Control Strategy Based on State Machine for Fuel Cell Hybrid Power System
-
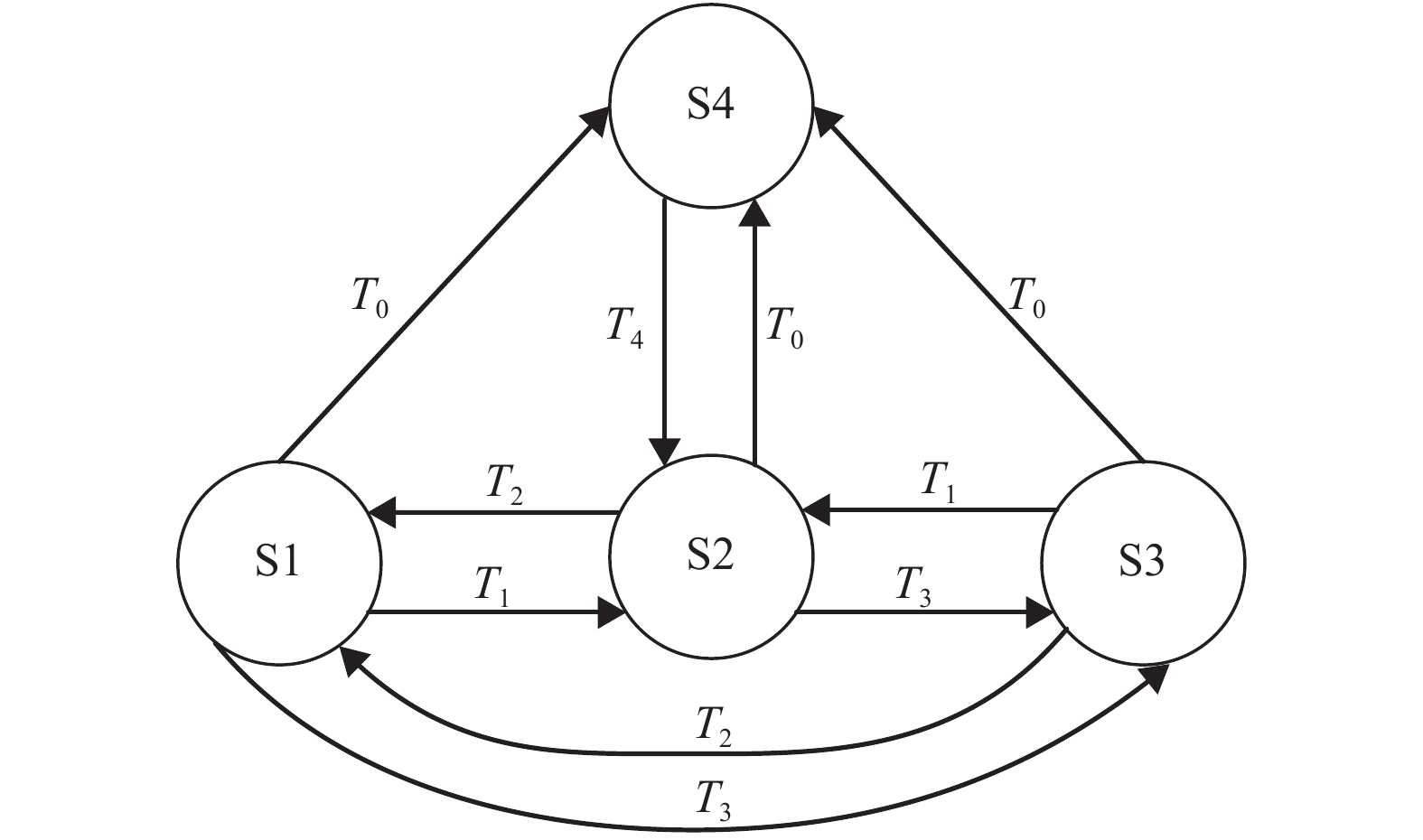
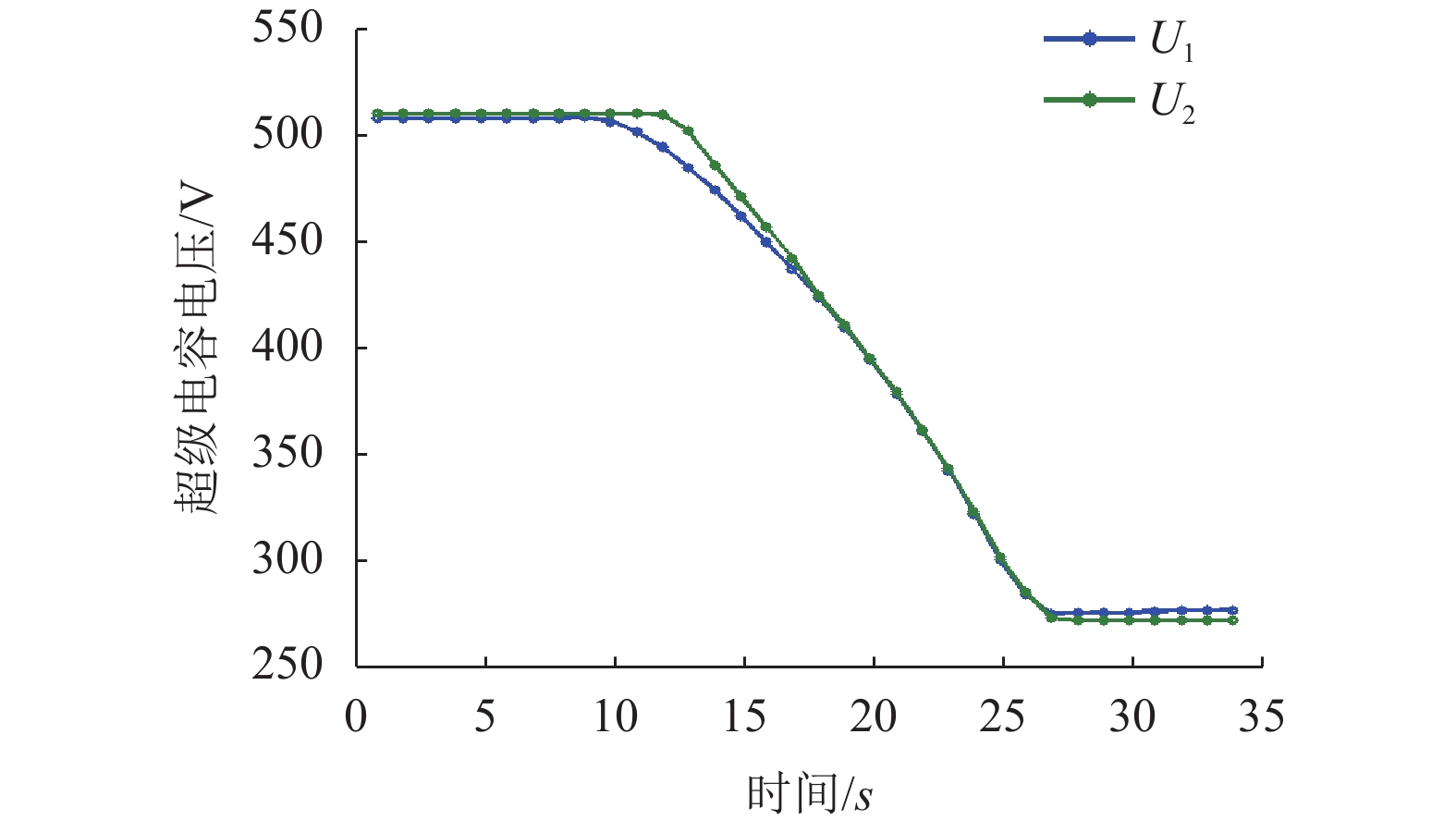
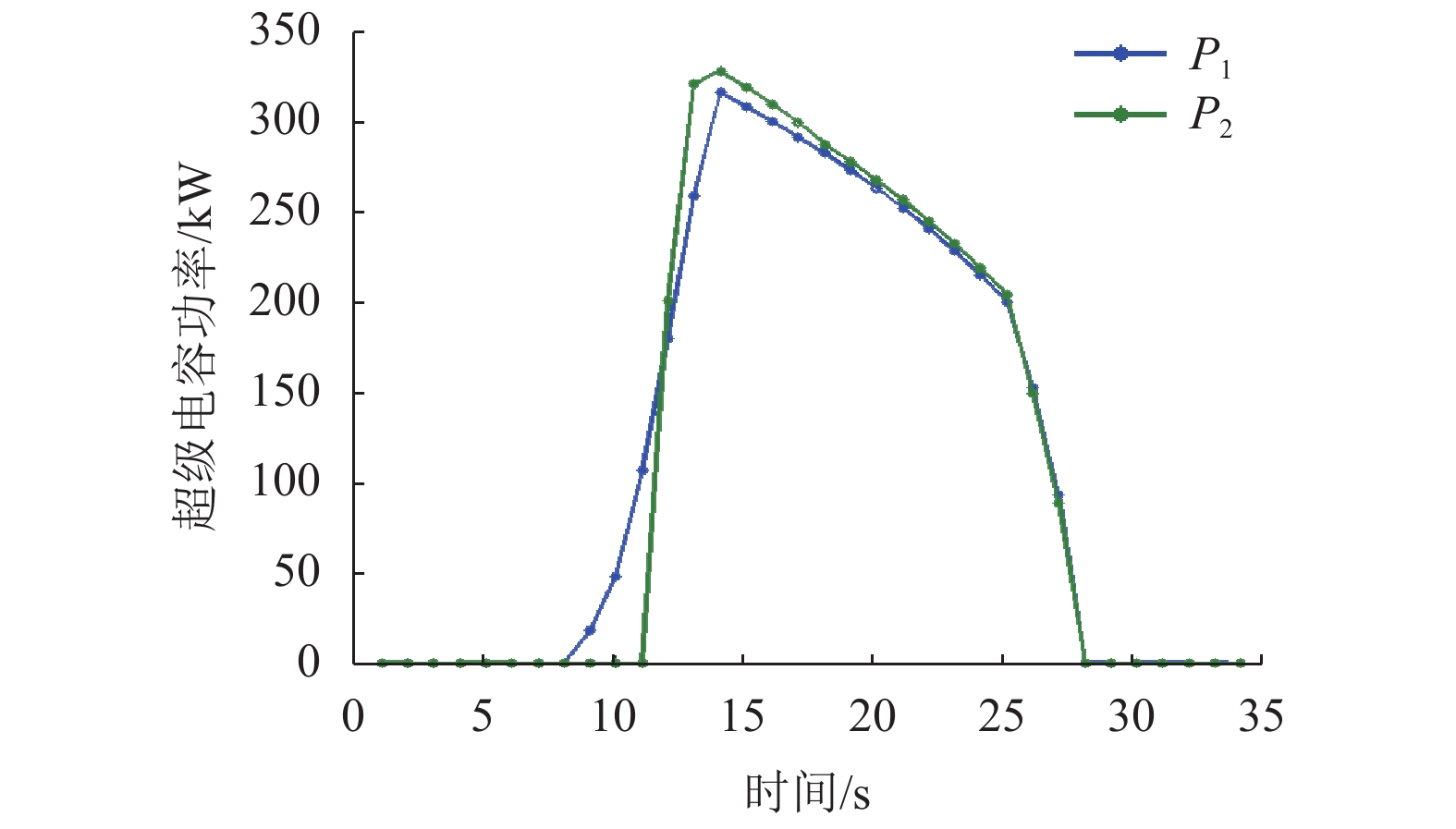
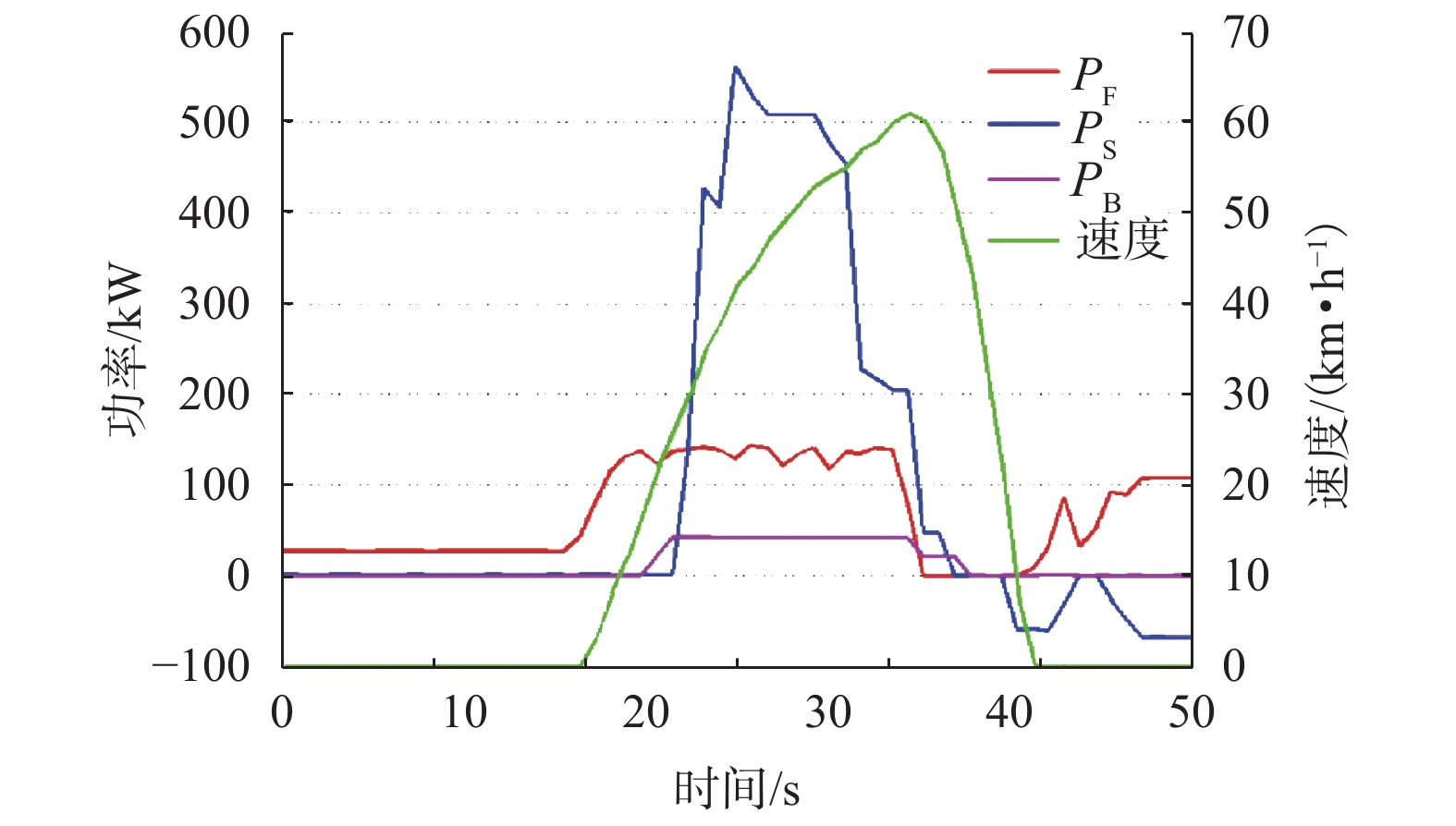
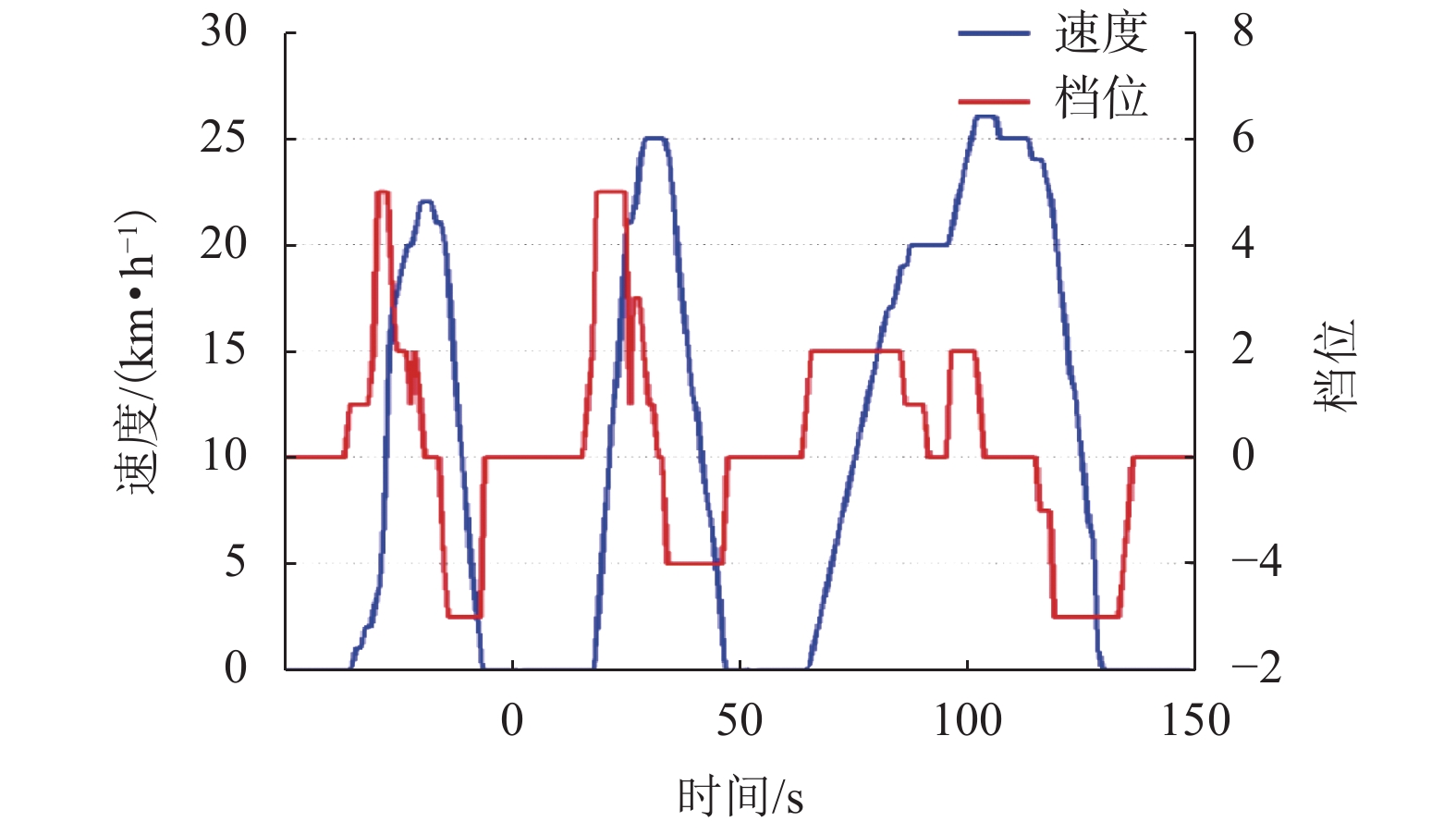
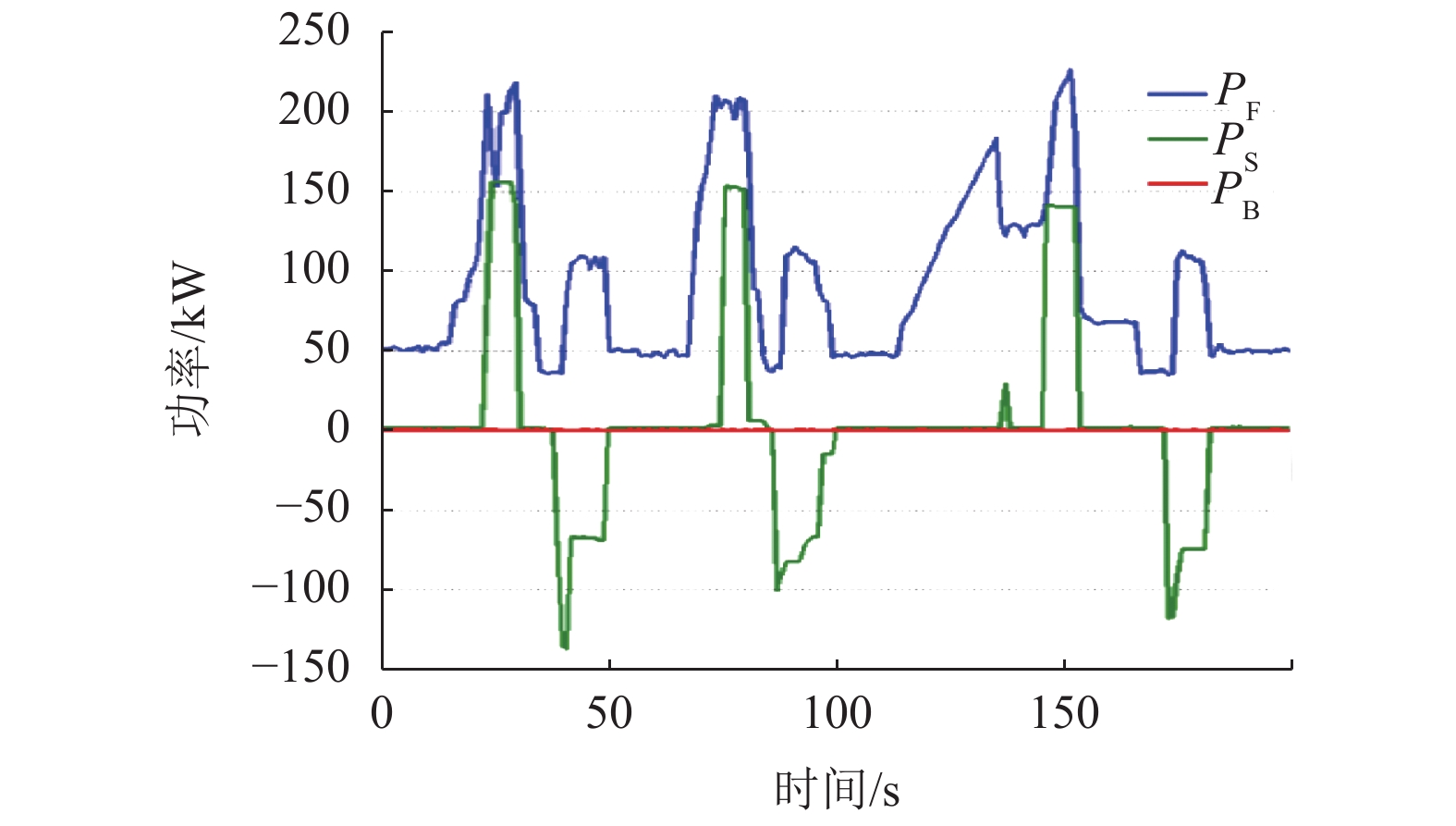
摘要: 针对由2套大功率氢燃料电池、超级电容和动力电池所构成的有轨电车用混合动力系统,提出能够满足运行工况需求的状态机控制能量管理策略. 首先,以状态机为基础构架,将有轨电车的运行划分为牵引、惰行、制动和故障4种状态;接着研究了4种运行状态下的能量管理策略,牵引状态采用基于自适应放电系数的均压算法,惰行状态采用改进的最大效率点跟随算法;然后基于4种状态,进行了整车实际运行;最后对比分析了功率跟随策略、状态机控制策略的能耗和电池堆效率. 研究结果表明:基于自适应放电系数的均压算法能够保证2套超级电容在牵引状态中均匀放电,避免了单套超级电容过度使用的情况;改进的最大效率点跟随算法使得燃料电池的平均效率提高了3.91%;此外,状态机控制策略与功率跟随策略的电堆效率分别为61.89%、57.98%,前者比后者节约了3.2%的氢气.Abstract: For the hybrid tram power system that consists of two sets of high-power fuel cells, supercapacitors and power batteries, an energy management strategy based on state machine is proposed to meet the requirements of operating conditions. First of all, the state machine is adopted as the basic architecture, and the operating state of the tram is divided into four states: traction, coasting, braking and fault. Then the energy management strategies that correspond to four states are studied. The voltage equalization algorithm based on the adaptive discharge coefficient is used in the traction state; and in the coasting state, the improved maximum efficiency point tracking algorithm is used. Then, according to the four operating states, the actual operation of the tram is carried out. Finally, the power consumption and the fuel cell system efficiency between the state-machine based control strategy and power tracking strategy is compared. The results show that the voltage equalization algorithm enables two sets of supercapacitors to be uniformly discharged in the traction state, which avoids the overuse of a single set of supercapacitors. The improved maximum efficiency point tracking algorithm increase the average efficiency of the fuel cell by 3.91%. In addition, the stack efficiency of the state-machine based control strategy and the power tracking strategy is 61.89% and 57.98%, respectively, and the former saves 3.2% of hydrogen.
-
Key words:
- fuel cell /
- supercapacitor /
- tram /
- state machine control
-
表 1 动力系统配置
Table 1. Power system configuration
参数名称 数值 燃料电池电压/V 440~710 燃料电池标称功率/kW 150 燃料电池电堆最大电流/A 320 超级电容电压/V 280~528 超级电容最大电流/A 700 超级电容容量/F 45 动力电池电压/V 279~396 动力电池最大电流/A 120 动力电池容量/A•h 20 储氢罐数量/个 4 储氢容量/kg 12 储氢压力/MPa 35 表 2 不同策略下氢耗量对比
Table 2. Comparison of hydrogen consumption under different strategies
策略 行驶距离/km 氢耗量/kg 平均氢耗量/(kg•km–1) 功率跟随 19.2 7.12 0.370 8 状态机控制 19.0 6.82 0.358 9 -
陈维荣,钱清泉,李奇. 燃料电池混合动力列车的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2009,44(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.01.001CHEN Weirong, QIAN Qingquan, LI Qi. Invest igation status and development trend of hybrid power train based on fuel cell[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2009, 44(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.01.001 沈训梁,陆云,李俊,等. 100%低地板有轨电车及其转向架发展现状[J]. 都市快轨交通,2013,26(5): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6073.2013.05.006 任成伟. 试论有轨道电车的电池系统及储能应用[J]. 科技展望,2017,27(2): 139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8289.2017.02.117 洪标. 有轨电车系统发展及相关问题阐述[J]. 工程技术(文摘版),2016(7): 286. 中国城市轨道交通协会. 城市轨道交通2014年度统计分析报告[R]. 北京: 中国城市轨道交通协会, 2015 HAN X, LI F, ZHANG T, et al. Economic energy management strategy design and simulation for a dual-stack fuel cell electric vehicle[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(16): 11584-11595. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.01.085 SAMI B S, SIHEM N, ZAFAR B, et al. Performance study and efficiency improvement of Hybrid Electric System dedicated to transport application[J]. Interna tional Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(17): 12777-12789. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.11.145 ZHANG W B, LI J Q, XU L F, et al. Optimization for a fuel cell/battery/capacity tram with equivalent consumption minimization strategy[J]. Energy Conversion & Management, 2017, 134: 59-69. LI Q , CHEN W , LIU Z , et al. Development of energy management system based on a power sharing strategy for a fuel cell-battery-supercapacitor hybrid tramway[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 279: 267-280. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.12.042 LI Q , YANG H , HAN Y , et al. A state machine strategy based on droop control for an energy management system of PEMFC-battery-supercapacitor hybrid tramway[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(36): 16148-16159. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.04.254 李奇, 陈维荣, 刘述奎, 等. 燃料电池混合动力车辆多能源管理策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2011(增1): 303-308Qi L, Weirong C, Shukui L et al. Energy management strategy for hybrid vehicle based on fuel cell[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2011(s1): 303-308 李奇. 质子交换膜燃料电池系统建模及其控制方法研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2011 陈维荣,张国瑞,孟翔,等. 燃料电池混合动力有轨电车动力性分析与设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(1): 1-8.CHEN Weirong, ZHANG Guorui, MENG Xiang, et al. Dynamic performance analysis and design of fuel cell hybrid locomotive[J]. Journal of southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(1): 1-8. 陈维荣,卜庆元,刘志祥,等. 燃料电池混合动力有轨电车动力系统设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(3): 430-436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.03.003CHEN Weirong, BU Qingyuan, LIU Zhixiang, et al. Power system design for a fuel cell hybrid power tram[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(3): 430-436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.03.003 FEROLDI D, CARIGNANO M. Sizing for fuel cell/ supercapacitor hybrid vehicles based on stochastic driving cycles[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 183: 645-658. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.09.008 VEGA D H, MARX N, BOULON L, et al. Maximum efficiency point tracking for hydrogen fuel cells[C]// Electrical & Computer Engineering. Tornoto: IEEE, 2014: 1-6 谢起成,赵广平. 燃料电池电动汽车氢消耗量的计算[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2005,45(11): 1534-1536. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2005.11.024XIE Q, ZHAO G. Hydrogen consumption for fuel cell vehicles[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2005, 45(11): 1534-1536. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2005.11.024 -




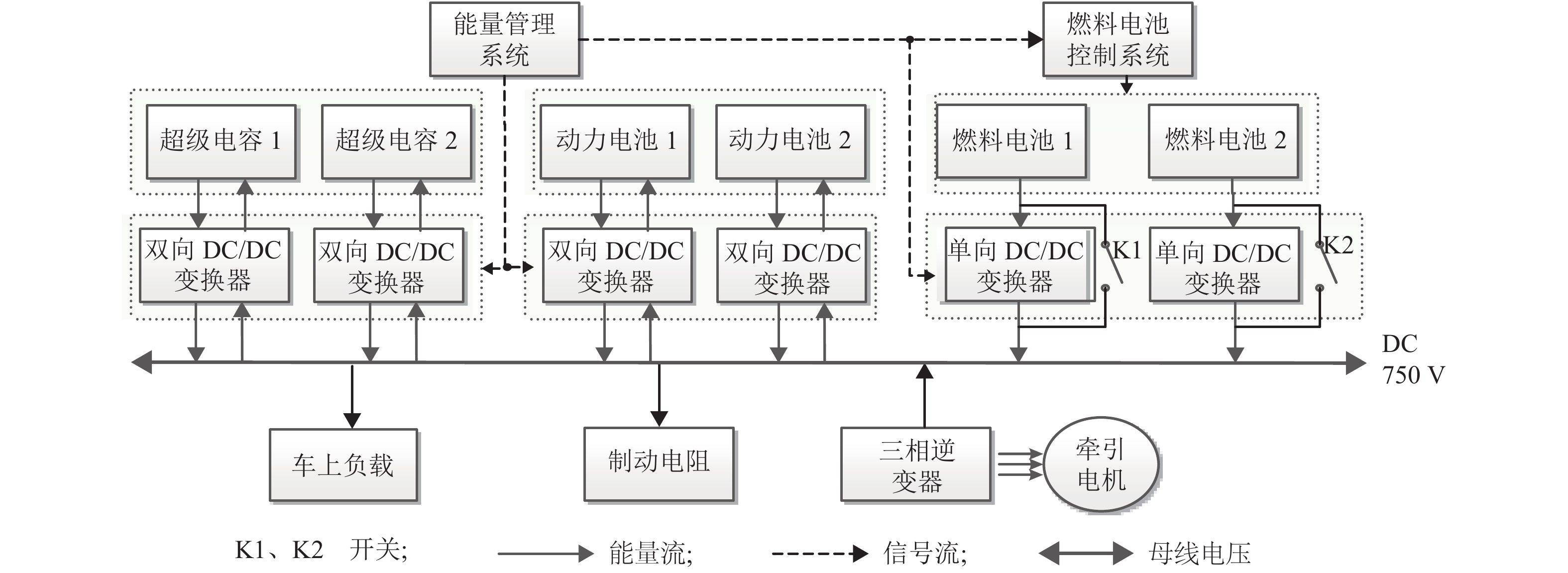
 下载:
下载: