲刷计算研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2004,25(2): 48-51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2004.02.010 梁利博,杨小亭,张新燕. 圆柱桥墩局部冲刷的试验研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2010(1): 104-109.LIANG Libo, YANG Xiaoting, ZHANG Xinyan. Experimental research on cylinder pier local scour[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2010(1): 104-109. NEIL C R. River bed scour: a review for bridge engineers[M]. Calgary: [s.n.], 1964: 1-37 SHEN H W, SCHNEIDER V R, KARAKI S. Local scour around bridge piers[J]. Proc. ASCE, 1969, 95(6): 1919-1940. JAIN S C, FISCHER E E. Scour around circular bridge piers at high Froude numbers[R]. Washington D. C.: Federal Highway Administration, 1979 SHEPPARD D M, MILLER W. Live-bed local pier scour experiments[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2006, 132(7): 635-642. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2006)132:7(635) QI Meilan, LI Jinzhao, CHEN Qigang. Comparison of existing equations for local scour at bridge piers:parameter influence and validation[J]. Natural Hazards, 2016, 82(3): 2089-2105. doi: 10.1007/s11069-016-2287-z SHEPPARD D M, MILLER W. Evaluation of existing equations for local scour at bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2014, 140(1): 14-23. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000800 LIANG Fayun, WANG C, HUANG M, et al. Experimental observations and evaluations of formulae for local scour at pile groups in steady currents[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2017, 35(2): 245-255. LEE T L, JENG D S, ZHANG G H, et al. Neural network modeling for estimation of scour depth around bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2007, 19(3): 378-386. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(07)60073-0 CARDOSO A H, BETTESS R. Effect of time and channel geometry on scour at bridge abutments[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1999, 125(4): 388-399. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1999)125:4(388) OLIVETO G, HAGER W H. Temporal evolution of clear-water pier and abutment scour[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2002, 128(9): 811-820. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2002)128:9(811) CHANG W Y, LAI J S, YEN C L. Evolution of scour depth at circular bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2004, 130(9): 905-913. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2004)130:9(905) MIA M F, NAGO H. Design method of time-dependent local scour at circular bridge pier[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2003, 129(6): 420-427. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2003)129:6(420) YANMAZ A M, ALTINBILEK H D. Study of time-dependent local scour around bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1991, 117(10): 1247-1268. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1991)117:10(1247) KOTHYARI U, GARDE R, RANGA R K. Temporal variation of scour around circular bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1992, 118(8): 1091-1106. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1992)118:8(1091) MELVILLE, B W, CHIEW Y M. Time scale for local scour at bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1999, 125(1): 59-65. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1999)125:1(59) 李成才. 桥墩局部冲刷试验及计算理论研究[D]. 南京: 河海大学, 2007 刘谨,刘芳亮,冯良平,等. 某跨海大桥桥墩基础冲刷试验研究[J]. 公路,2012(10): 61-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0451-0712.2012.10.014 ZHAO Ming, ZHU Xiansong, CHENG Liang, et al. Experimental study of local scour around subsea caissons in steady currents[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2012, 60(1): 30-40. ATAIE-ASHTIANI B, BEHESHTI A A. Experimental investigation of clear-water local scour at pile groups[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2006, 132(10): 1100-1104. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2006)132:10(1100) 卢中一, 高正荣, 杨程生. 大型沉井基础施工过程中局部冲刷试验研究[C]//第十四届中国海洋(岸)工程学术讨论会论文集(下册). 北京: 海洋出版社, 2009, 1139-1146 张新燕,吕宏兴,沈波. 圆柱桥墩局部冲刷机理试验研究[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2012(2): 34-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2012.02.006ZHANG Xinyan, LÜ Hongxing, SHEN Bo. Experimental studies on local scour mechanism of cylinder bridge piers[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2012(2): 34-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2012.02.006 梁发云,王琛,黄茂松,等. 沉井基础局部冲刷形态的体型影响效应与动态演化[J]. 中国公路学报,2013,29(9): 779-782.LIANG Fayun, WANG Chen, HUANG Maosong, et al. Scale effects on local scour configurations around caisson foundation and dynamic evolution[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2013, 29(9): 779-782. BAKER C J. The position of points of maximum and minimum shear stress upstream of cylinders mounted normal to flat plates[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1985, 18: 263-274. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(85)90085-6 SUMER B M, FREDSØE J. The mechanics of scour in the marine environment[M]. Singapore: World Scientific, 2002: 149-228 ZHAO M, CHENG L. Numerical investigation of local scour below a vibrating pipeline under steady currents[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2010, 57: 397-406. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2009.11.008 ZHAO M, CHENG L, ZANG Z. Experimental and numerical investigation of local scour around a submerged vertical circular cylinder in steady currents[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2010, 57: 709-721. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2010.03.002 LU J Y, SHI Z Z, HONG J H, et al. Temporal variation of scour depth at non-uniform cylindrical piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2011, 137(1): 45-56. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000272 林海峰,王萍. 泰州大桥夹江桥动床模型试验研究[J]. 中国工程学科,2010,12(4): 86-89. ETTEMA R, MELVILLE B W, BARKDOLL B. Scale effect in pier-scour experiments[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1998, 124(6): 639-642. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1998)124:6(639) ETTEMA R, KIRKIL G, MUSTE M. Similitude of large-scale turbulence in experiments on local scour at cylinders[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2006, 132(1): 33-40. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2006)132:1(33) LEE S O, STURM T. Scaling issues for laboratory modeling of bridge pier scour[C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Scour and Erosion. Tokyo: ISSMGE, 2008: 111-115 HUANG Wenrui, YANG Qiping, XIAO Hong. CFD modeling of scale effects on turbulence flow and scour around bridge piers[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2009, 38(5): 1050-1058. 韦雁机,叶银灿,吴珂,等. 桩周局部冲刷三维数值模拟[J]. 海洋工程,2009,27(4): 61-66.WEI Yanji, YE Yincan, WU Ke, et al. 3D numerical modeling of flow and scour around a circular pile[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2009, 27(4): 61-66. 贠鹏. 桥墩局部冲刷的数值模拟研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012 ZHU Zhiwen, LIU Zhenqing. CFD prediction of local scour hole around bridge piers[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012, 19(1): 273-281. doi: 10.1007/s11771-012-1001-x XIONG W, CAI C S, KONG B, et al. CFD simulation and analyses for bridge-scour development using a dynamic-mesh updating technique[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2016, 30(1): 1-10. SAGHRAVANI S F, AZHARI A. Simulation of clear water local scour around a group of bridge piers using an eulerian 3D,two-phase model[J]. Progress in Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2012, 12(5): 333-341. doi: 10.1504/PCFD.2012.049097 KIM H S, NABI M, KIMURA I, et al. Numerical investigation of local scour at two adjacent cylinders[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2014, 70: 131-147. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2014.04.018 BURKOW M, GRIEBEL M. A full three dimensional numerical simulation of the sediment transport and the scouring at a rectangular obstacle[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2015, 125: 1-10. OLSEN N R B, MELAEN M C. Three-dimensional calculation of scour around cylinders[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1993, 119(9): 1048-1054. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1993)119:9(1048) LEO C, VAN R. Application of sediment pick-up function[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1986, 112(9): 867-874. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1986)112:9(867) LEO C, VAN R, HENK V R, et al. Field verification of 2D and 3D suspended sediment Models[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1990, 116(10): 1270-1288. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1990)116:10(1270) OLSEN N R B. Three-dimensional CFD modeling of self-forming meandering channel[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2003, 129(5): 366-372. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2003)129:5(366) YOUNG G K, DOU X, SAFFARINIA K, et al. Testing abutment scour model[C]//Water Resources Engineering Conference. Virginia: ASCE, 1998: 180-185 KASSEM A, SALAHELDIN T M, IMRAN J, et al. Numerical modeling of scour in cohesive soils around artificial rock island of cooper river bridge[J]. Transportation Research Record:Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2003, 1851: 45-50. doi: 10.3141/1851-05 MILLARD S G, BUNGEY J H, THOMAS C, et al. Assessing bridge pier scour by radar[J]. NDT & E International, 1997, 31(4): 251-258. PARK I, LEE J, CHO W. Assessment of bridge scour and riverbed variation by a ground penetrating radar[C]//10th International Conference on Ground Penetrating Radar. Delft: IEEE, 2005, 411-414 FALCO F D, MELE R. The monitoring of bridges for scour by sonar and sediment[J]. NDT &E International, 2002, 35(2): 117-123. HUNT B E. Scour monitoring programs for bridge health[C]//Proceedings of 6th International Bridge Engineering Conference. Boston: National Academy of Engineering, 2005, 531-536 YU X, ZABILANSKY L J. Time domain reflectometry for automatic bridge scour monitoring[J]. Geotechnical Special Publication, 2006, 149: 152-159. YU Xinbao, YU Xiong. Algorithm for time domain reflectometry bridge scour measurement system[C]//Proceeding of the 7th International Symposia on Field Measurements in Geomechanics. Boston: ASCE, 2007: 1-10 LIN Y B, CHANG K C, LAI J S, et al. Application of optical fiber sensors on local scour monitoring[C]//Proceeding of IEEE Sensors. Vienna: IEEE, 2004, 832-835 LIN Y B, CHEN J C, CHANG K C, et al. Real-time monitoring of local scour by using fiber Bragg grating sensors[J]. Smart Materials & Structures, 2005, 14(4): 664-670. LU J Y, HONG J H, SU C C, et al. Field measurements and simulation of bridge scour depth variation during floods[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2008, 134(6): 810-821. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2008)134:6(810) 梁发云,王琛. 桥墩基础局部冲刷防护技术的对比分析[J]. 结构工程师,2014,30(5): 779-782.LIANG Fayun, WANG Chen. Review on countermeasures to bridge piers from local scour[J]. Structural Engineers, 2014, 30(5): 779-782. LAGASSE P F, CLOPPER P E, ZEVENBERGEN L W, et al. NCHRP report 593: countermeasures to protect bridge piers from scour[R]. Washington D. C.: Transportation Research Board, 2007 BARKDOLL B D, ETTEMA R, MELVILLE B W. NCHRP report 587: countermeasures to protect bridge abutments from scour[R]. Washington D. C.: Transportation Research Board, 2007 CHIEW Y M. Scour protection at bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1992, 118(9): 1260-1269. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1992)118:9(1260) ZARRATI A R, GHOLAMI H, MASHAHIR M B. Application of collar to control scouring around rectangular bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 2004, 42(1): 97-103. doi: 10.1080/00221686.2004.9641188 KUMAR V, RANGARAJU K G, VITTAL N. Reduction of local scour around bridge piers using slot and collar[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1999, 125(12): 1302-1305. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1999)125:12(1302) MELVILLE B W, HADFIELD A C. Use of sacrificial piles as pier scour countermeasures[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1999, 125(11): 1221-1224. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1999)125:11(1221) HAQUE A, RAHMAN M M, ISLAM G T, et al. Scour mitigation at bridge piers using sacrificial piles[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research,China, 2007, 22(1): 49-59. TAFAROJNORUZ A, GAUDIO R. Evaluation of flow-altering countermeasures against bridge pier scour[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2012, 138(3): 297-305. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000512 WANG C, LIANG F Y, YU X. Experimental and numerical investigation of sacrificial piles to diminish local scour around pile groups[J]. Natural Hazards, 2017, 85: 1417-1435. doi: 10.1007/s11069-016-2634-0 LAGASSE P F, CLOPPER P E, ZEVENBERGEN L W, et al. NCHRP report 593: countermeasures to protect bridge piers from scour[R]. Washington D. C.: Transportation Research Board, 2007 LAUCHLAN C S, MELVILLE B W. Riprap protection at bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2001, 127(5): 412-418. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2001)127:5(412) LIM F H, CHIEW Y M. Parametric study of riprap failure around bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 2001, 39(1): 61-72. doi: 10.1080/00221680109499803 PARKER G, TOROESCOBAR C, VOIGT R L. Countermeasures to protect bridge piers from scour[R]. Minnesota: University of Minnesota, 1998 LAGASSE P F, ZEVENBERGEN L W, SCHALL J D, et al. Bridge scour and stream instability countermeasures[R]. Washington D. C.: FHWA, 2001 LAGASSE P F. 1998 Scanning review of European practice for bridge scour and stream instability countermeasures[R]. Washington D. C.: Transportation Research Board of the National Academies, 1999 BEZGIN N O. Finite element modeling of soil structure interaction for drilled shaft foundation[D]. New Brunswick: The State University of New Jersey, 2005 AVENT R R, ALAWADY M. Bridge scour and substructure deterioration:case study[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2005, 10(3): 247-254. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(2005)10:3(247) DANIELS J, HUGHES D, RAMEY G E, et al. Effects of bridge pile bent geometry and levels of scour and P loads on bent pushover loads in extreme flood/scour events[J]. Practice Periodical on Structural Design and Construction, 2007, 12(2): 122-134. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0680(2007)12:2(122) HUGHES D, RAMEY G E, HUGHES M L. Bridge pile bent number of piles and X-bracing system:impact on pushover capacity as scour increases[J]. Practice Periodical on Structural Design and Construction, 2007, 12(2): 82-95. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0680(2007)12:2(82) LIN C, BENNETT C, HAN J, et al. Scour effects on the response of laterally loaded piles considering stress history of sand[J]. Computers & Geotechnics, 2010, 37(7): 1008-1014. LIN C. Evaluation of lateral behavior of pile-supported bridges under scour conditions[D]. Kansas: University of Kansas, 2012 BROMS B B. Lateral resistance of piles in cohesionless soils[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 1964, 90(SM2,Part 1): 27-63. BROMS B B. Lateral resistance of piles in cohesionless soils[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 1964, 90(SM3,Part 1): 123-156. POULOS H G. Behavior of laterally loaded piles:I-single piles[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 1971, 97(5): 711-731. HETÉNYI M. Beams on elastic foundation; theory with applications in the fields of civil and mechanical engineering[D]. Michigan: The University of Michigan Press, 1964 REESE L C, VAN IMPE W F, HOLTZ R D. Single piles and pile groups under lateral loading[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2000, 55(1): 9-10. NI S H, HUANG Y H, LO K F. Numerical investigation of the scouring effect on the lateral response of piles in sand[J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2011, 26(3): 320-325. KUO Y S, ACHMUS M, KAO C S. Practical design considerations of monopile foundations with respect to scour[C]//Proceedings of Global Wind Power Conference 2008. Beijing: Global Wind Energy Council, 2008: 29-31 LI F, HAN J, LIN C. Effect of scour on the behavior of laterally loaded single piles in marine clay[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2013, 31(3): 271-289. LIN C, HAN J, BENNETT C, et al. Analysis of laterally loaded piles in sand considering scour hole dimensions[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2014, 140(6): 04014024. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001111 REESE L C, COX W R, KOOP F D. Analysis of laterally loaded pile in sand[C]//Proceedings of the 6th Annual Offshore Technology Conference. Houston: OTC, 1974: 95-104 杨晓峰,张陈蓉,袁聚云. 砂土中考虑冲刷的水平受荷桩等效应变楔方法[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(10): 2946-2950.YANG Xiaofeng, ZHANG Chenrong, YUAN Juyun. Equivalent-strain wedge method for laterally loaded pile in sand considering scouring effect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(10): 2946-2950. ASHOUR M, NORRIS G, PILLING P. Lateral loading of a pile in layered soil using the strain wedge model[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 1998, 124(4): 303-315. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1998)124:4(303) DIAMANTIDIS D, ARNESEN K. Scour effects in piles structures-a sensitivity analysis[J]. Ocean Engineering, 1986, 13(5): 497-502. doi: 10.1016/0029-8018(86)90035-1 ACHMUS M, KUO Y S, ABDELRAHMAN, K. Numerical investigation of scour effect on lateral resistance of windfarm monopiles[C]//20th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. Beijing: ISOPE, 2010: 619-623 MCCONNELL J R, CANN, M. Assessment of bridge strength and stability under scour conditions[C]//Proceedings of ASCE SEI 2010 Structures Congress. Orlando: ASCE, 2010: 121-132 FOTI S, SABIA D. Influence of foundation scour on the dynamic response of an existing bridge[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2011, 16(2): 295-304. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000146 -




 下载:
下载: