Aerodynamic Noise Investigation of Metro Vehicle Auxiliary Converter
-
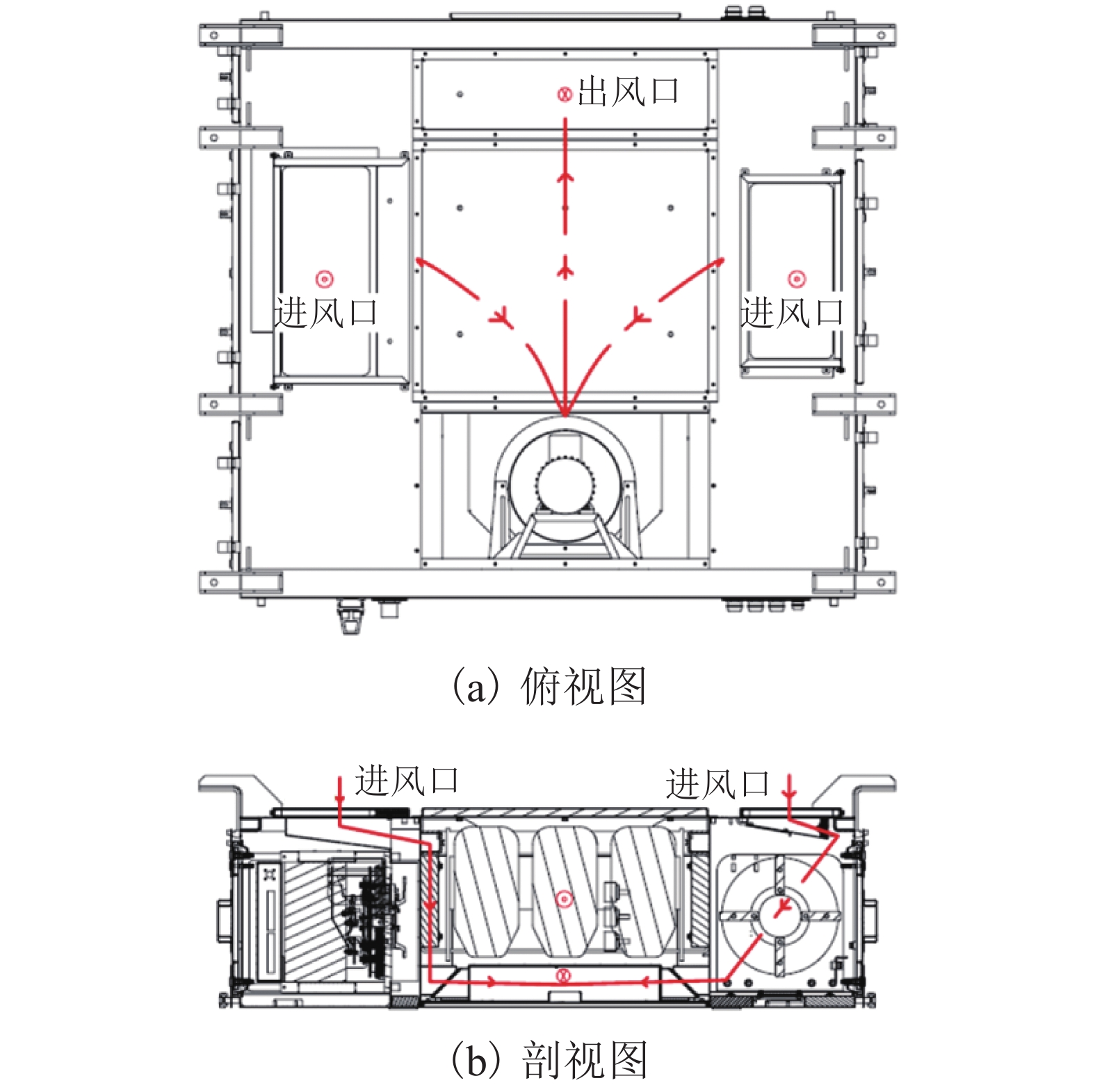
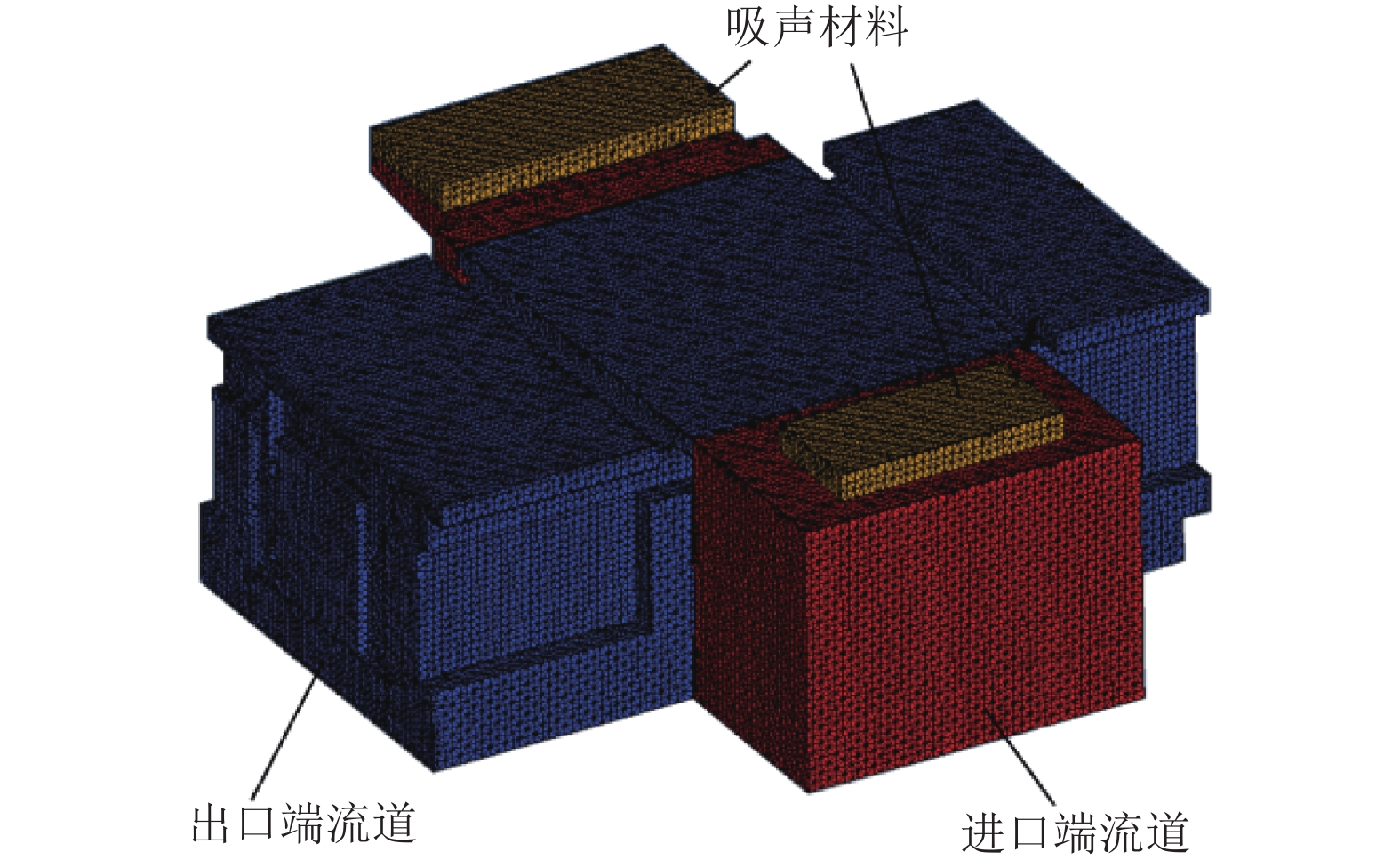
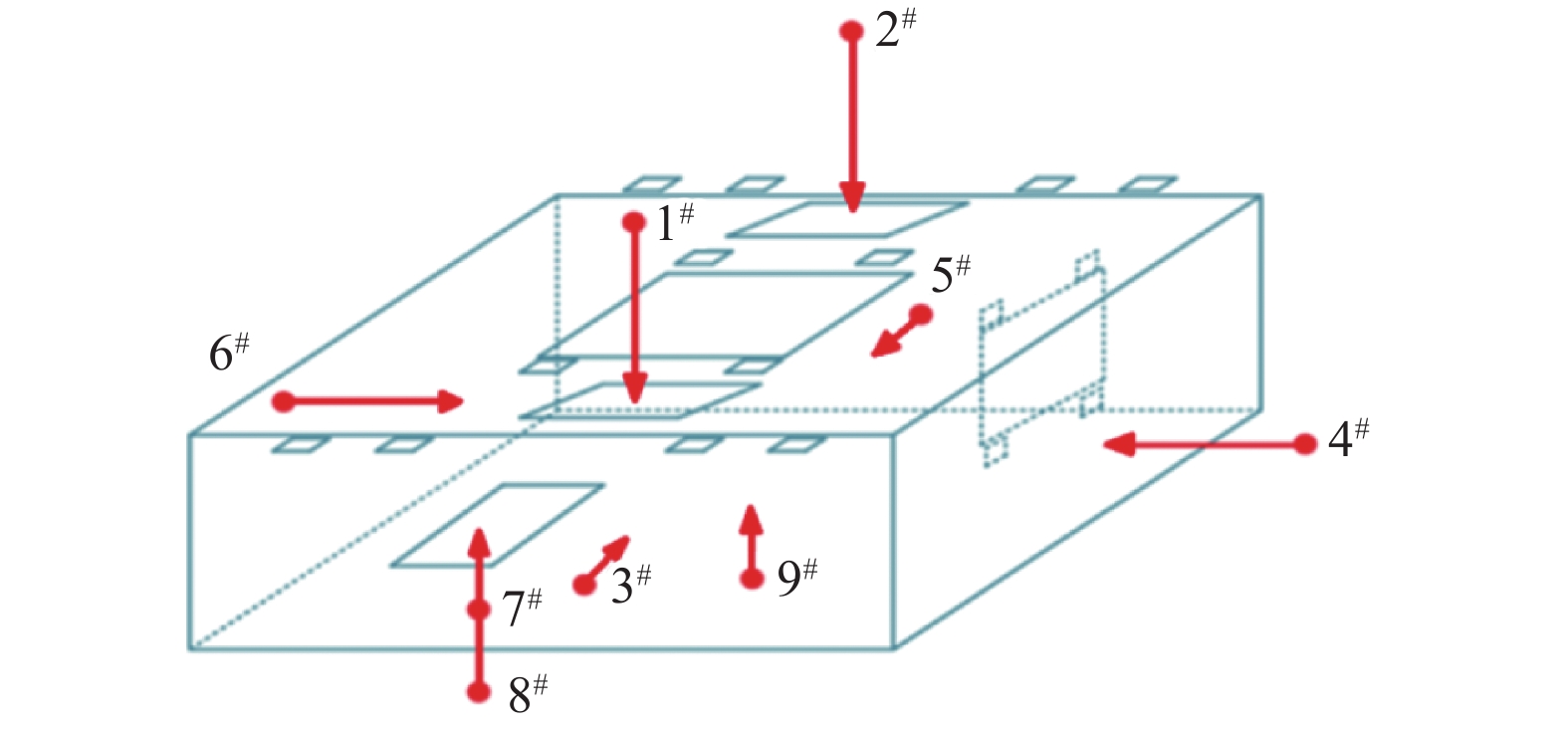
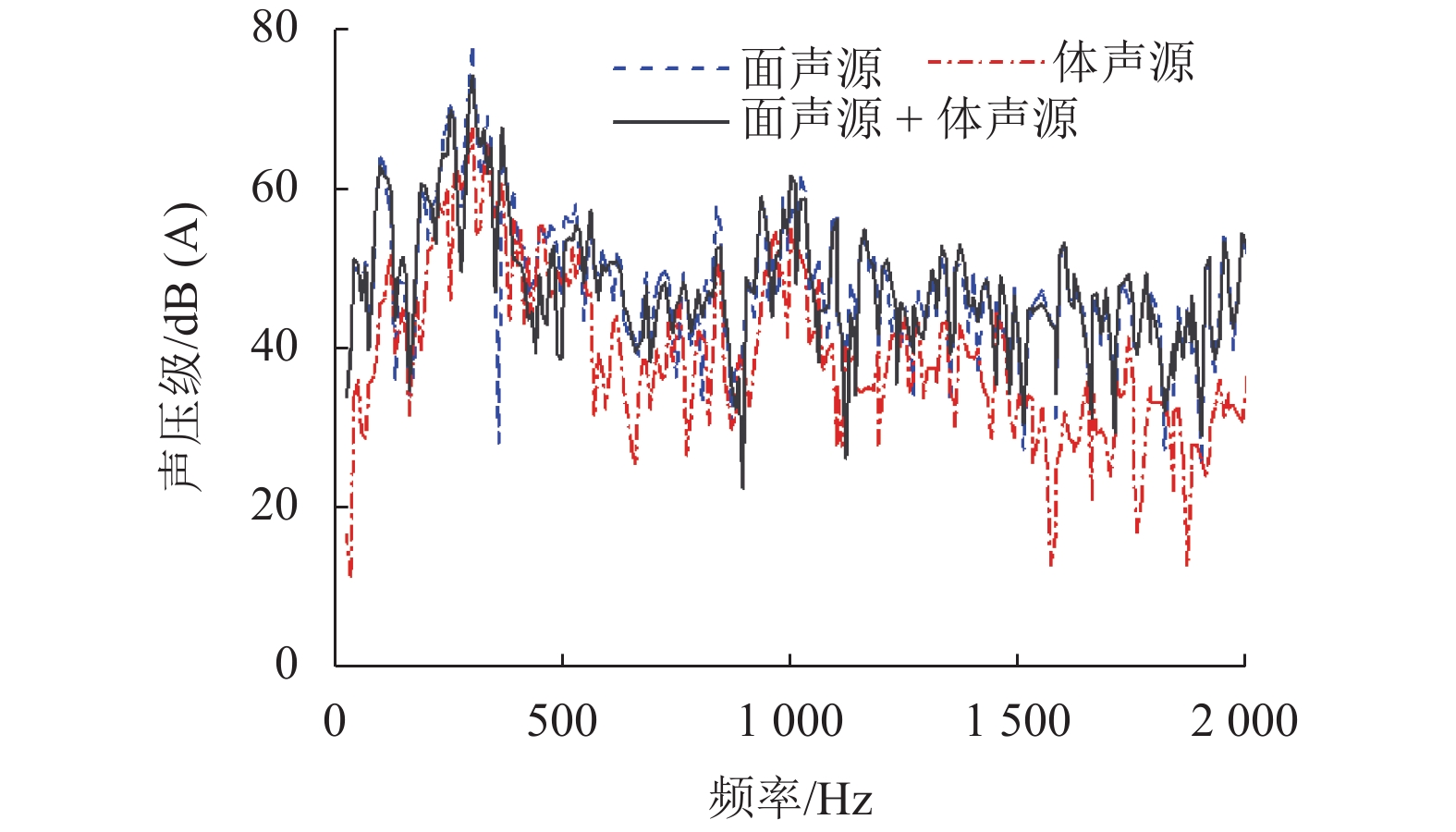
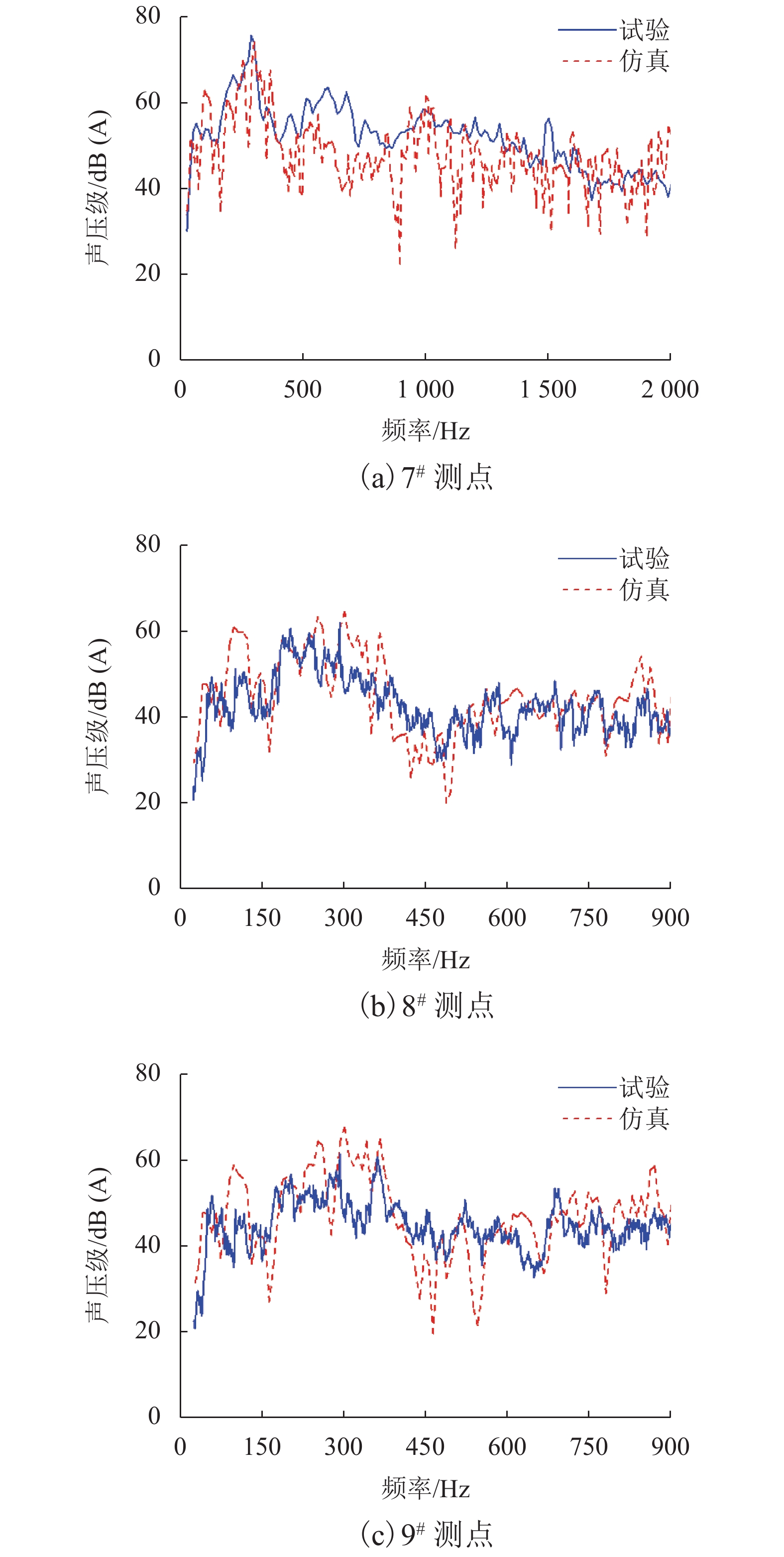
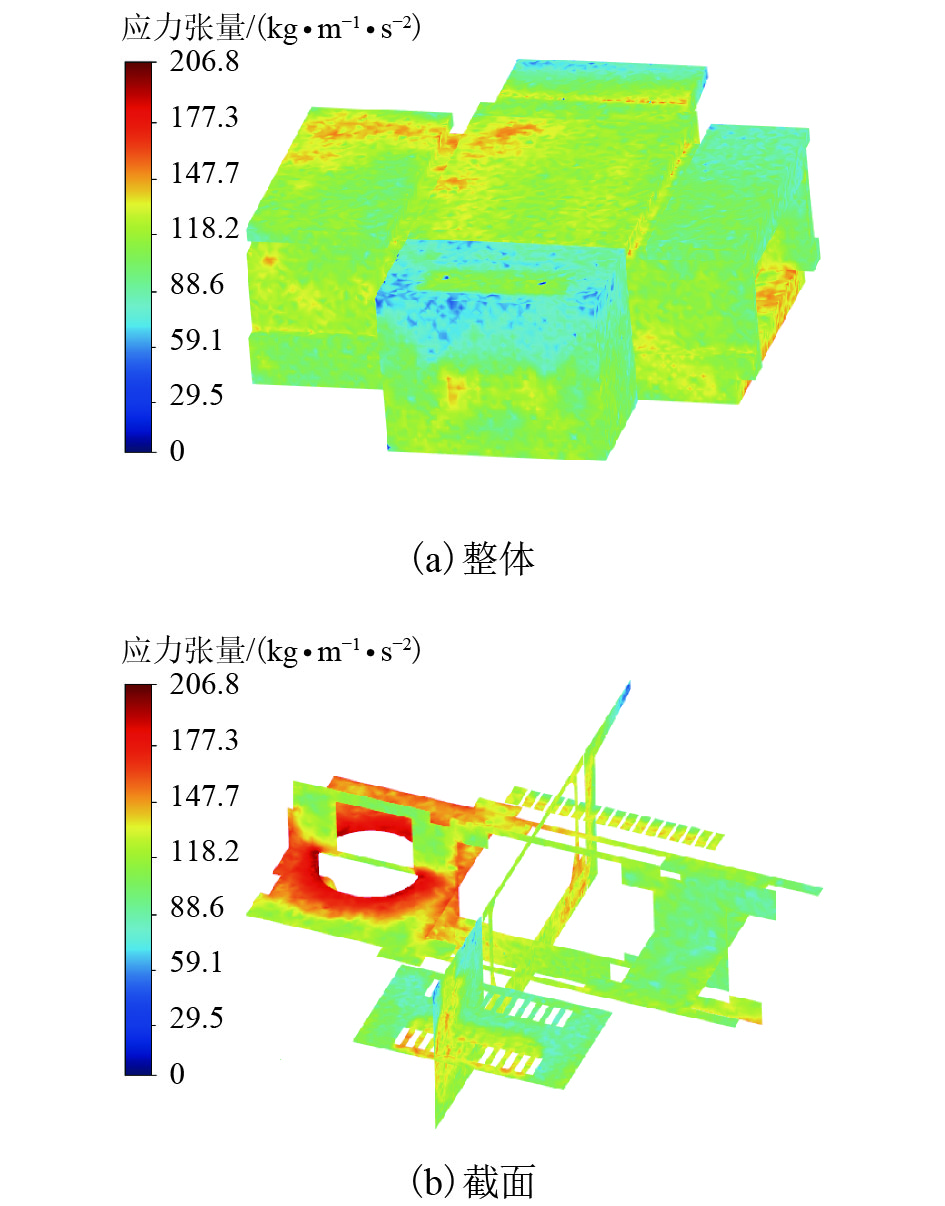
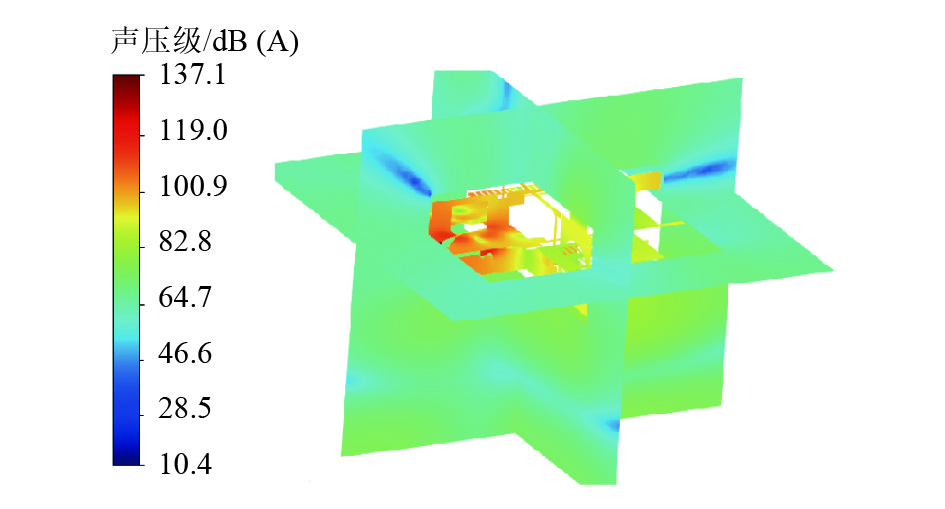
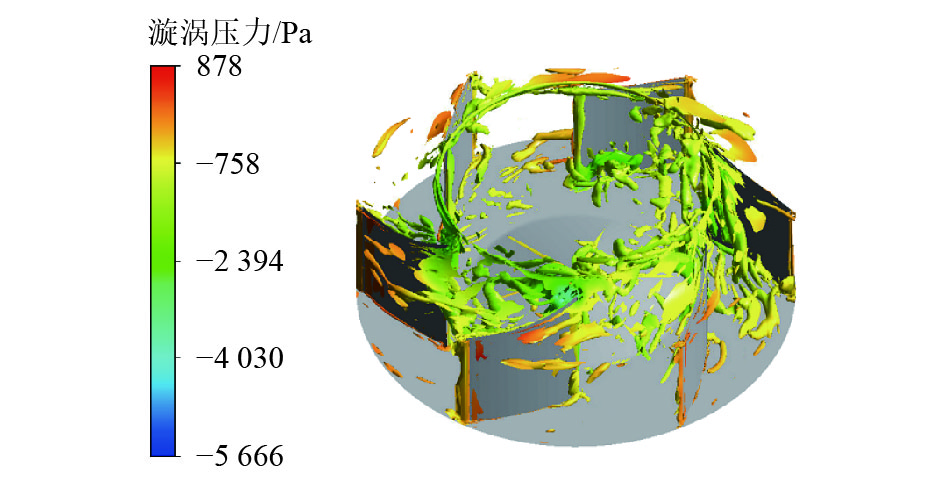
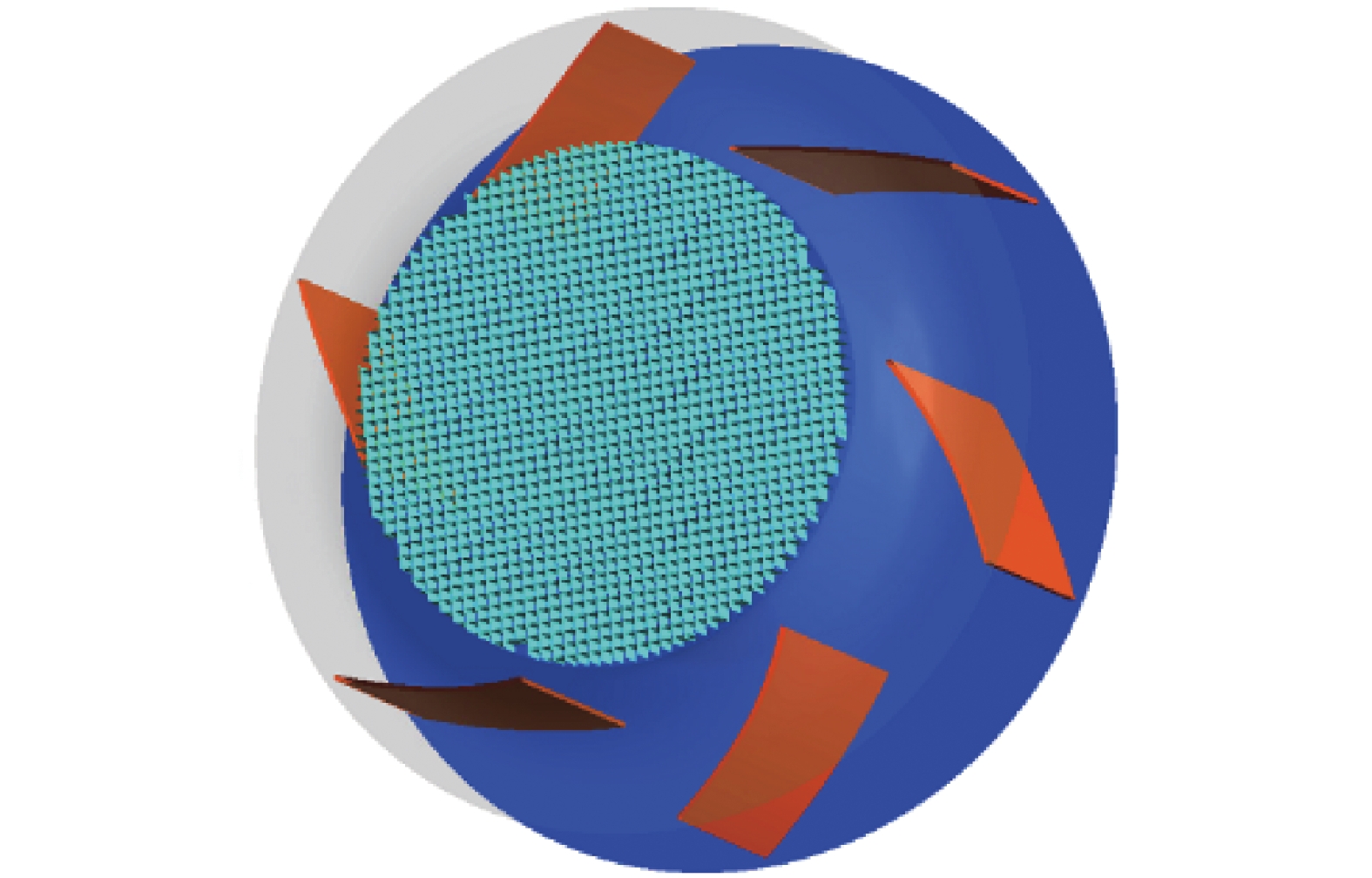
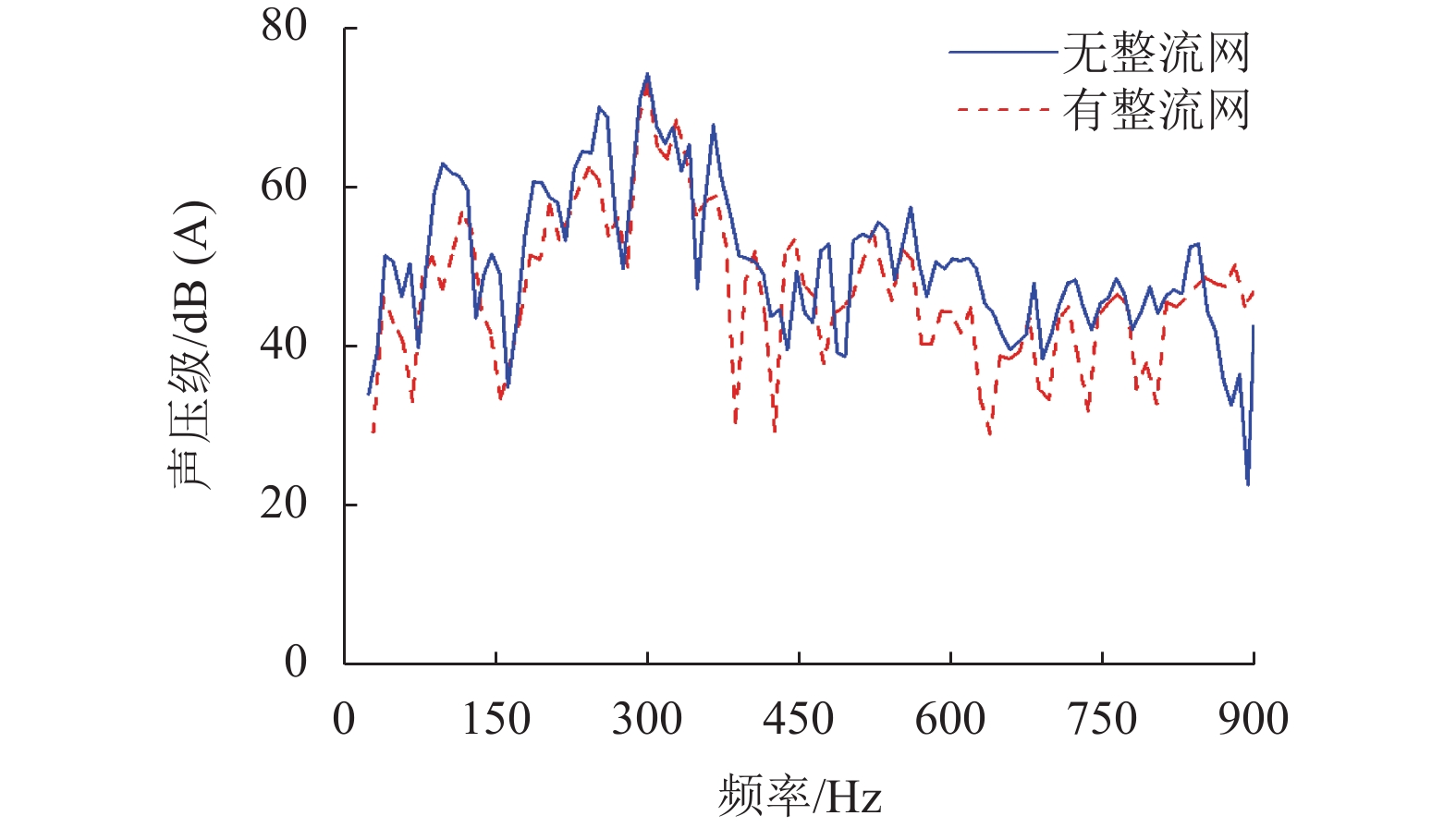
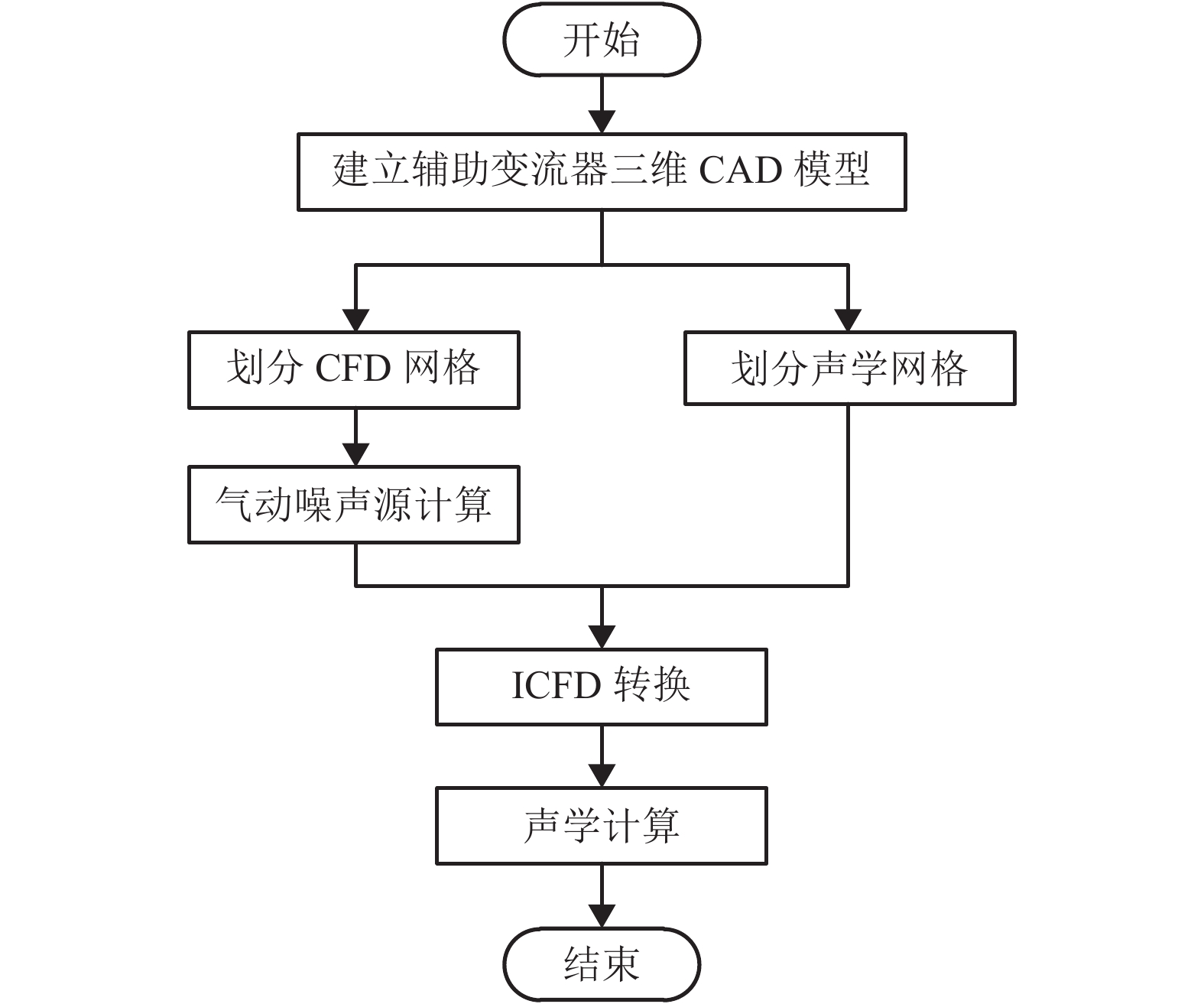
摘要: 为了解决地铁车辆辅助变流器噪声超标1.5 dB(A)的问题,基于数值模拟和噪声测试相结合的方法,对辅助变流器的气动噪声特性进行了分析. 首先通过大涡模拟计算辅助变流器的气动噪声源,然后基于声类比法计算气动噪声源在流道和外部空间的声传播,最后分析风机与流道的涡流和噪声分布云图,对比各测点声压级频谱仿真和试验结果的变化趋势. 研究结果表明:在距离出风口0.4 m处仿真和试验的峰值频率均为290 Hz,量值仅相差5%,说明仿真方法正确可行;风机进口速度不均匀度过大、风机叶片涡流过多是导致风机噪声过大的原因;通过在风机进口增加方形整流网,改善了风机进口速度不均匀度,减少了风机叶片涡流,实现相同测点总声压级降低2.5 dB(A).Abstract: To solve the problem of a 1.5 dB (A) noise excess in a metro vehicle auxiliary converter, the aerodynamic noise characteristics of an auxiliary converter are investigated by combining a numerical simulation with a noise test. First, the noise from aerodynamic sources in the auxiliary converter was calculated using a large eddy simulation. Then, the sound propagation of aerodynamic sources of noise through ducts and surrounding spaces was calculated, based on an acoustic analogy method. Finally, the vortex and noise distribution contours in the fan and duct area were analysed, and trends in the simulation and test results of the sound pressure level spectrum at the test points were compared. The results indicate that at a distance of 0.4 m from the outlet, the peak frequency is 290 Hz under both conditions, and there is a 5% difference in amplitude. This demonstrates that the simulation method is correct and feasible. The vortex and noise distribution contours in the fan and duct area indicate that the inhomogeneity of air velocity at the fan inlet, and the significant vortex in the vicinity of the blade, are major contributions to the primary noise source, which is around the fan. By adding a thin, square-shaped honeycomb in front of the fan inlet, the velocity is rendered more uniform, and the overall sound pressure level is reduced by approximately 2.5 dB (A) at the test point.
-
Key words:
- metro vehicle /
- auxiliary converter /
- aerodynamic noise /
- acoustic analogy /
- large eddy simulation
-
表 1 前20阶空腔模态频率
Table 1. 20 lowest-order mode frequencies of cavity Hz
阶次 频率 阶次 频率 1 70.14 11 283.79 2 82.36 12 300.61 3 106.44 13 311.58 4 191.87 14 312.38 5 210.89 15 323.05 6 219.42 16 339.41 7 226.37 17 351.97 8 227.91 18 360.01 9 247.14 19 364.64 10 257.33 20 371.32 -
张晓排,刘岩,钟志方. 地铁车内噪声特性[J]. 噪声与振动控制,2010,30(2): 69-71 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2010.02.069ZHANG Xiaopai, LIU Yan, ZHONG Zhifang. Characteristics of noise in subway cars[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2010, 30(2): 69-71 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2010.02.069 薛红艳,刘岩,张晓排,等. 地铁车辆车内噪声分布规律[J]. 噪声与振动控制,2016,36(2): 126-129XUE Hongyan, LIU Yan, ZHANG Xiaopai, et al. Distribution law of the internal noise in metro cars[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2016, 36(2): 126-129 任海,肖友刚. 地铁车内噪声的成因及控制策略[J]. 铁道车辆,2009,47(4): 25-28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2009.04.009REN Hai, XIAO Yougang. Causes to noise inside metro cars and control measures[J]. Rolling Stock, 2009, 47(4): 25-28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2009.04.009 颜猛,贺才春,郭福林,等. 轨道车辆用变流器的气动噪声控制[J]. 大功率变流技术,2015(6): 49-52YAN Meng, HE Caichun, GUO Fulin, et al. Aerodynamic noise control of the converter for railway vehicle[J]. High Power Converter Technology, 2015(6): 49-52 魏周艳,颜猛,刘清,等. 强迫风冷式地铁辅助变流器的噪声控制[J]. 大功率变流技术,2016(4): 46-49WEI Zhouyan, YAN Meng, LIU Qing, et al. Noise control of forced air-cooled metro auxiliary converter[J]. High Power Converter Technology, 2016(4): 46-49 李启良,钟立元,王毅刚,等. 汽车空调气动噪声数值与试验研究[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(4): 620-624LI Qiliang, ZHONG Liyuan, WANG Yigang, et al. Experimental and numerical investigations of aerodynamic noise for automotive air-conditioning[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2016, 44(4): 620-624 LEE S, HEO S, CHEONG C. Prediction and reduction of internal blade-passing frequency noise of the centrifugal fan in a refrigerator[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2010, 33(6): 1129-1141 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2010.03.006 BROATCH A, GALINDO J, NAVARRO R, et al. Methodology for experimental validation of a CFD model for predicting noise generation in centrifugal compressors[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2014(50): 134-144 左曙光,韩惠君,苏虎,等. 燃料电池车用旋涡风机气动噪声及影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报 (工学版),2013,43(6): 1453-1458ZUO Shuguang, HAN Huijun, SU Hu, et al. Analysis of aerodynamic noise and influence factors of a regenerative blower used in air supply system of fuel cell cars[J]. Journal of Jilin Univesiry (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2013, 43(6): 1453-1458 刘晓良,祁大同,毛义军,等. 串列叶片式前向离心风机气动与噪声特性的优化研究[J]. 应用力学学报,2009,26(1): 40-44LIU Xiaoliang, QI Datong, MAO Yijun, et al. Aerodynamic optimization and noise characteristic for forward swept centrifugal fan with tandem blades[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2009, 26(1): 40-44 叶学民,张建坤,李春曦. 叶顶形状对轴流风机气动噪声影响的数值研究[J]. 动力工程学报,2017,37(7): 558-568YE Xuemin, ZHANG Jiankun, LI Chunxi. Aerodynamic acoustic characteristics of fan axial flow fan with different blade tips[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2017, 37(7): 558-568 王树立. 低噪声离心通风机进风口的设计计算[J]. 流体机械,1994(5): 22-25WANG Shuli. A method of optimum design of the fan interior for noise reduction[J]. Fluid Machinery, 1994(5): 22-25 LIGHTHILL M J. On sound generated aerodynamically I. general theory[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A,Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1952, 211(1107): 564-587 doi: 10.1098/rspa.1952.0060 LIGHTHILL M J. On sound generated aerodynamically II. turbulence as a source of sound[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A,Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1954, 222(1148): 1-32 doi: 10.1098/rspa.1954.0049 CURLE N. The influence of solid boundaries upon aerodynamic sound[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A,Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1955, 23(1187): 505-514 YAKHOT V, ORSZAG S A, THANGAM S, et al. Development of turbulence models for shear flows by a double expansion technique[J]. Physics of Fluids A, 1992, 4(7): 1510-1520 doi: 10.1063/1.858424 LESIEUR M, METAIS O, COMTE P. Large-eddy simulations of turbulence[M]. London: Cambridge University Press, 2005: 50-91 -




 下载:
下载: