Study on Partial-Wear-Factor Model Monorail Vehicle Running Wheel
-
摘要: 走行轮胎偏磨损导致换胎频繁是影响跨座式单轨交通运营成本的重要因素之一. 为快速评估不同单轨车辆设计方案的走行轮胎偏磨损状态,采用因子分析方法分析了影响走行轮偏磨损的10个评价指标,建立了走行轮胎偏磨损因子模型,提出了依据走行轮胎偏磨损因子得分高低评价车辆设计方案优劣的方法. 研究结果发现:影响走行轮胎偏磨损的因子得分排序依次为走行轮纵横向参数因子、导向轮轴距因子、走行轮垂向刚度因子和导向轮垂距因子;建立的走行轮偏磨损因子模型和偏磨损因子得分公式能快速评估不同单轨车辆结构设计方案下的走行轮胎偏磨损状态,从而为跨座式单轨车辆转向架开发设计提供了一种有效的优化设计方法.Abstract: Frequent tire changes caused by running tire abrasion play an important role in affecting the cost of monorails. For rapid assessing the partial wear state of monorail vehicle running wheels on the different vehicle design, the factor analysis method was adopted to study the 10 evaluation indices that influence partial wear, the partial-wear factor model was established and a method was proposed for evaluating the merits and demerits of vehicle design schemes by the score of running wheels’ partial wear factor. The findings indicate the principal factors influencing partial wear in order of importance are the horizontal and vertical parameters, wheel base orientation, vertical stiffness of the running wheel, and vertical distance of the guiding wheel. The partial-wear-factor model and the partial-wear-factor score formula can quickly and reliably be used to evaluate the partial-wear state of the running wheel in different monorail vehicle structure designs. It provides an effective optimization design method for the development of bogies for monorail vehicles.
-
Key words:
- running-wheel partial wear /
- factor analysis /
- evaluation index /
- factor score /
- weight
-
表 1 走行轮偏磨损评价指标取值范围
Table 1. Factor analysis range variable of running wheel partial wear
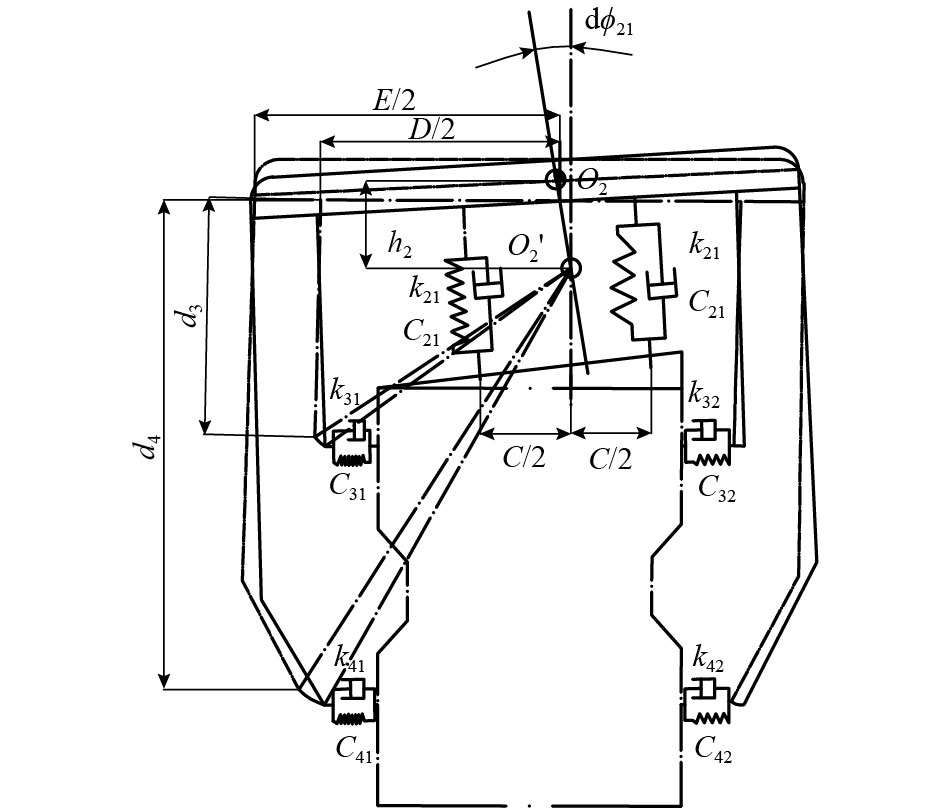
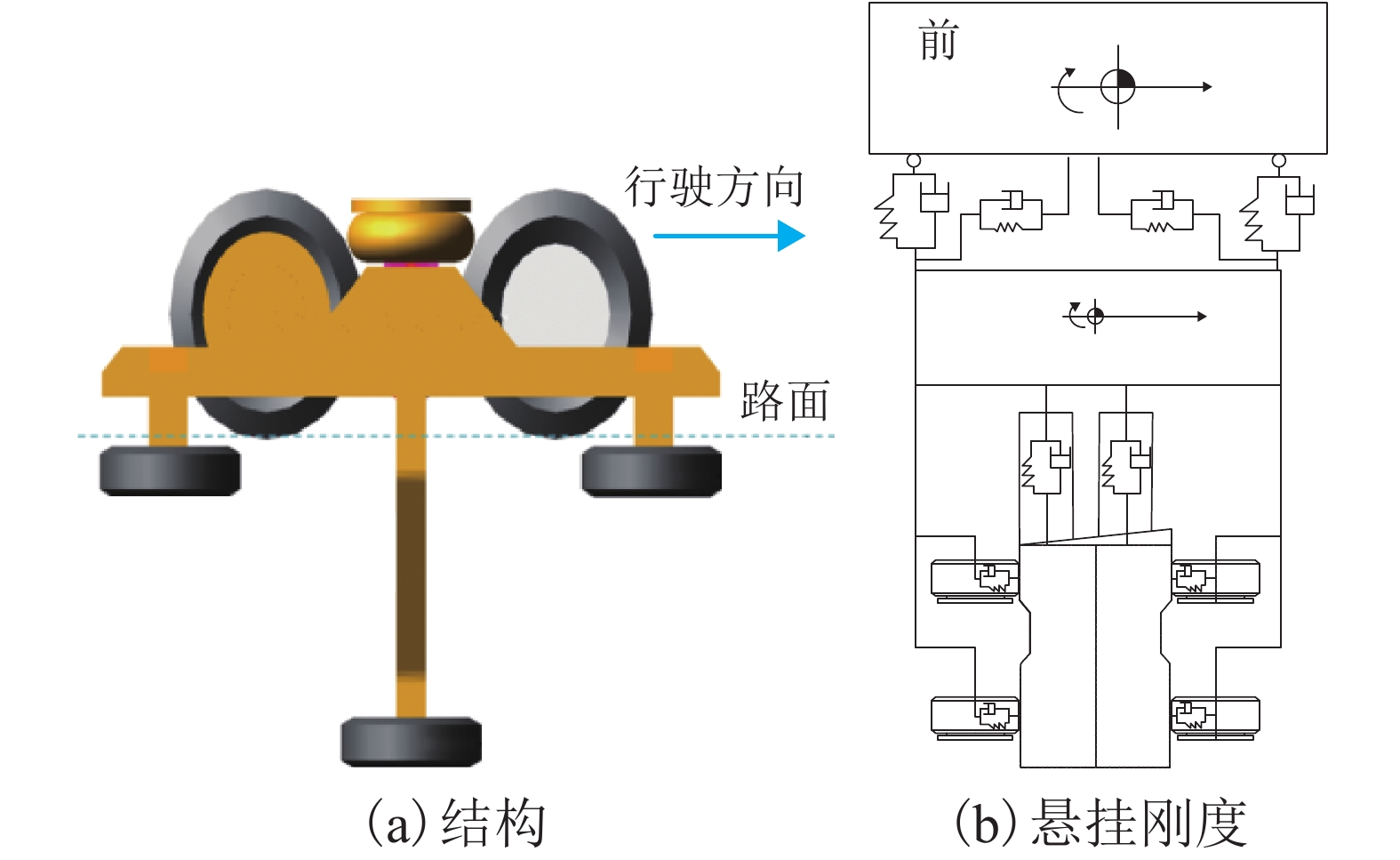
评价指标 上限 下限 走行轮垂向刚度Kzz/(kN•m–1) 1 110 1 510 走行轮纵向滑移刚度Kzx/(kN•m–1) 459.2 659.2 走行轮侧偏刚度Kzα/(kN•m–1) 253.1 453.1 水平轮垂向刚度Kdz/(kN•m–1) 950 1 350 空气弹簧垂向刚度Kqz/(kN•m–1) 140 180 走行轮轴距L1/m 1.4 1.6 前导向轮轴距L2/m 1.15 1.35 后导向轮轴距L3/m 1.15 1.35 导向轮垂距L4/m 0.62 0.69 稳定轮垂距L5/m 1.6 1.8 表 2 单轨车辆结构和悬挂参数原始数据
Table 2. Original data of structure and suspension parameters of running wheel
序号 Kqz/(N•m–1) Kdz/(N•m–1) L1/m L2/m L3/m L4/m L5/m Kzα/(N•m–1) Kzx/(N•m–1) Kzz/(N•m–1) 1 246 400 1 114 000 1.44 1.200 1.40 0.620 1.800 441 121 648 800 8 503 600 2 179 200 1 088 800 1.46 1.250 1.13 0.680 1.730 284 321 534 800 2 212 400 $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ 292 185 600 1 145 200 1.4 1.260 0.66 1.150 0.635 1.790 273 521 508 800 293 185 600 1 350 000 1.41 1.280 0.67 1.150 0.660 1.790 276 721 508 800 表 3 相关系数
Table 3. Correlation coefficient
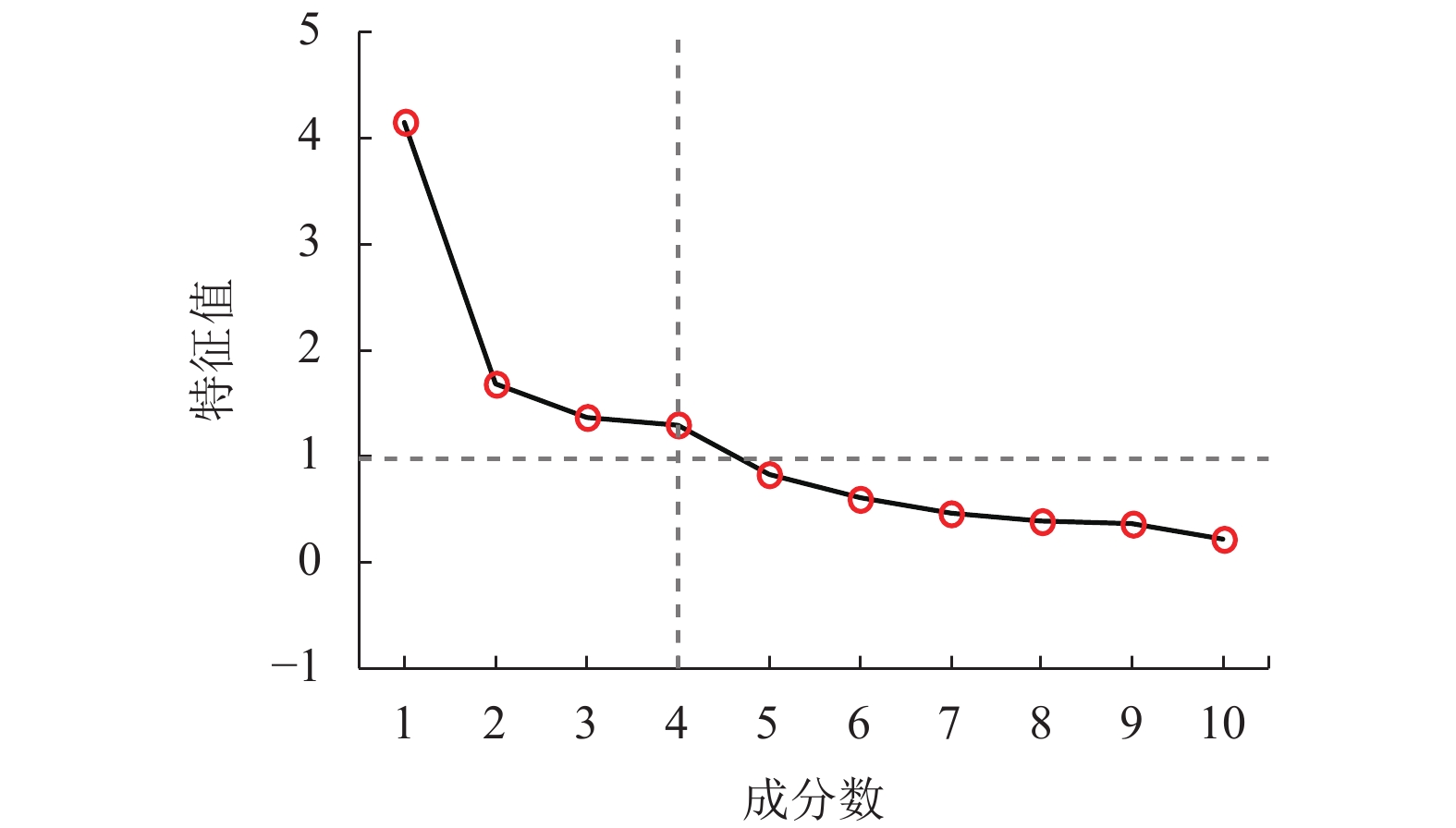
评价指标 Kqz Kdz L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 Kzα Kzx Kzz Kqz 1 –0.248 –0.136 –0.114 –0.116 –0.199 –0.367 0.816 0.649 0.642 Kdz –0.248 1 –0.718 0.070 –0.245 0.028 0.864 –0.683 –0.624 –0.288 L1 –0.136 –0.718 1 0.157 0.123 0.038 –0.436 0.600 0.307 0.138 L2 –0.114 0.070 0.157 1 –0.228 0.074 0.060 0.143 –0.257 0.217 L3 –0.116 –0.245 0.123 –0.228 1 0.248 –0.172 0.307 0.446 0.512 L4 –0.199 0.028 0.038 0.074 0.248 1 –0.138 0.012 –0.057 –0.034 L5 –0.367 0.864 –0.436 0.060 –0.172 –0.138 1 –0.497 –0.494 –0.079 Kzα 0.816 –0.683 0.600 0.143 0.307 0.012 –0.497 1 0.532 0.589 Kzx 0.649 –0.624 0.307 –0.257 0.446 –0.057 –0.494 0.532 1 0.617 Kzz 0.642 –0.288 0.138 0.217 0.512 –0.034 –0.079 0.589 0.617 1 表 4 特征值及其贡献率
Table 4. Eigenvalues and contribution rates
主成分 初始特征值 提取平方和载入 旋转平方和载入 特征值$\lambda_i$ 方差贡献
率/%累积方差
贡献率/%特征值${\lambda_i}$ 方差贡献
率/%累积方差
贡献率/%特征值$\lambda_i$ 方差贡献
率/%累积贡献
率/%第1个 4.154 41.539 41.539 4.153 4.154 41.539 3.993 39.932 39.932 第2个 1.686 16.863 58.402 1.676 1.686 58.402 1.943 19.433 59.365 第3个 1.373 13.730 72.132 1.626 1.373 72.132 1.295 12.954 72.319 第4个 1.303 13.029 85.161 1.262 1.303 85.161 1.284 12.842 85.161 表 5 旋转后因子载荷
Table 5. Rotation factor load
评价指标 主因子 T1 T2 T3 T4 Kdz –0.849 0.155 –0.018 0.058 Kzα 0.822 0.038 0.337 0.011 L5 –0.765 0.121 0.080 –0.199 L1 0.777 0.235 0.039 0.007 Kzx 0.620 –0.497 –0.257 –0.112 L2 0.057 0.874 0.239 0.078 L3 0.188 –0.558 0.472 0.393 L4 0.019 –0.046 –0.034 0.959 Kqz 0.042 –0.042 0.034 –0.099 Kzz 0.091 0.124 0.910 –0.053 表 6 因子得分系数
Table 6. Component score coefficient
评价指标 主因子 T1 T2 T3 T4 Kqz –0.017 0.011 0.042 0.117 Kdz –0.307 0.040 0.126 0.091 L1 0.311 0.232 –0.107 –0.037 L2 0.057 0.630 0.173 0.075 L3 –0.067 –0.387 0.363 0.275 L4 –0.013 0.072 –0.069 0.871 L5 –0.283 0.005 0.202 –0.183 Kzα 0.254 0.097 0.146 –0.011 Kzx 0.151 –0.314 0.125 –0.156 Kzz –0.111 0.081 0.761 –0.066 表 7 3种单轨车辆设计方案参数
Table 7. Design parameters of three kinds of monorail
设计方案 Kqz Kdz L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 Kzα Kzx Kzz 1 186 400 1 043 200 1.58 1.11 1.28 0.675 1.62 383 721 656 400 2 741 200 2 174 800 1 135 200 1.47 1.23 1.25 0.690 1.73 435 121 560 800 4 987 600 3 185 600 1 350 000 1.41 1.12 1.15 0.630 1.79 302 321 508 800 6 687 200 表 8 3种设计方案因子得分及排名
Table 8. Factor scores and ranking of three designs
设计方案 因子1得分 因子2得分 因子3得分 因子4得分 综合得分G 综合排名 1 3.908 –3.044 0.474 –3.935 4.28 Ⅲ 2 1.974 –0.837 1.351 –1.270 4.33 Ⅱ 3 –0.817 –1.847 –1.163 –0.928 5.84 Ⅰ -
熊嘉阳,邓永权,曹亚博,等. 重载铁路轮轨磨耗及其对安全运行的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(2): 302-308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.02.018XIONG Jiayang, DENG Yongquan, CAO Yabo, et al. Wheel-Rail wear on heavy haul lines and its influences on running stability of trains[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(2): 302-308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.02.018 KENJIRO G, TAKAOMI N, MOTOMI H, ET al. A curving simulation for a monorail car[C]//11th Mini Conference on Vehicle System Dynamics Identification and Anomalies, Hungary Budapest. [S.l.]: Technical University of Budapest, 2008: 171~177 HORN J L. A rationale and test for the number of factors in factor analysis[J]. Psychnmetrica, 1965, 30(2): 179-185. doi: 10.1007/BF02289447 李雄峰,陈鹏宇,韩文奇. 因子分析法在泥石流危险性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2016,27(1): 55-61.LI Xiongfeng, CHEN Pengyu, HAN Wenqi, et al. Application of factor analysis to debris flow risk assessment[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2016, 27(1): 55-61. 马水山,王志旺,张漫. 滑坡监测资料的因子分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2002,21(7): 1003-1006. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2002.07.013MA Shuishan, WANG Zhiwang, ZHANG Man. The factor analysis of landslide monitoring data[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 21(7): 1003-1006. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2002.07.013 文孝霞,杜子学,左长永,等. 曲线工况下跨座式单轨走行轮侧偏刚度对轮胎磨损的影响[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2014,14(2): 41-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2014.02.008WEN Xiaoxia, DU Zixue, ZUO Changyong, et al. Influence of cornering stiffness of straddle-type monorail running wheel on tire wear under curve negotiating[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2014, 14(2): 41-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2014.02.008 赵建军,贺宇航,黄润秋,等. 基于因子分析法的边坡稳定性评价指标权重[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(2): 325-330. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.02.018ZHAO Jianjun, HE Yuhang, HUANG Runqiu, et al. Weights of slope stability evaluation indexes based on factor analysis method[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(2): 325-330. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.02.018 门宝辉,梁川. 基于变异系数权重的水质评价属性识别模型[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2005,37(10): 1373-1375. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2005.10.020MEN Baohui, LIANG Chuan. Attribute recognition model-based variation coefficient weight for evaluating water quality[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2005, 37(10): 1373-1375. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2005.10.020 刘鹏飞,王开云,翟婉明. 驱动工况下重载机车与轨道动态相互作用[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(2): 302-308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.01.003LIU Pengfei, WANG Kaiyun, ZHAI Wanming, et al. Dynamics interaction between heavy-haul locomotive and track under driving conditions[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(2): 302-308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.01.003 文孝霞,杜子学,许舟洲,等. 基于降低走行轮偏磨损的单轨车辆结构参数优化研究[J]. 现代制造工程,2016(12): 9-15.WEN Xiaoxia, DU Zixue, XU Zhouzhou et al. Influence research of structural parameters on running wheel shoulder wear of the monorail vehicle[J]. Modern Manufacturing Engineering, 2016(12): 9-15. 杜子学,李云川,文孝霞,等. 基于SIMPACK/ISIGHT的跨座式单轨列车走行轮偏磨研究与优化[J]. 铁道车辆,2016(4): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7610.2016.04.001DU Zixue, LI Yunchuan, WEN Xiaoxia et al. Research on side wear of the running wheel for straddle type monorail train based on SIMPACK/ISIGHT and the optimization[J]. Rolling Stock, 2016(4): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7610.2016.04.001 -




 下载:
下载: