Multi-Objective Optimum Design for in-Wheel Motor Based on Improved Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm
-
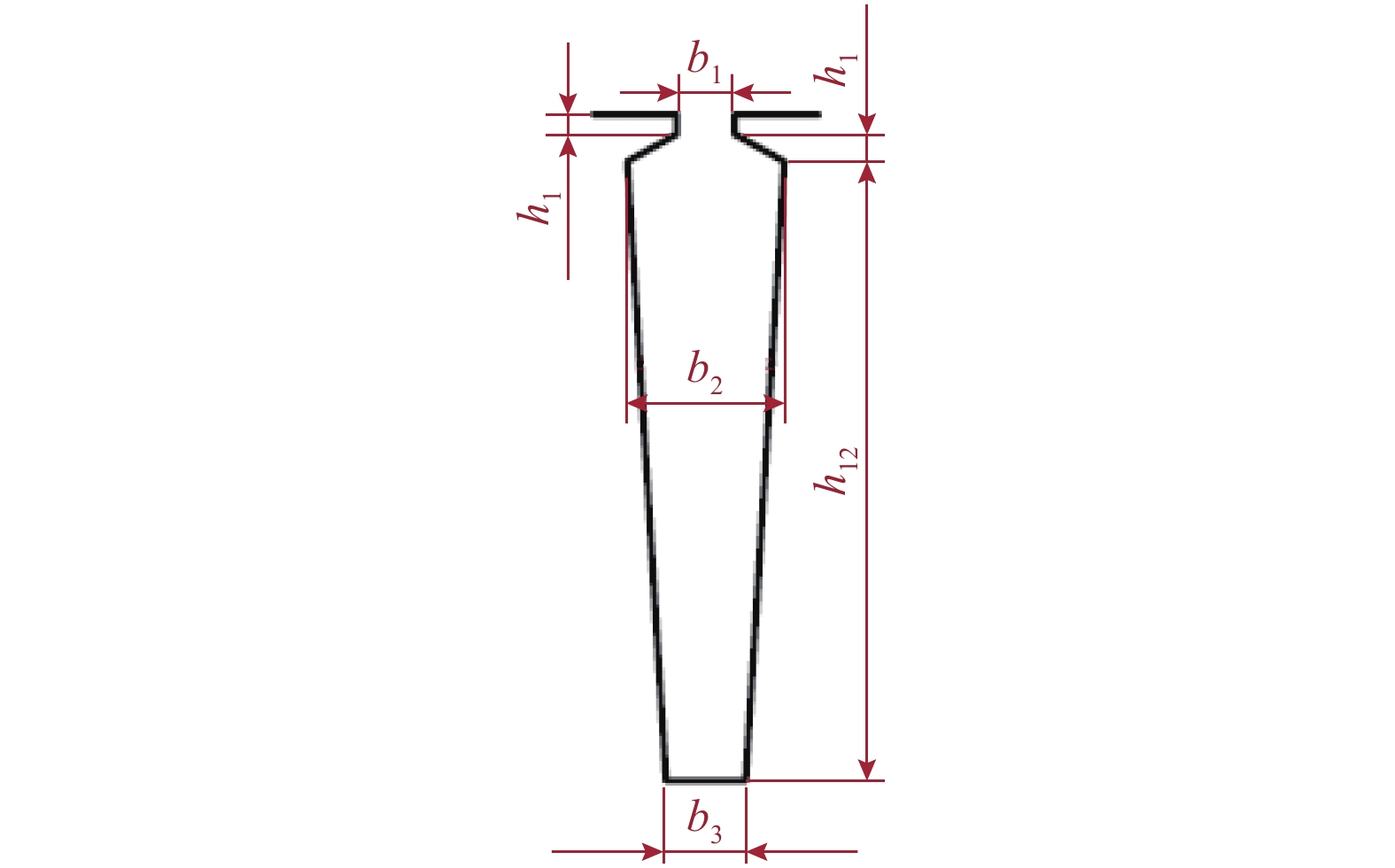
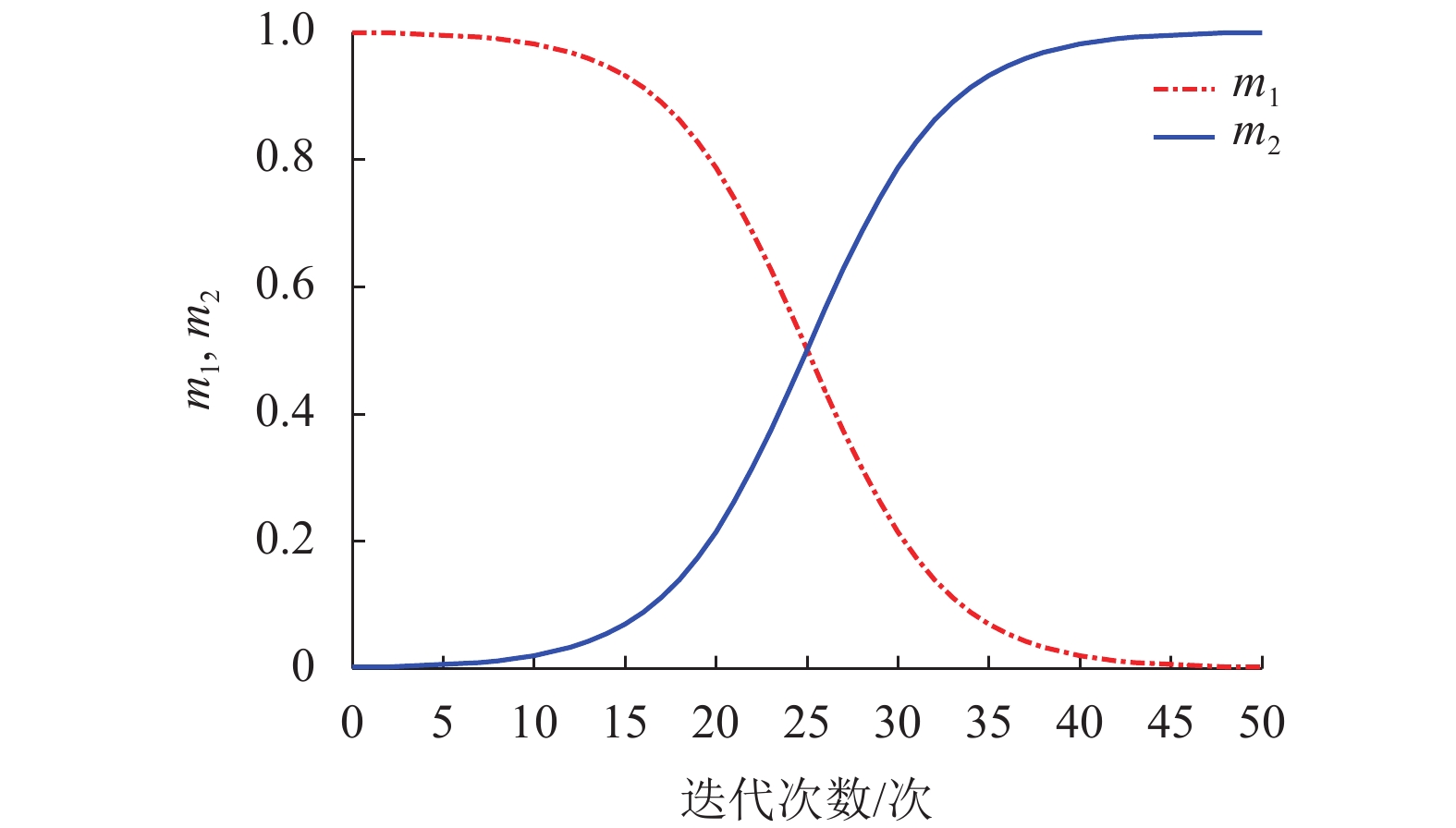
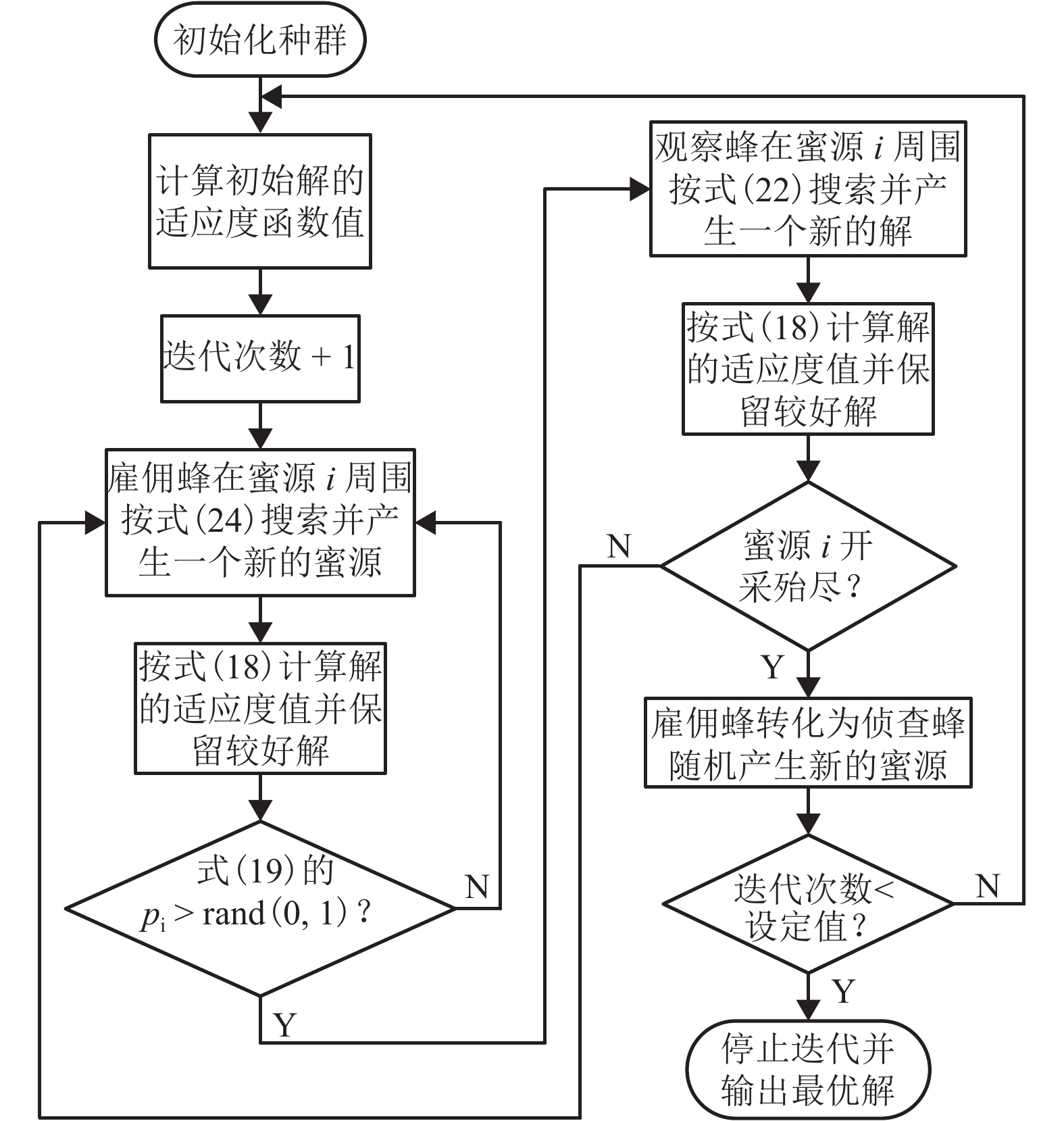
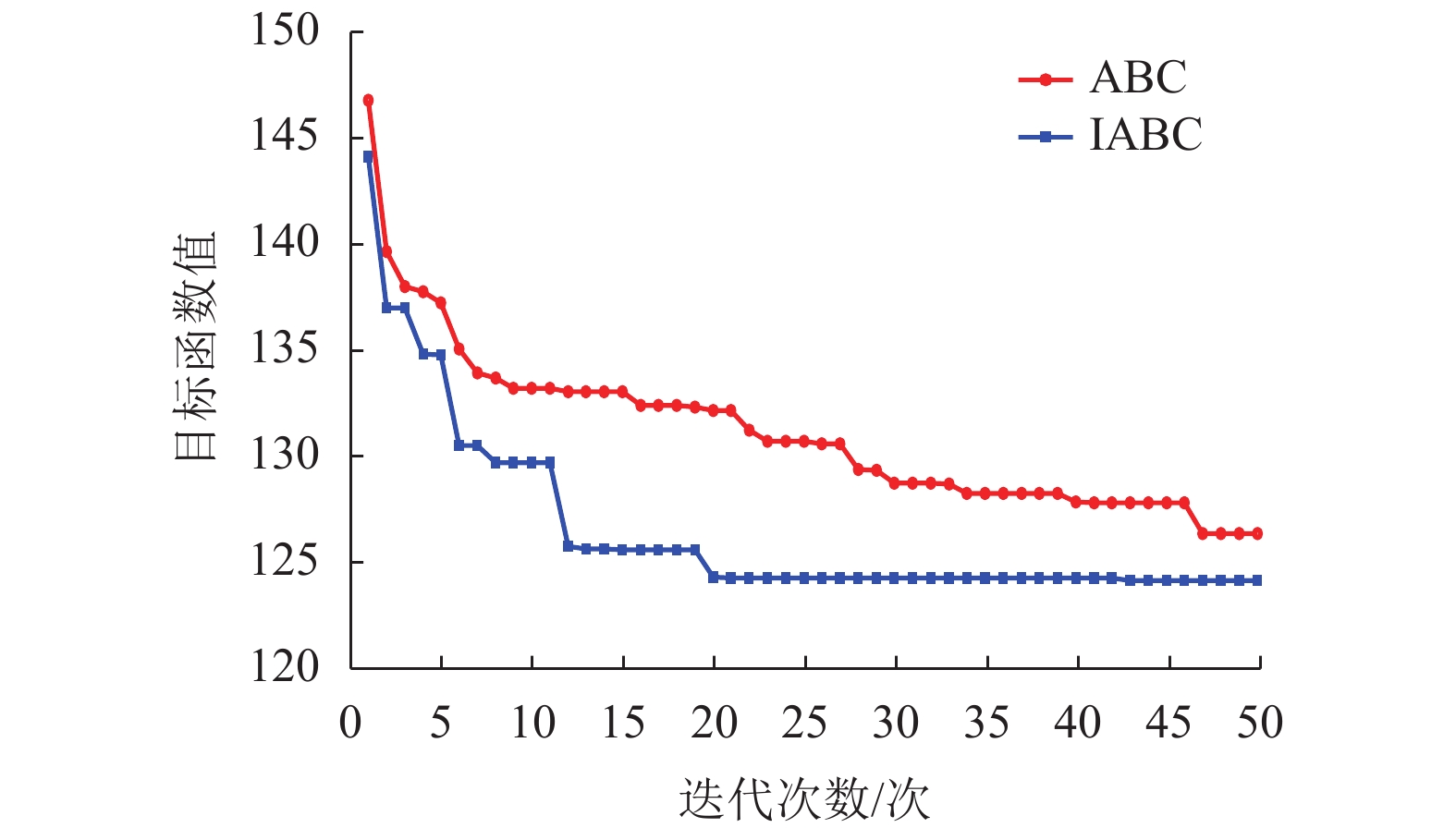
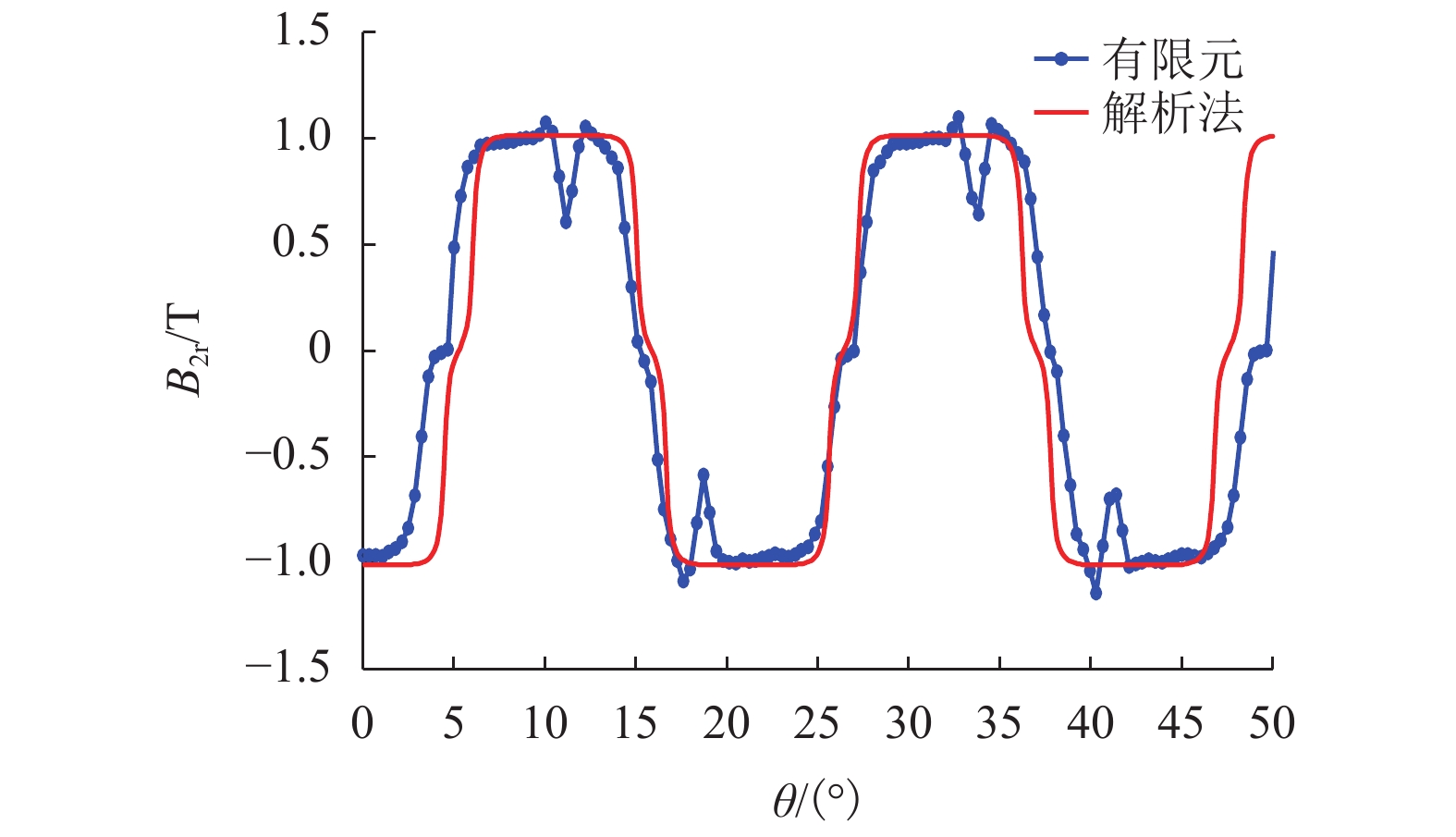
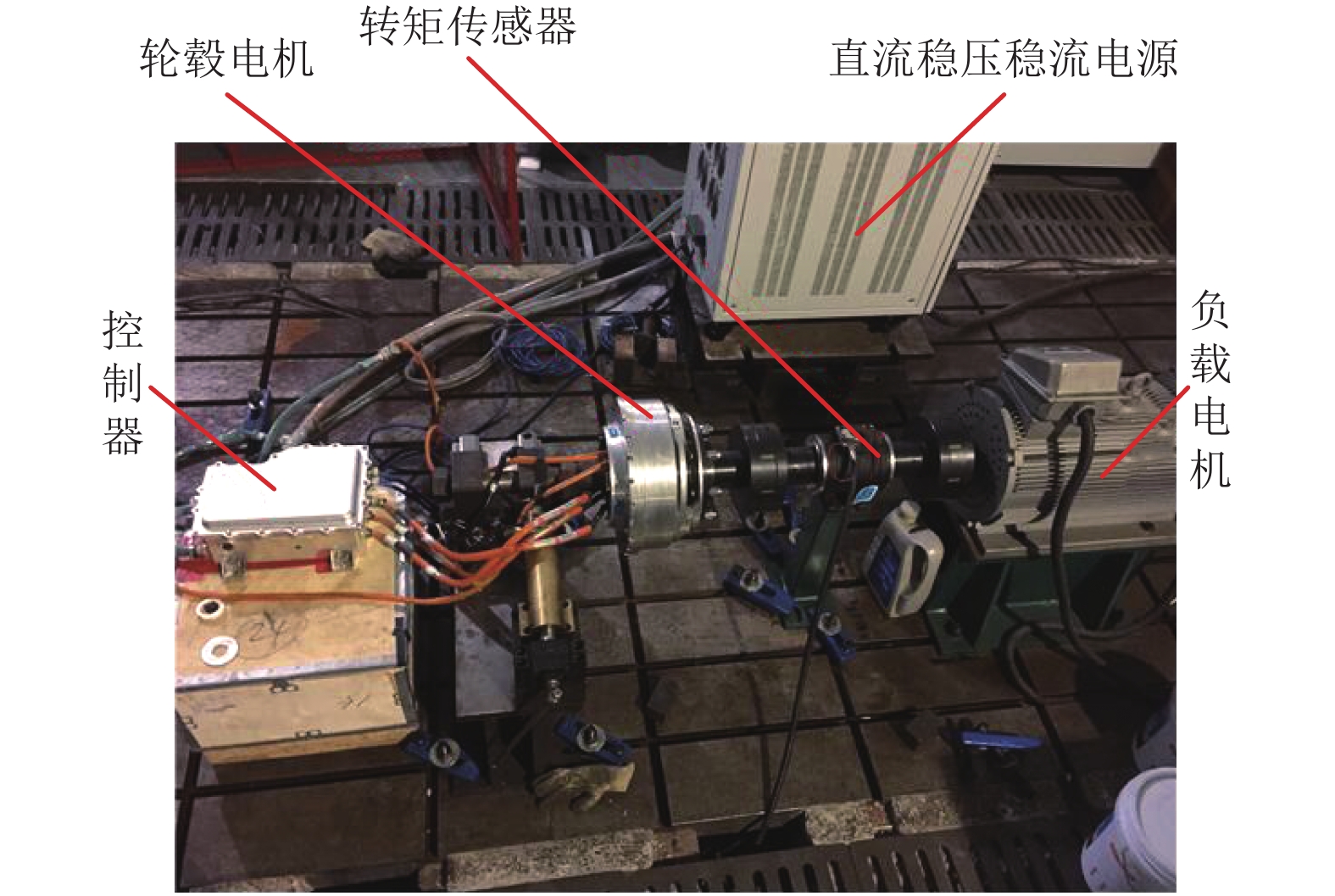
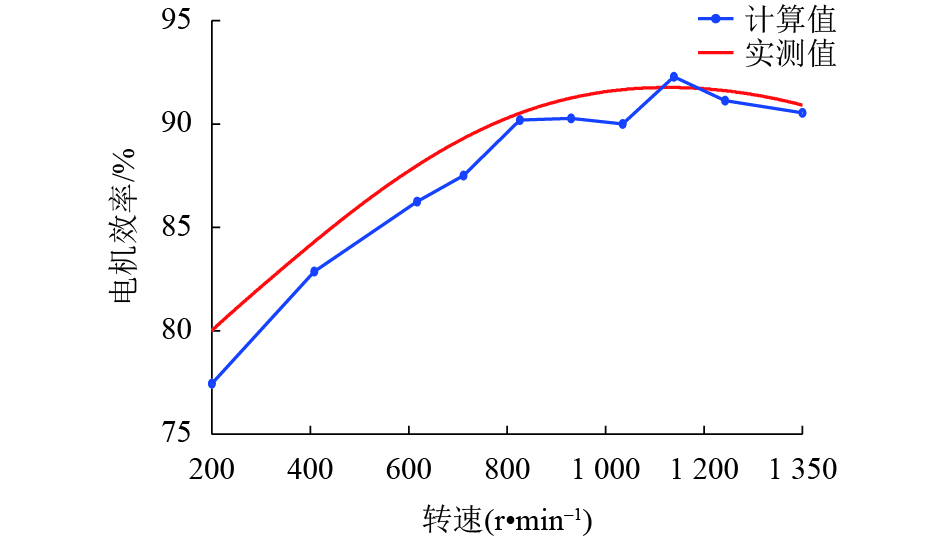
摘要: 为了提高轮毂电机功率密度、降低其材料成本,提出一种改进的人工蜂群算法对轮毂电机性能进行优化设计. 首先利用磁路法建立外转子永磁式轮毂电机各项性能的表达式;其次通过引入个体极值、群体极值以及一对异步缩放因子来克服传统人工蜂群算法收敛速度较慢、探索与开发能力不平衡等缺点;以磁极对数、气隙长度、永磁体厚度等电磁参数为设计变量,将电机的有效质量、功率损耗和材料成本线性加权组成单目标函数,并采用障碍函数法将有约束的非线性目标函数转化为非约束的形式;最后利用遗传算法、传统人工蜂群算法和改进的人工蜂群算法对轮毂电机进行优化设计,并通过有限元法和样机实验验证了计算结果的正确性. 研究结果表明:相较于传统人工蜂群算法,改进的人工蜂群算法使目标函数收敛速度更快;相较于遗传算法和传统人工蜂群算法,改进后的算法使目标函数值最小;相较于原设计方案,优化后轮毂电机有效质量降低13.4%,材料成本降低34.4%,功率损耗降低44.2%,电机效率提高12.0%.Abstract: In order to improve the power density of the in-wheel motor and reduce its material cost, an improved artificial bee colony (IABC) algorithm was proposed to optimize the performance of the in-wheel motor. Firstly, the expressions for the performances of the permanent-magnet in-wheel motor with outer rotor were established by magnetic circuit method. Secondly, individual extremum, population extremum and a pair of asynchronous scaling factors were introduced to overcome the shortcomings of traditional artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm, such as slow convergence speed, and imbalance in exploration and development. The effective mass, power loss and material cost of the motor were linearly weighted to form a single objective function with the electromagnetic parameters such as number of pole pairs, air-gap clearance and permanent magnet thickness as design variables, and the constrained non-linear objective function was transformed into a non-constrained one by the barrier function method. Finally, the genetic algorithm (GA), traditional ABC algorithm and IABC algorithm were used to optimize the design of the in-wheel motor respectively. The correctness of the calculation results was verified by finite element method and prototype experiment. The results show that the IABC algorithm makes the objective function converge faster than the traditional ABC algorithm. Compared with the GA and traditional ABC algorithm, the IABC algorithm minimizes the objective function value. Compared with the original design, the effective quality of the in-wheel motor is reduced by 13.4%, material cost is reduced by 34.4%, power loss is reduced by 44.2%, and the efficiency is increased by 12.0%.
-
表 1 优化后的设计变量值
Table 1. Optimized design variable values
算法 p δ/cm Q1 hm/cm L/cm Ns Di1/cm d11/mm 初始方案 28 0.10 54 0.46 4.2 40 19.00 1.3 GA 22 0.10 52 0.32 3.8 34 19.20 1.4 ABC 20 0.12 50 0.30 3.5 34 19.37 1.5 IABC 16 0.12 48 0.30 3.5 32 19.50 1.4 表 2 初始方案和各种算法优化结果
Table 2. Results of initial design and optimized design with different algorithms
算法 电机有效
质量/kg电机材料
成本/元功率
损耗/W效率/% 初始方案 24.17 1 169.5 2 345.2 78.68 GA 22.15 880.3 1 972.3 82.07 ABC 21.42 826.4 1 537.8 86.02 IABC 20.92 766.8 1 307.9 88.11 -
卢东斌,欧阳明高,谷靖,等. 电动汽车永磁同步电机最优制动能量回馈控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2013,33(3): 83-91.LU Dongbin, OUYANG Minggao, GU Jing, et al. Optimal regenerative braking control for permanent magnet synchronous motors in electric vehicles[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(3): 83-91. ROMERAL L, URRESTY J C. Modeling of surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motors with stator winding interturn faults[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2011, 58(5): 1576-1585. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2010.2062480 孙跃,谭若兮,唐春森,等. 一种应用于电动汽车的新型耦合机构优化设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2018,53(5): 1078-1086.SUN Yue, TAN Ruoxi, TANG Chunsen, et al. Optimized design of new coupling mechanism for electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(5): 1078-1086. RAHIDEH A, KORAKIANITIS T, RUIZ P, et al. Optimal brushless DC motor design using genetic algorithms[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2010, 322(22): 3680-3687. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.07.025 陈齐平,舒红宇,任凯,等. 基于改进遗传算法的微型电动车轮毂电机优化设计[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2012,43(8): 3013-3018.CHEN Qiping, SHU Hongyu, REN Kai, et al. Optimization design of driving in-wheel motor of micro-electric vehicle based on improvement genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(8): 3013-3018. 李立毅,唐勇斌,刘家曦,等. 多种群遗传算法在无铁心永磁直线同步电机优化设计中的应用[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2013,33(15): 69-77.LI Liyi, TANG Yongbin, LIU Jiaxi, et al. Application of the multiple population genetic algorithm in optimum design of air-core permanent magnet linear synchronous motors[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(15): 69-77. NGUYEN T D, LANFRANCHI V. Comparison of optimization algorithms for the design of a brushless DC machine with travel-time minimization[C]//2009 8th International Symposium on Advanced Electromechanical Motion Systems & Electric Drives Joint Symposium. Lille: IEEE, 2009: 1-6 ANDERSEN S B, SANTOS I F. Evolution strategies and multi-objective optimization of permanent magnet motor[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2012, 12(2): 778-792. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2011.10.013 王晓远,高鹏. 基于进化策略的轮毂电机永磁体结构优化设计[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2015,35(4): 979-984.WANG Xiaoyuan, GAO Peng. Optimal design of permanent magnets of in-wheel motor based on evolution strategy[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35(4): 979-984. LI S, YANG M. Particle swarm optimization combined with finite element method for design of ultrasonic motors[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2008, 148(1): 285-289. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2008.08.004 NAVARDI M J, BABAGHORBARI B, KETABI A. Efficiency improvement and torque ripple minimization of switched reluctance motor using FEM and seeker optimization algorithm[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2014, 78(2): 237-244. KARABOGA D, BASTURK B. A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm[J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 2007, 39(3): 459-471. doi: 10.1007/s10898-007-9149-x KARABOGA D, AKAY B. A comparative study of artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2009, 214(1): 108-132. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2009.03.090 KARABOGA D, OZTURK C. A novel clustering approach: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2011, 11(1): 652-657. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2009.12.025 KARABOGA D, BASTURK B. On the performance of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2008, 8(1): 687-697. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2007.05.007 毕晓君,王艳娇. 改进人工蜂群算法[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报,2012,33(1): 117-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7043.201102020BI Xiaojun, WANG Yanjiao. A modified artificial bee colony algorithm and its application[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2012, 33(1): 117-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7043.201102020 毕晓君,王艳娇. 加速收敛的人工蜂群算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术,2011,33(12): 2755-2761. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.12.34BI Xiaojun, WANG Yanjiao. Artificial bee colony algorithm with fast convergence[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2011, 33(12): 2755-2761. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.12.34 ZHU G, KWONG S. Gbest-guided artificial bee colony algorithm for numerical function optimization[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2010, 217(7): 3166-3173. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2010.08.049 GAO W, LIU S, HUANG L. A global best artificial bee colony algorithm for global optimization[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2012, 236(11): 2741-2753. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2012.01.013 KARABOGA D, GORKEMLI B. A combinatorial artificial bee colony algorithm for traveling salesman problem[C]//2011 International Symposium on Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications. Turkey: IEEE, 2011: 50-53 WANG X, TANG L. An adaptive multi-population differential evolution algorithm for continuous multi-objective optimization[J]. Information Sciences, 2016, 348(2): 124-141. MARINI F, WALCZAK B. Particle swarm optimization (PSO). A tutorial[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2015, 149(5): 153-165. doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2015.08.020 -





 下载:
下载: