Experiment Study on Non-limit Passive Earth Pressure of Clay under Different Displacement Modes
-
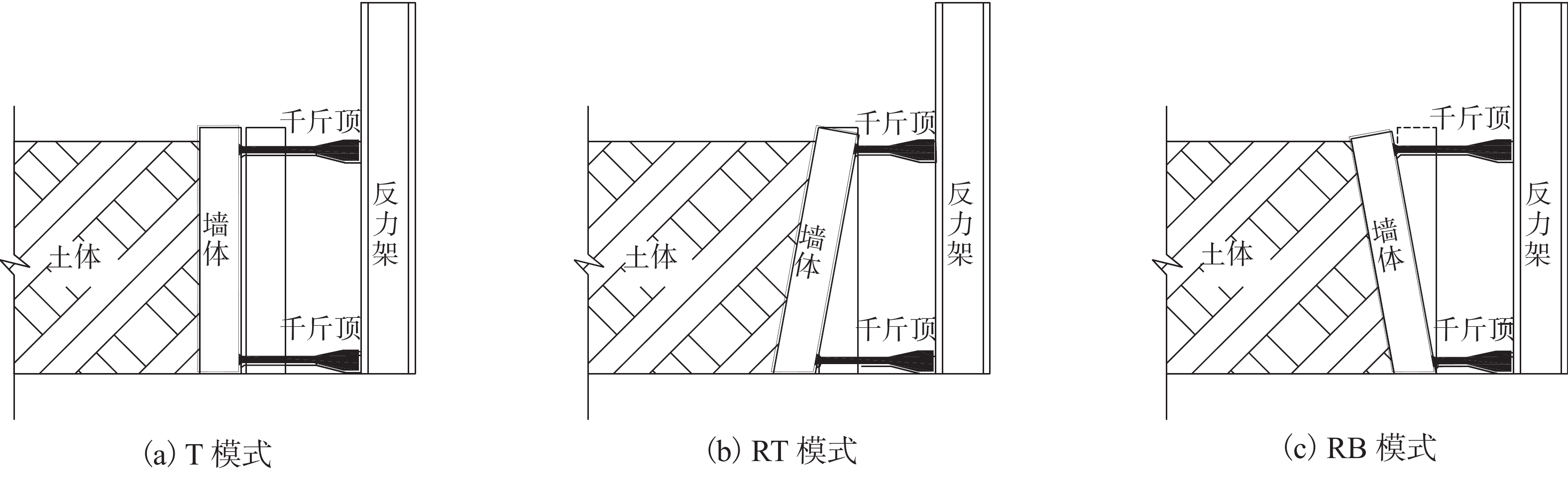
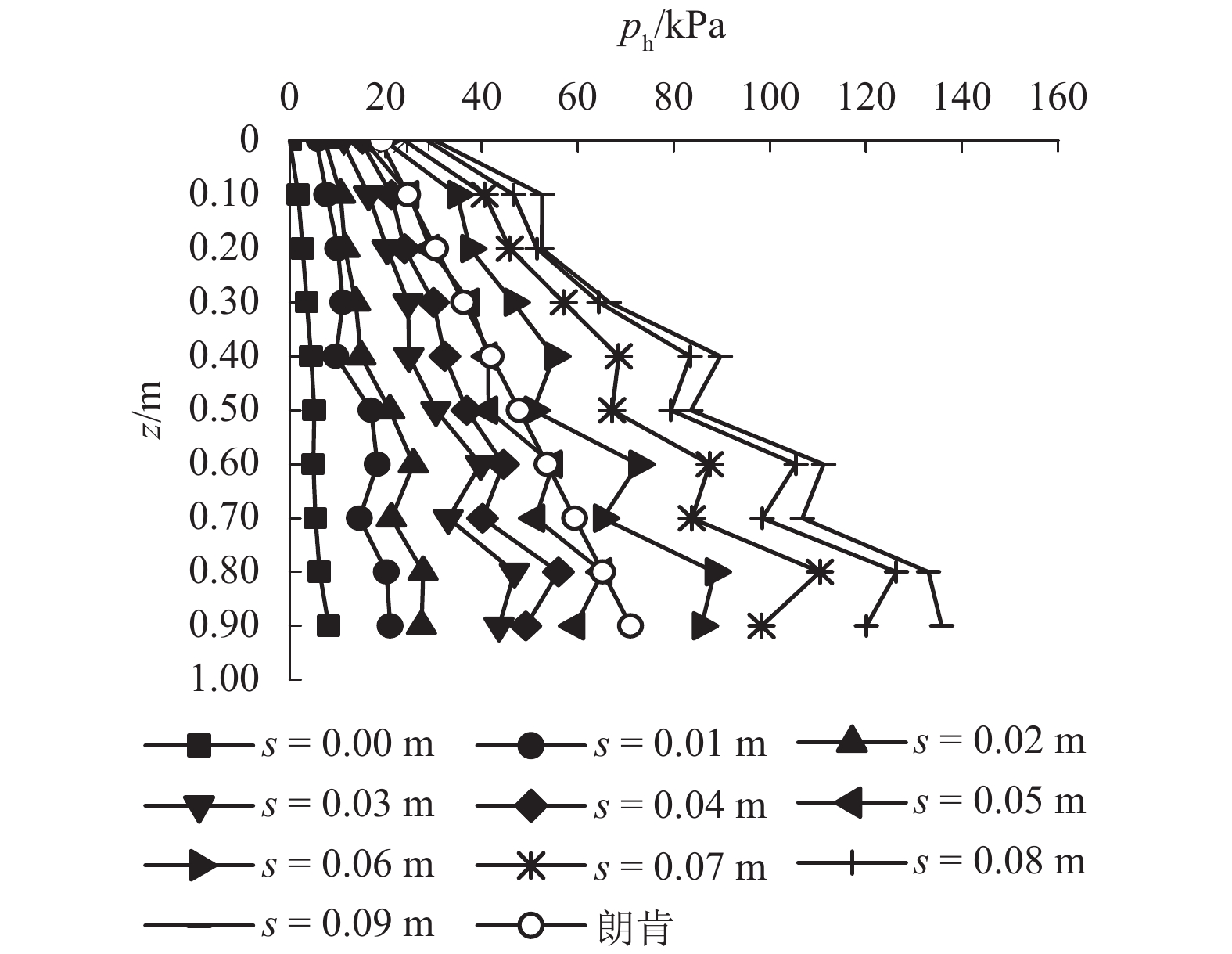
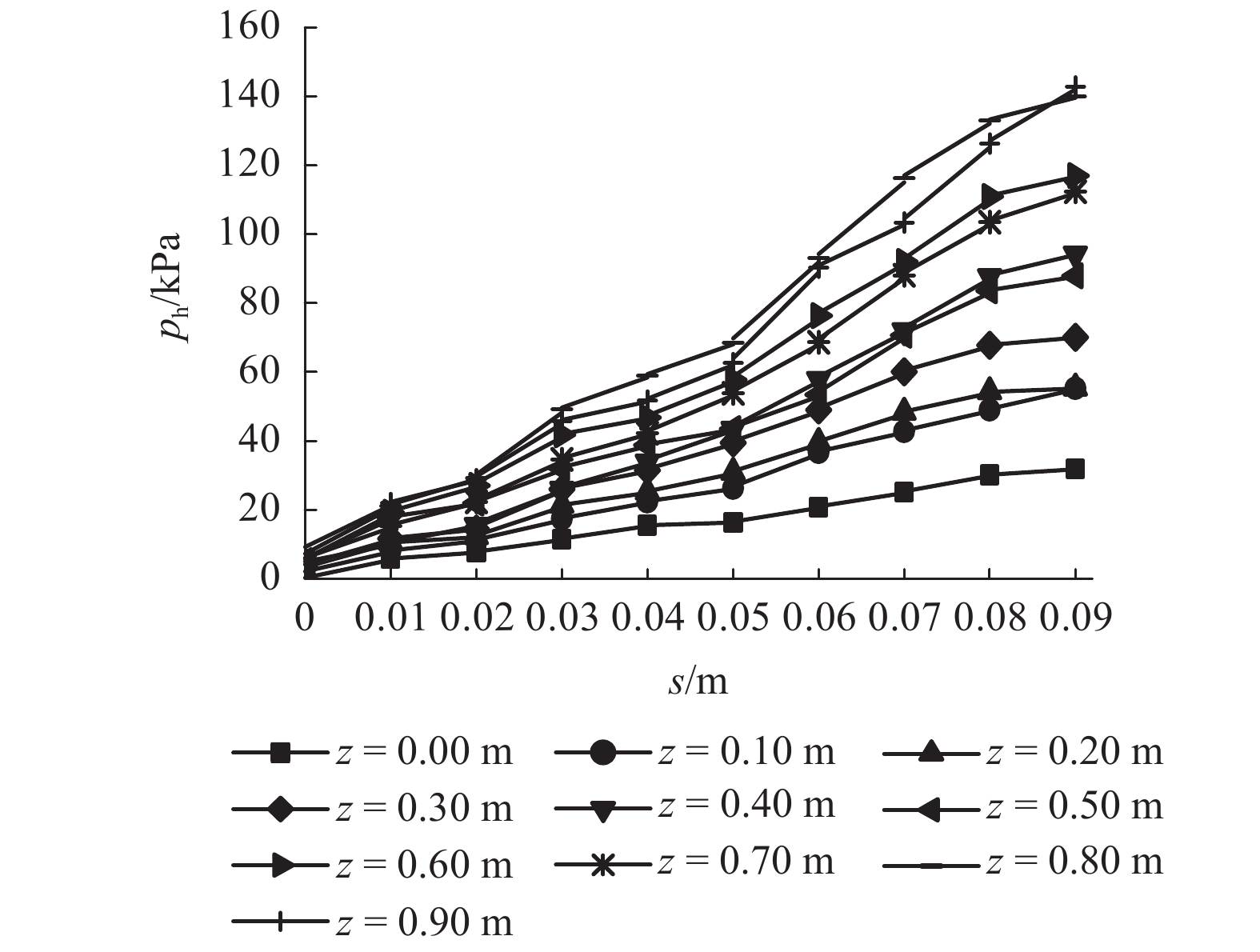
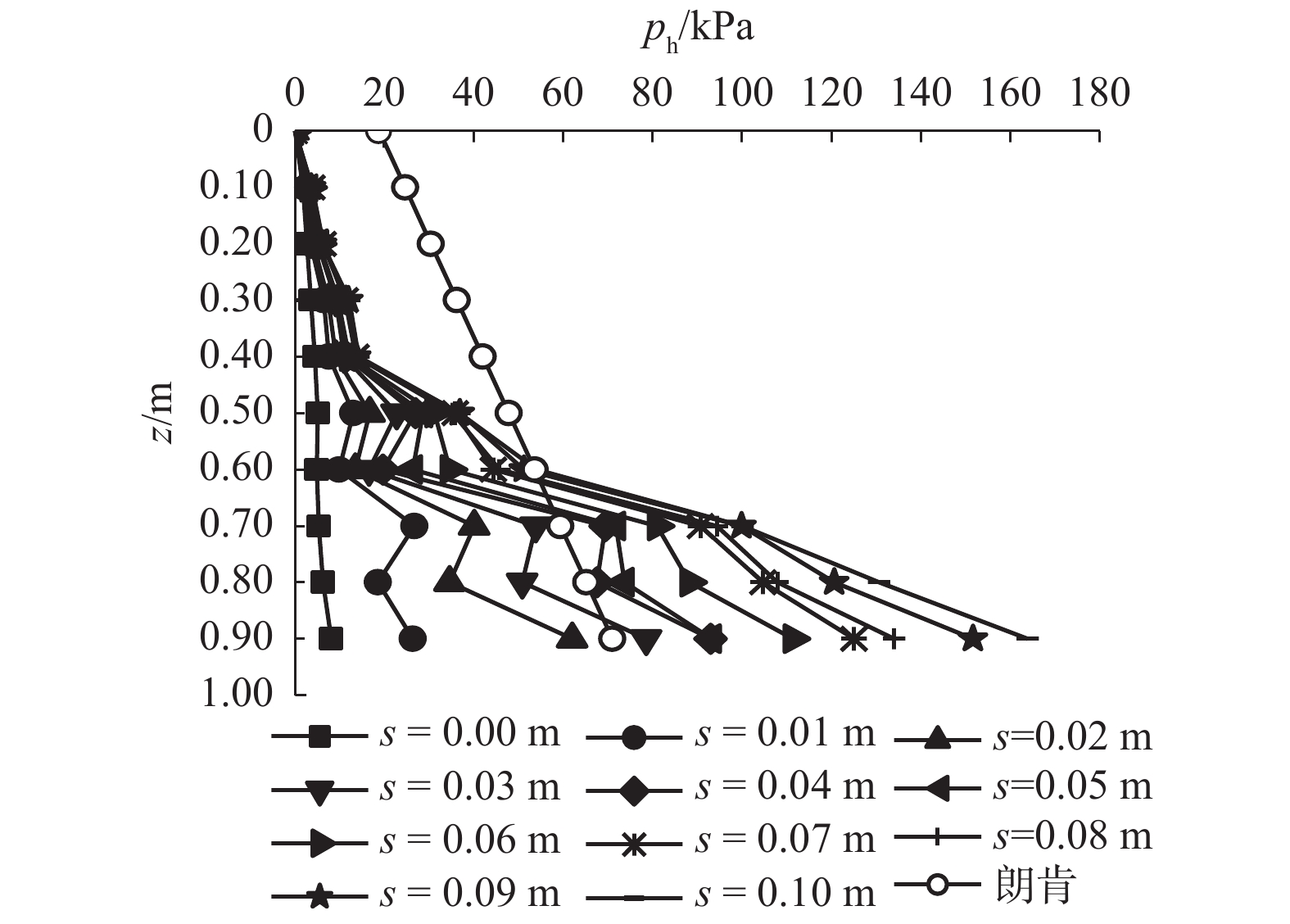
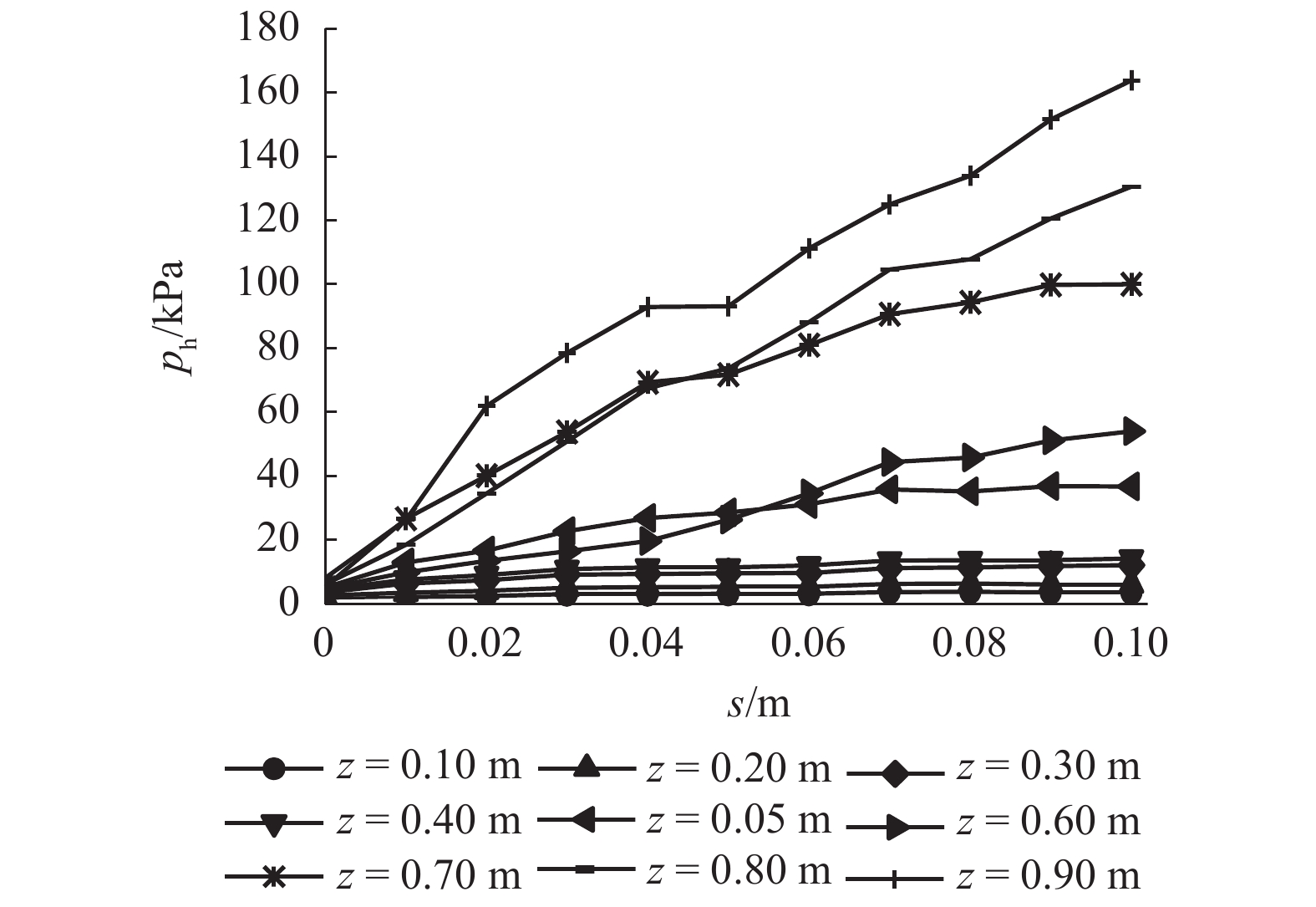
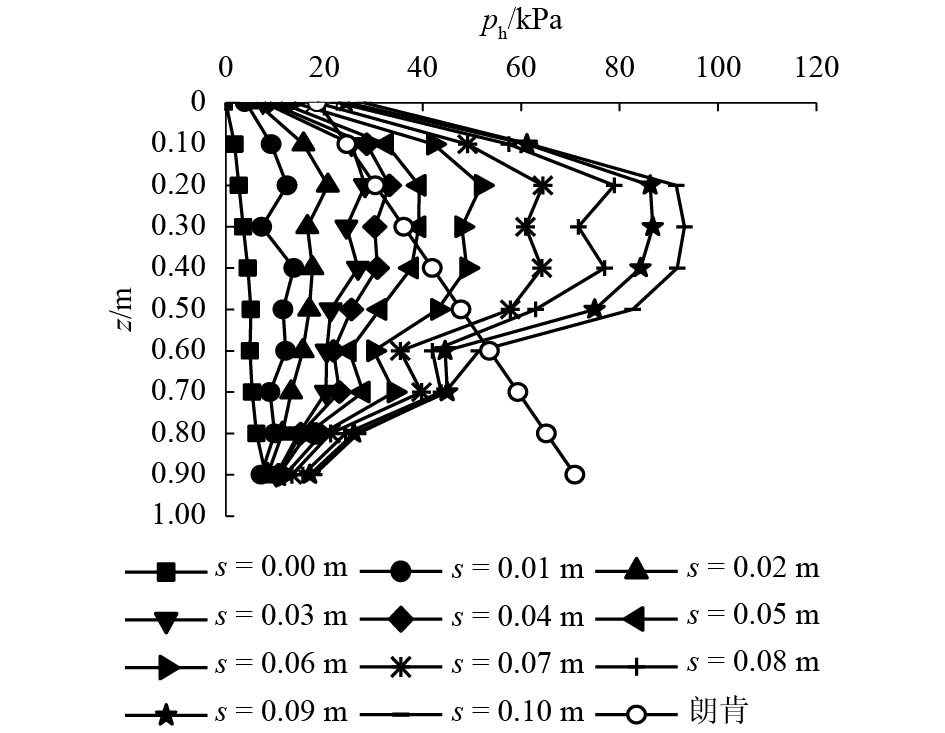
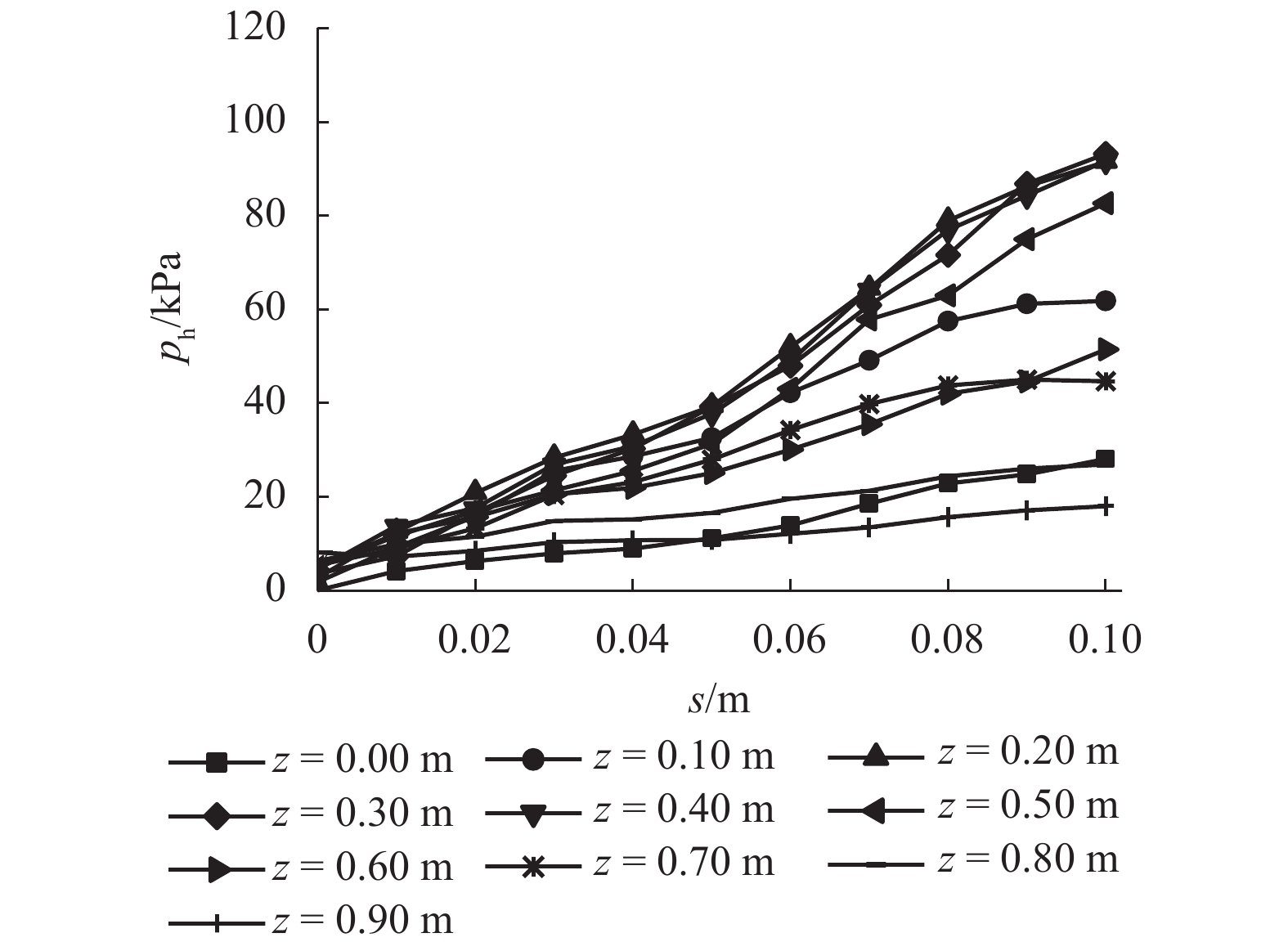
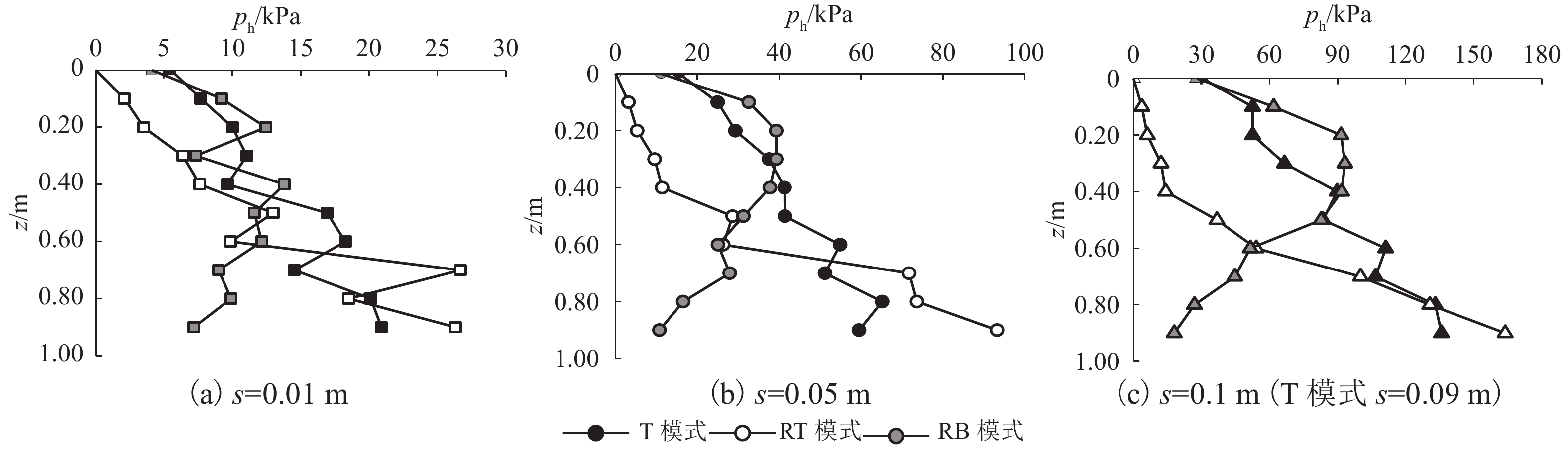
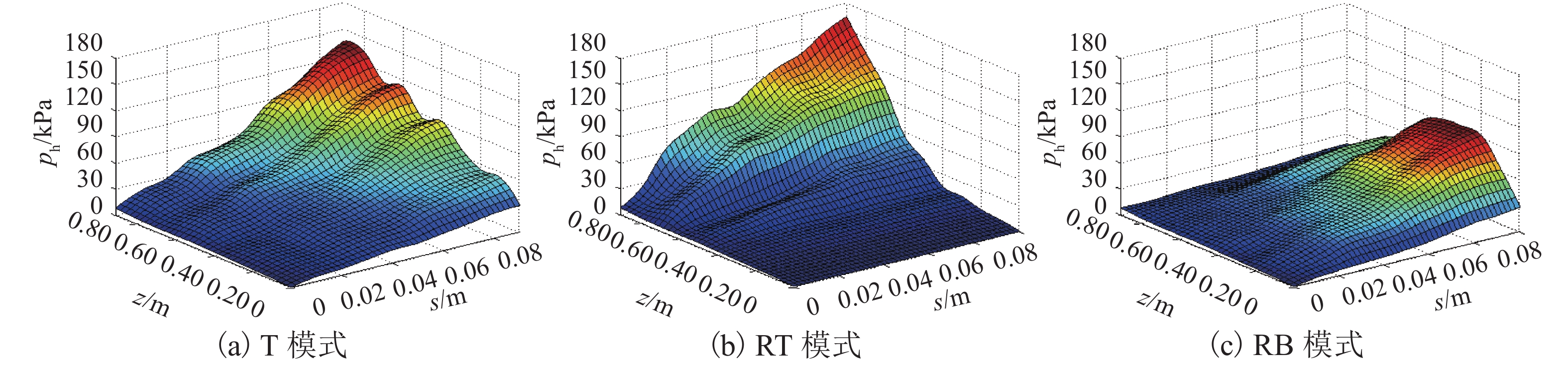
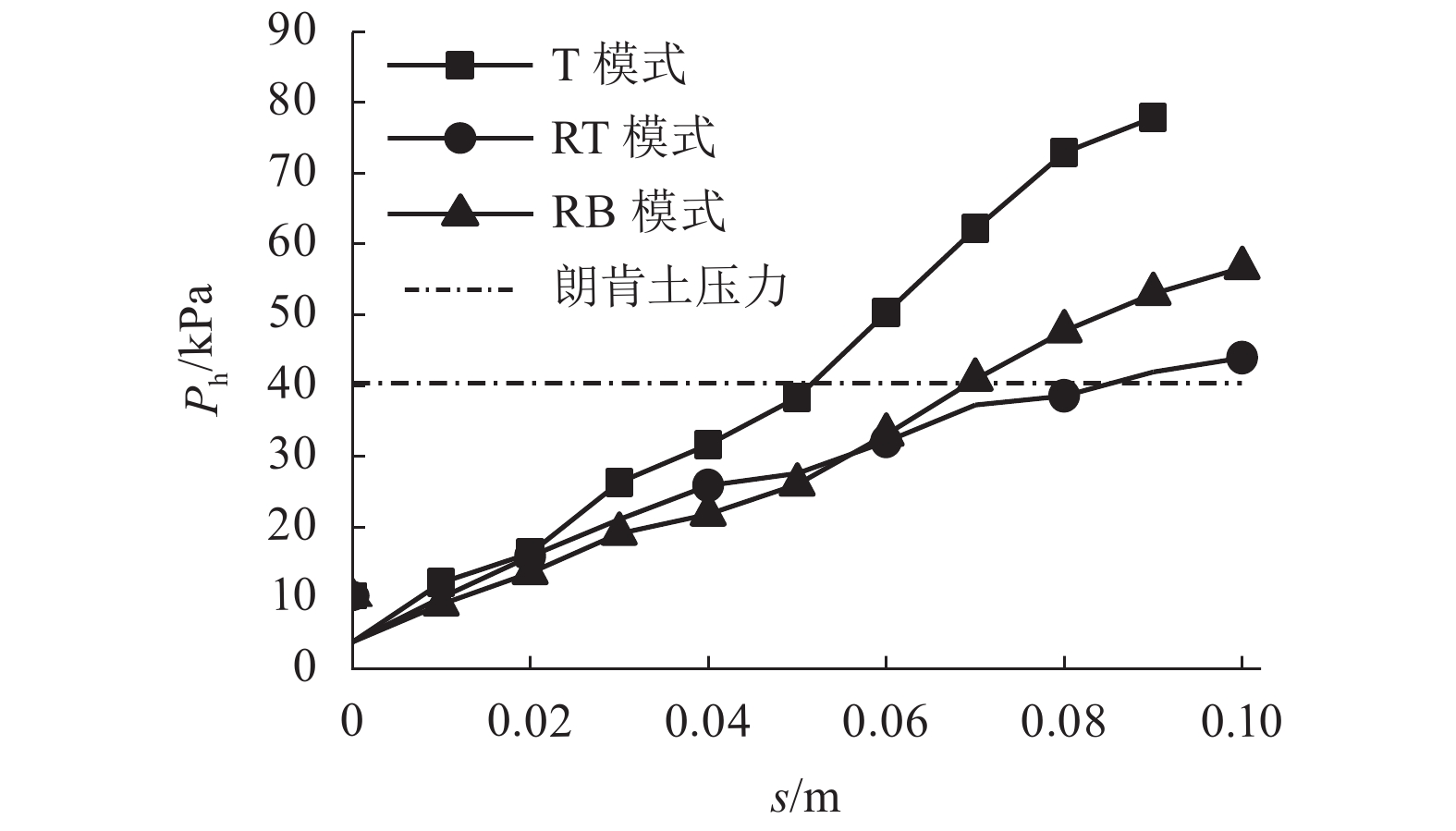
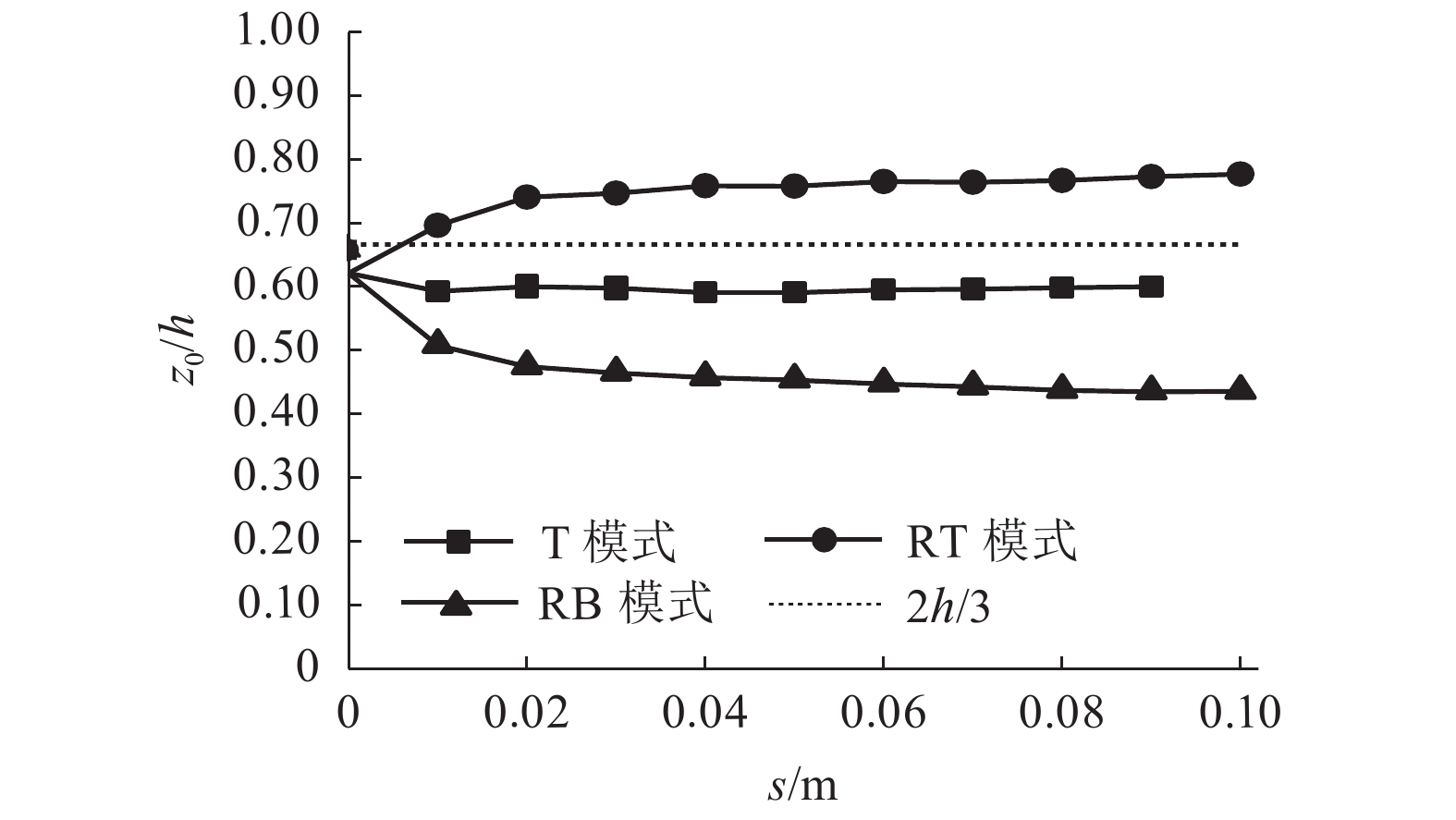
摘要: 为了揭示墙体平动和转动模式下黏土非极限被动土压力分布规律,采用自制模型箱,进行了墙体平动和转动模式下黏土非极限土压力试验,研究了墙体变位模式以及墙体位移大小对侧土压力的影响规律细化方法,首先进行了室内试验,得到了黏土的基本物理参数,其次进行了模型箱和测试仪器的固定安装,最后进行了挡土墙平移模式(T模式)、绕墙顶转动模式(RT模式)以及绕墙底转动模式(RB模式)3种模式下的土压力试验. 试验结果表明:T模式下,非极限侧土压力沿墙体深度的增加总体趋势增大,局部会有减小趋势,总体接近线性分布,当土体达到极限破坏时,靠近加载墙体处土体表面形成阶梯状错层;RT模式下,侧土压力随墙体的深度总体接近凹曲线分布,上部侧土压力随深度增加较慢,下部侧土压力随深度增加较快,当土体达到极限破坏时,靠近加载墙体处土体表面产生裂纹,模型箱中部土体表面鼓起;RB模式下,侧土压力随墙体的深度的增加先增大后减小,总体接近凸曲线分布,当土体达到极限破坏时,靠近加载墙体处土体表面形成阶梯状错层,其阶梯状错层范围要小于平动模式工况;三者非极限侧土压力合力随着压缩位移的增大而增大,当压缩位移相同时,RT模式下土压力合力与T模式下土压力合力比值在0.53~0.97之间,RB模式下土压力合力与T模式下土压力合力比值在0.65~0.83之间. 结论中是否有可以量化的数据,参考附件模板修改.Abstract: In order to reveal the depth distribution law of the non-limit passive earth pressure of clay on a rigid retaining wall under different displacement modes, translation and rotation experiments were carried out using the self-made model box. The influence of the three modes and corresponding displacement on the lateral earth pressure were studied. Firstly, laboratory experiments were carried out, and the basic physical parameters of clay were obtained. Secondly, the model box and test instruments were installed. Finally, earth pressure experiments under three modes of the retaining wall: translation (T-mode), rotation around the top of the retaining wall (RT-mode), and rotation around the bottom of the retaining wall (RB-mode) were carried out. The following conclusions are reached: In the T-mode, the lateral earth pressure generally increased with increasing soil depth except in some local parts, presenting an approximately linear distribution. When the soil reaches the limit state, step-like staggered floors are formed in the vicinity of the wall; In the RT-mode, the lateral earth pressure grow more slowly in the upper wall but more quickly in the lower wall as depth increased, presenting a concave curve. When the soil reaches the limit state, cracks are formed in the vicinity of the wall, and the soil summones up in the middle of the box; In the RB-mode, the lateral earth pressure grow more quickly in the upper wall but more slowly in the lower wall as depth increased, presenting a convex curve. When the soil reaches the limit state, step-like staggered floors are formed in the vicinity of the wall, with the scope smaller than that in the T-mode. The resultant forces of these three lateral earth pressures increase with increasing compressive displacement, reaching the maximum increasing magnitude in the T-mode. When the compression displacement is the same, the ratio of the earth pressure resultant force in the RT-mode and T-mode is between 0.53 and 0.97; the ratio of the earth pressure resultant force in the RB-mode and T-mode is between 0.65 and 0.83.
-
表 1 土体物理参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of soil
参数 数值 φ/(°) 34 c/kPa 5 γ/(kN•m–3) 15.73 w/% 7.97 ${\rho _{{\rm{d}}\max }}$/(kg•m–3) 1 920 wp/% 22.7 表 2 非极限侧土压力合力比值
Table 2. Ratio of non-limit soil pressure resultant force
压缩位移/m PRT/PT PRB/PT 0.01 0.83 0.75 0.02 0.97 0.83 0.03 0.80 0.73 0.04 0.82 0.69 0.05 0.72 0.68 0.06 0.64 0.66 0.07 0.60 0.66 0.08 0.53 0.65 0.09 0.54 0.68 -
BANG S. Active earth pressure behind retaining walls[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1985, 111(3): 407-412. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1985)111:3(407) TERZAGHI K. Large retaining wall test[J]. Enginnering News Record, 1934, 112: 58-69. TERZAGHI K, PECK R B. Soil mechanics in engineering practice[J]. Soil Science, 2014, 68(5): 149-150 ROSCOE K H. The influence of strains in soil mechanics[J]. Geotechnique, 1970, 20(2): 129-170. doi: 10.1680/geot.1970.20.2.129 SHERIF M A, FANG Y, SHERIF R I. Ka and K0 behind rotating and non-yielding walls[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1984, 110(1): 41-56. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1984)110:1(41) FANG Y, ISHIBASHI I. Static earth pressures with various wall movements[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1986, 120(8): 317-333. FANG Y S, CHEN T J, WU B F. Passive earth pressures with various wall movements[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1994, 120(8): 1307-1323. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1994)120:8(1307) NAKAI T. Finite element computations for active and passive earth pressure problems of retaining wall[J]. Journal of the Japanese Society of Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering, 1985, 25(3): 98-112. MATSUZAWA H, HAZARIKA H. Analyses of active earth pressure against rigid retaining wall subjected to different modes of movement[J]. Journal of the Japanese Geotechnical Society, 1996, 36(3): 51-65. 周应英,任美龙. 刚性挡土墙主动土压力的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,1990,12(2): 19-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1990.02.003ZHOU Yingying, REN Meilong. An experimental study on active earth pressure behind rigid retaining wall[J]. Chinese Jounal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1990, 12(2): 19-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1990.02.003 尹紫红,赵丰年,高雪,等. 多量程土压力盒标定工装及试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2018,53(6): 121-129.YIN Zihong, ZHAO Fengnian, GAO Xue, et al. Research on calibration equipment for multi-range earth pressure cell and calibration experimentation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(6): 121-129. 周应英. 桥用刚性挡土墙的土压力模型试验研究[J]. 中外公路,1988,4(1): 48-56.ZHOU Yingying. Studies on the earth pressure on a rigid wall of bridge[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 1988, 4(1): 48-56. 罗强,蔡英,邵启豪. 成都粘土重力式挡土墙的工程试验[J]. 西南交通大学学报,1995,30(3): 270-274.LUO Qiang, CAI Ying, SHAO Qihao. Experiment study on gravity retaining wall filled with chengdu clay[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 1995, 30(3): 270-274. 徐日庆,陈页开,杨仲轩. 刚性挡墙被动土压力模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2002,24(5): 569-575. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2002.05.006XU Riqing, CHEN Yekai, YANG Zhongxuan, et al. Experimental research on the passive earth pressure acting on a rigid wall[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2002, 24(5): 569-575. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2002.05.006 徐日庆,龚慈,魏纲,等. 考虑平动位移效应的刚性挡土墙土压力理论[J]. 浙江大学学报,2005,39(1): 119-122. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2005.01.022XU Riqing, GONG Ci, WEI Gang, et al. Theory of earth pressure against rigid retaining walls considering translational movement effect[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University, 2005, 39(1): 119-122. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2005.01.022 陈页开,汪益敏,徐日庆,等. 刚性挡土墙主动土压力数值分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(6): 989-995. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.06.019CHEN Yekai, WANG Yimin, XU Riqing, et al. Numerical analyses of active earth pressure on rigid retaining wall[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(6): 989-995. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.06.019 龚慈,魏纲,徐日庆. RT模式下刚性挡墙土压力计算方法研究[J]. 岩土力学,2006,27(9): 1588-1592. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.09.033GONG Ci, WEI Gang, XU Riqing. Earth pressure against rigid retaining wall rotating about top[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(9): 1588-1592. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.09.033 杨庆光, 刘杰, 何杰, 等. 平移模式下挡墙非极限土压力计算方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(增刊1): 3399-3406YANG Qingguang, LIU Jie, HE Jie, et al. A method for calculating unlimited earth pressure of retaining wall with translation mode[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(S1): 3399-3406 许雷挺,张治成,张戎泽,等. 砂土中挡墙不同变位模式主动土压力模型试验[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2017,13(5): 1296-1302.XU Leiting, ZHANG Zhicheng, ZHANG Rongze, et al. Model test on active earth pressure in sand induced by the movement of retaining wall[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2017, 13(5): 1296-1302. 张刚,孔亮,马良荣,等. 考虑平动位移效应的黏性填土挡土墙土压力计算[J]. 宁夏大学学报,2008,29(4): 325-328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2328.2008.04.011ZHANG Gang, KONG Liang, MA Liangrong, et al. Computational of earth pressure of retaining wall with cohesive backfill considering translational movement effect[J]. Journal of Ningxia University, 2008, 29(4): 325-328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2328.2008.04.011 娄培杰. 黏性土填料下考虑土拱效应的非极限主动土压力计算方法[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(4): 988-994.LOU Peijie. A method to calculate the active earth pressure with considering soil arching effect under the nonlimit state of clayey soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(4): 988-994. 徐日庆,廖斌,吴渐,等. 黏性土的非极限主动土压力计算方法研究[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(1): 148-154.XU Riqing, LIAO Bin, WU Jian, et al. Computational method for active earth pressure of cohesive soil under nonlimit state[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(1): 148-154. -





 下载:
下载: