Semi-Supervised Method for Chinese Word Sense Disambiguation
-
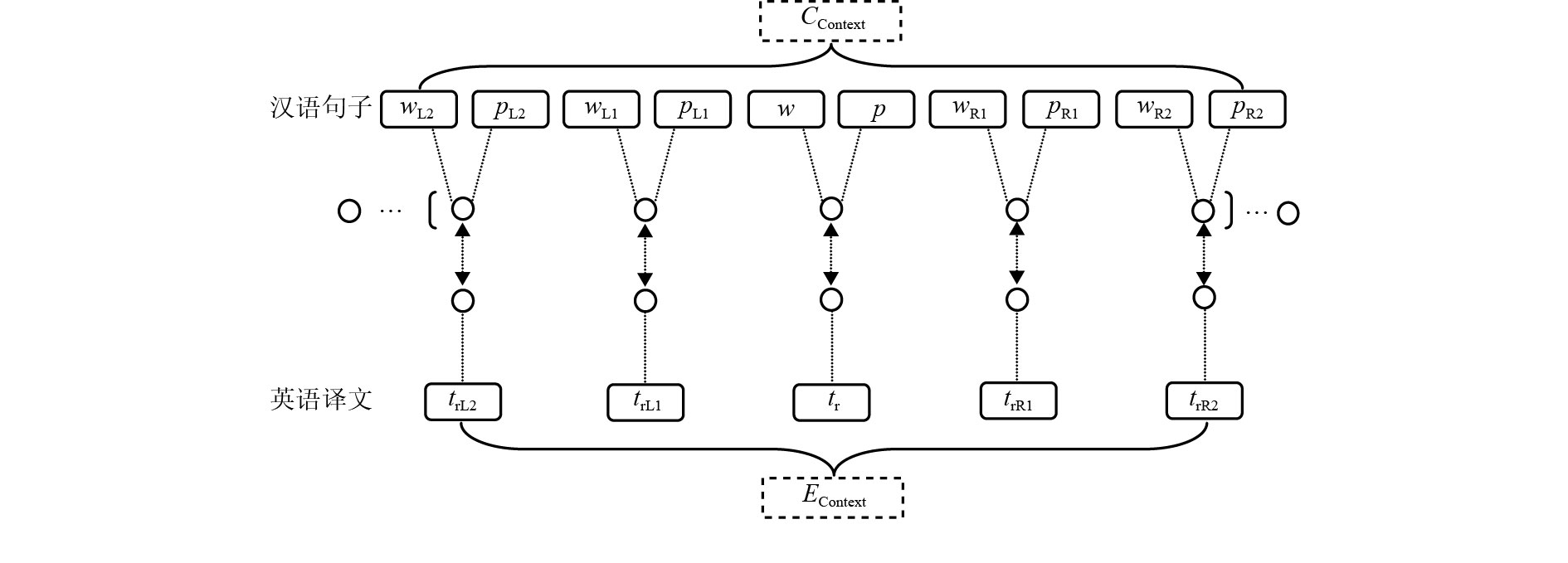
摘要: 为了解决自然语言处理领域中的一词多义问题,本文提出了一种利用多种语言学知识和词义消歧模型的半监督消歧方法. 首先,以歧义词汇左、右邻接词单元的词形、词性和译文作为消歧特征,来构建贝叶斯 (Bayes) 词义分类器,并以歧义词汇左、右邻接词单元的词形和词性作为消歧特征,来构建最大熵 (maximum entropy,ME) 词义分类器;其次,采用Co-Training算法并结合大量无标注语料来优化词义消歧模型;再次,进行了优化实验,在实验中,使用SemEval-2007:Task#5的训练语料和哈尔滨工业大学的无标注语料来优化贝叶斯分类器和最大熵分类器;最后,对优化后的词义消歧模型进行测试. 测试结果表明:与基于支持向量机 (support vector machine,SVM) 的词义消歧方法相比,本文所提出方法的消歧准确率提高了0.9%. 词义消歧的性能有所提高.Abstract: To solve the problem of a word having multiple meanings in the natural language processing (NLP) field, a semi-supervised disambiguation method, that uses a range of word sense disambiguation (WSD) models and linguistic knowledge has been proposed in this paper. First, words, parts of speech and translations were used as discriminative features, which were extracted from word units adjacent to the left and right of an ambiguous word. A word sense classifier was constructed using a Bayes model, following which a word sense classifier based on a maximum entropy (ME) model was constructed. Second, a Co-Training algorithm, based on a multitude of unannotated corpora, was adopted to optimize the WSD model. Third, optimization experiments were conducted in which training corpus in SemEval-2007: Task#5 and a large number of unannotated corpora from Harbin Institute of Technology were applied to optimize the Bayesian classifier and the maximum entropy classifier. Finally, the optimized WSD model was tested. Test results demonstrate an increase in the disambiguation accuracy of the proposed method by 0.9% compared to WSD models based on support vector machines, thereby exhibiting an improvement in WSD performance.
-
表 1 特征函数的值
Table 1. Values of feature functions
Si Ffeature fj(Si,Ffeature) 子女 是 1(j = 1) 子女 v 1(j = 2) 子女 中华 1(j = 3) 子女 nz 1(j = 4) 子女 的 1(j = 5) 子女 u 1(j = 6) 子女 共同 1(j = 7) 子女 b 1(j = 8) 其它情况 fj(Si,Ffeature) = 0, j = $1{\simfont\text{,}}\!\!\!2{\simfont\text{,}}\!\!\!\cdots{\simfont\text{,}}\!\!\!8$ 表 2 测试语料的消歧准确率
Table 2. Disambiguation accuracy of test corpus
词汇 实验1 实验2 实验3 本 48.0 72.0 84.0 补 85.0 50.0 50.0 旗帜 72.2 83.3 83.3 动摇 75.0 75.0 76.5 镜头 66.7 60.0 60.0 使 81.3 75.0 87.5 望 100.0 69.2 69.2 长城 76.2 61.9 61.9 成立 55.6 63.0 66.7 队伍 54.5 40.9 40.9 赶 61.1 55.6 61.1 天地 84.0 80.0 80.0 表面 50.0 61.1 61.1 菜 55.6 38.9 50.0 单位 88.2 76.5 76.5 儿女 45.0 100.0 100.0 机组 100.0 100.0 100.0 气象 93.8 81.3 81.3 震惊 71.4 92.9 92.9 中医 93.8 93.8 93.8 平均准确率 72.9 71.5 73.8 -
王李冬,张引,吕明琪. 基于词组主题建模的文本语义压缩算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(4): 755-763. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.04.027WANG Lidong, ZHANG Yin, LÜ Mingqi. Document semantic compression algorithm based on phrase topic model[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(4): 755-763. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.04.027 翟东海,崔静静,聂洪玉,等. 基于语义相似度的话题关联检测方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(3): 517-522. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.03.021ZHAI Donghai, CUI Jingjing, NIE Hongyu, et al. Topic link detection method based on semantic similarity[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(3): 517-522. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.03.021 杨陟卓,黄河燕. 基于语言模型的有监督词义消歧模型优化研究[J]. 中文信息学报,2014,28(1): 19-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2014.01.003YANG Zhizhuo, HUANG Heyan. Supervised WSD model optimization based on language model[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2014, 28(1): 19-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2014.01.003 JUDITA P. DALE: a word sense disambiguation system for biomedical documents trained using automatically labeled examples[C]//Proceedings of the NAACL HLT 2013 Demonstration Session. Atlanta: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2013: 1-4 RAGANATO A. Neural sequence learning models for word sense disambiguation[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Copenhagen: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017: 1167-1178 IACOBACCI I, PILEHVAR M T, NAVIGLI R. Embeddings for word sense disambiguation: an evaluation study[C]//Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Berlin: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016: 897-907 SHINNOU H, SASAKI M, KOMIYA K. Learning under covariate shift for domain adaptation for word sense disambiguation[C]//Proceedings of the 29th Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information and Computation. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2015: 215-223 郭瑛媚,史晓东,陈毅东,等. 基于话题分布相似度的无监督评论词消歧方法[J]. 北京大学学报,2013,49(1): 95-101.GUO Yingmei, SHI Xiaodong, CHEN Yidong, et al. Unsupervised opinion word disambiguation based on topic distribution similarity[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2013, 49(1): 95-101. 李旭,刘国华,张东明. 一种改进的汉语全文无指导词义消歧方法[J]. 自动化学报,2010,36(1): 184-187.LI Xu, LIU Guohua, ZHANG Dongming. An improved word sense disambiguation method for Chinese full-words based on unsupervised learning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(1): 184-187. SUNNY M, RITWIK M, MARTIN R, et al. That's sick dude!: automatic identification of word sense change across different timescales[C]//Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Baltimore: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014: 1020-1029 KOUNO K, SHINNOU H, SASAKI M, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation for word sense disambiguation using stacked denoising autoencoder[C]//Proceedings of the 29th Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information and Computation. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2015: 224-231 PANCHENKO A, MARTEN F, RUPPERT E, et al. Unsupervised, knowledge-free, and interpretable word sense disambiguation[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 EMNLP System Demonstrations. Copenhagen: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017: 91-96 CEM A, JANYCE W, RADA M, et al. Iterative constrained clustering for subjectivity word sense disambiguation[C]//Proceedings of the 14th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Gothenburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014: 269-278 KAVEH T, HWEE T N. Semi-supervised word sense disambiguation using word embeddings in general and specific domains[C]//Human Language Technologies: the 2015 Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the ACL. Denver: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2015: 314-323 KAVEH T, HWEE T N. One million sense-tagged instances for word sense disambiguation and induction[C]//Proceedings of the 19th Conference on Computational Language Learning. Beijing: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2015: 338-344 鹿文鹏,黄河燕,吴昊. 基于领域知识的图模型词义消歧方法[J]. 自动化学报,2014,40(12): 2836-2850.LU Wenpeng, HUANG Heyan, WU Hao. Word sense disambiguation with graph model based on domain knowledge[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(12): 2836-2850. PERSHINA M. Personalized page rank for named entity disambiguation[C]//Human Language Technologies: the 2015 Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the ACL. Denver: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2015: 238-243 RICHARD J, LUIS N P. Combining relational and distributional knowledge for word sense disambiguation[C]//Proceedings of the 20th Nordic Conference of Computational Linguistics. Vilnius: Linköping University Electronic Press, 2015: 69-78 IVAN L A. Improving selection of synsets from Wordnet for domain-specific word sense disambiguation[J]. Computer Speech and Language, 2017, 41(1): 128-145. JIN P, WU Y F, YU S W. SemEval-2007 task 5: multilingual Chinese-English lexical sample task[C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluations. Prague: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2007: 19-23 -




 下载:
下载:

