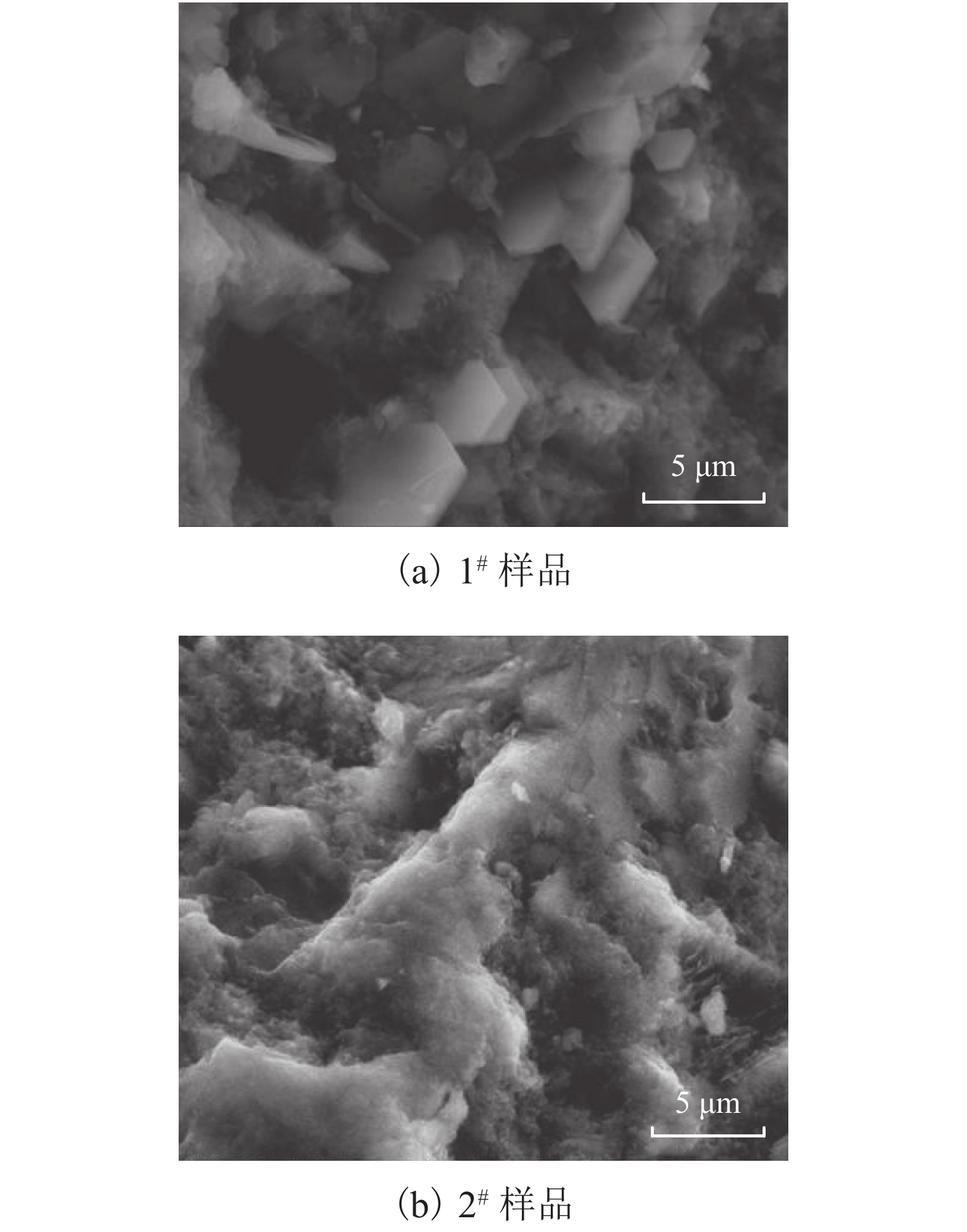
Flexural Fatigue Performance of Concrete Prepared with Low-Heat Portland Cement
-
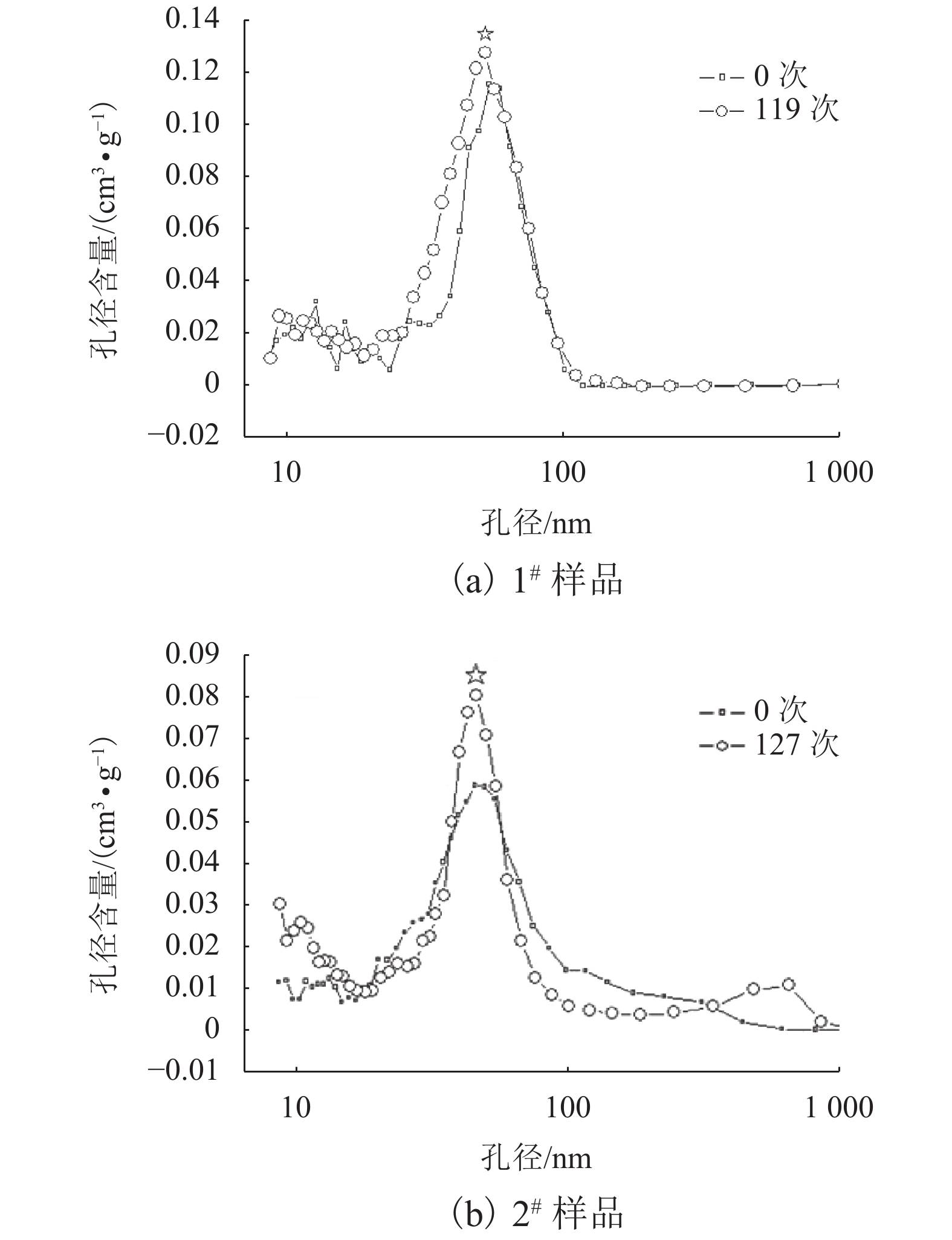
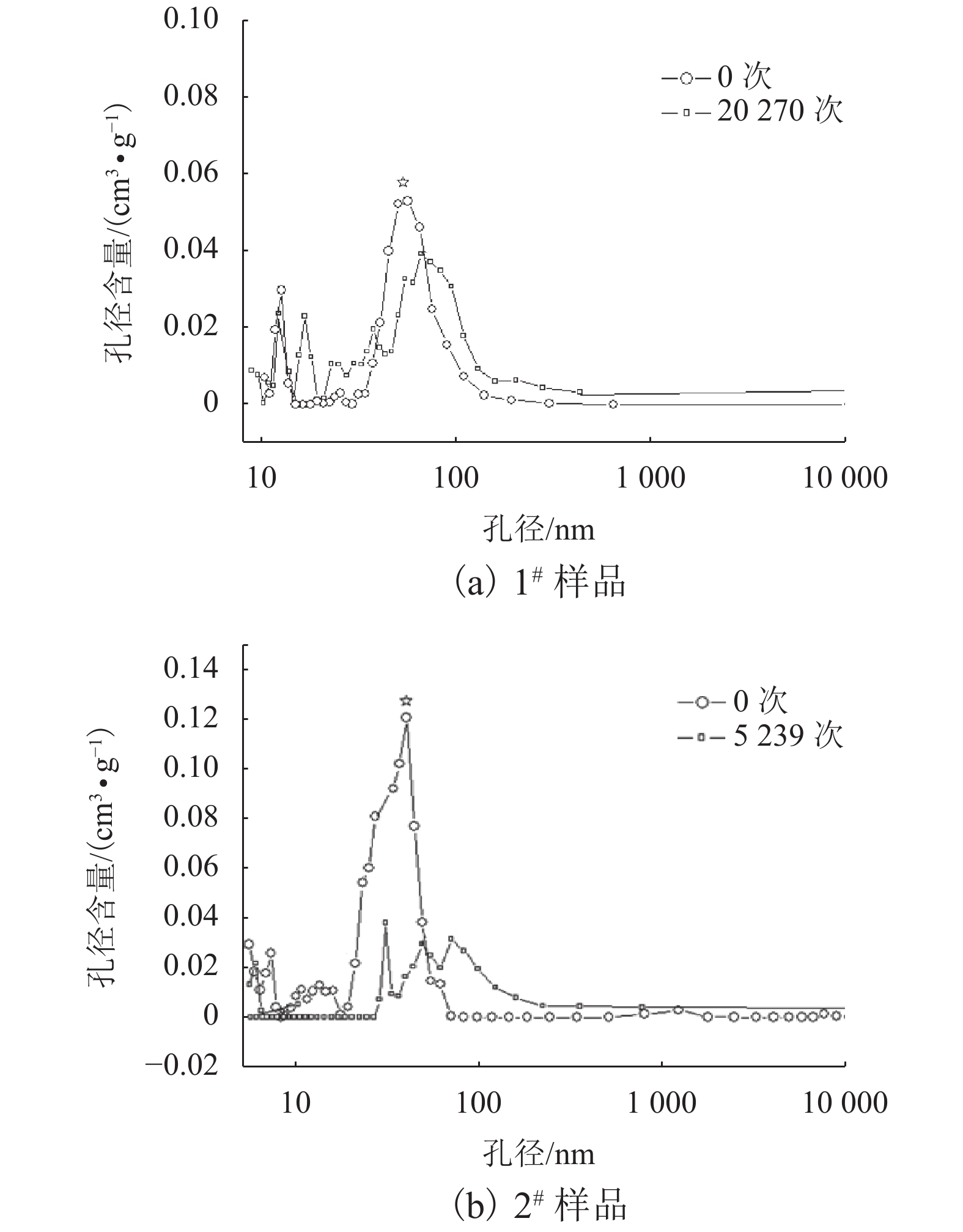
摘要: 为研究胶凝材料的差异对混凝土疲劳特性的影响,采用4点加载的弯曲疲劳实验方法,对比研究了不同应力水平下低热硅酸盐水泥和同强度等级的普通硅酸盐水泥配制混凝土的弯曲疲劳特性,利用DTA-TG、SEM和MIP探讨了两种不同水泥配制混凝土的微观组成结构差异及其对疲劳特性的影响. 实验结果表明:28、90 d和180 d标准养护条件下的低热水泥混凝土在应力水平为0.75~0.90时的弯曲疲劳寿命均高于普通硅酸盐水泥混凝土;3.49 MPa应力荷载下,养护龄期由28 d延长至180 d,两种混凝土的弯曲疲劳寿命分别提高了230 452及8 168倍,90 d与180 d养护龄期的低热硅酸盐水泥混凝土的疲劳寿命分别是普通硅酸盐水泥混凝土的4.76倍及19.88倍,养护龄期越长,低热水泥混凝土抗疲劳性能的优势越显著;低热水泥混凝土水化产物中C-S-H凝胶多,Ca(OH)2含量少,加载后最可几孔径与大孔含量的增幅较低(<10%),致使其在疲劳荷载作用下裂缝源生成的可能性减少,裂缝扩展能力降低,抗疲劳能力增强.Abstract: To investigate the influence of cementing materials on the fatigue performance of concretes, the flexural fatigue performance of concretes prepared with low-heat Portland cement and ordinary Portland cement at different stresses was studied by a four-point bending fatigue test method. Additionally, the relationship between microstructure and fatigue performance was studied by using DTA-TG, SEM, and MIP methods. It was observed that in comparison to the ordinary Portland cement, the low-heat Portland cement is favourable for the improvement of the fatigue life of the concrete under the same stress lever (0.75–0.90). As the curing age was extended from 28 days to 180 days, the flexural fatigue life of both the kinds of concrete with a loading of 3.49 MPa was increased by 230 452 times in low-heat Portland cement concrete and 8 168 times in case of ordinary Portland cement concrete. The fatigue life of low-heat Portland cement concrete on the 90th day and 180th day was 4.76 and 19.88 times higher than that of ordinary Portland cement concrete, respectively. The longer the curing age the better the anti-fatigue performance of low-heat cement concretes. The microstructure study indicated that low-heat Portland cement concrete consisted more C-S-H gel and less Ca(OH)2. Furthermore, low-heat Portland cement concrete had lower increase (less than 10%) on the most probable pore size; and the proportion of large pores after fatigue loading reduced the crack propagation and enhanced the anti-fatigue performance.
-
Key words:
- low-heat Portland cement /
- concrete /
- anti-fatigue performance /
- stress lever
-
表 1 熟料的化学成分和矿物组成(wB)
Table 1. Chemical and mineral composition of clinker
水泥编号 烧失量 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO SO3 C3S C2S C3A C4AF C1 0.49 24.73 4.71 4.98 62.21 1.52 0.35 21.52 54.66 4.04 15.41 C2 0.63 21.19 5.07 4.21 65.15 1.71 0.80 60.17 14.96 6.30 12.80 表 2 水泥的物理性能
Table 2. Physical properties of cement
水泥编号 标准稠度/% 凝结时间/min 比表面积/(㎡•㎏–1) 抗压强度/MPa 抗折强度/MPa 水化热/(kJ•kg–1) 初凝 终凝 3 d 28 d 3 d 28 d 3 d 7 d C1 22.0 100 145 376 15.0 43.2 3.8 7.7 197.0 216.0 C2 24.2 130 180 358 28.4 52.5 5.4 8.5 304.0 333.0 表 3 混凝土配合比及其物理性能
Table 3. Mix propotion and physical properties of concrete
编号 水泥/
(kg•m–3)石/
(kg•m–3)砂/
(kg•m–3)水/
(kg•m–3)减水剂/
(kg•m–3)坍落度/
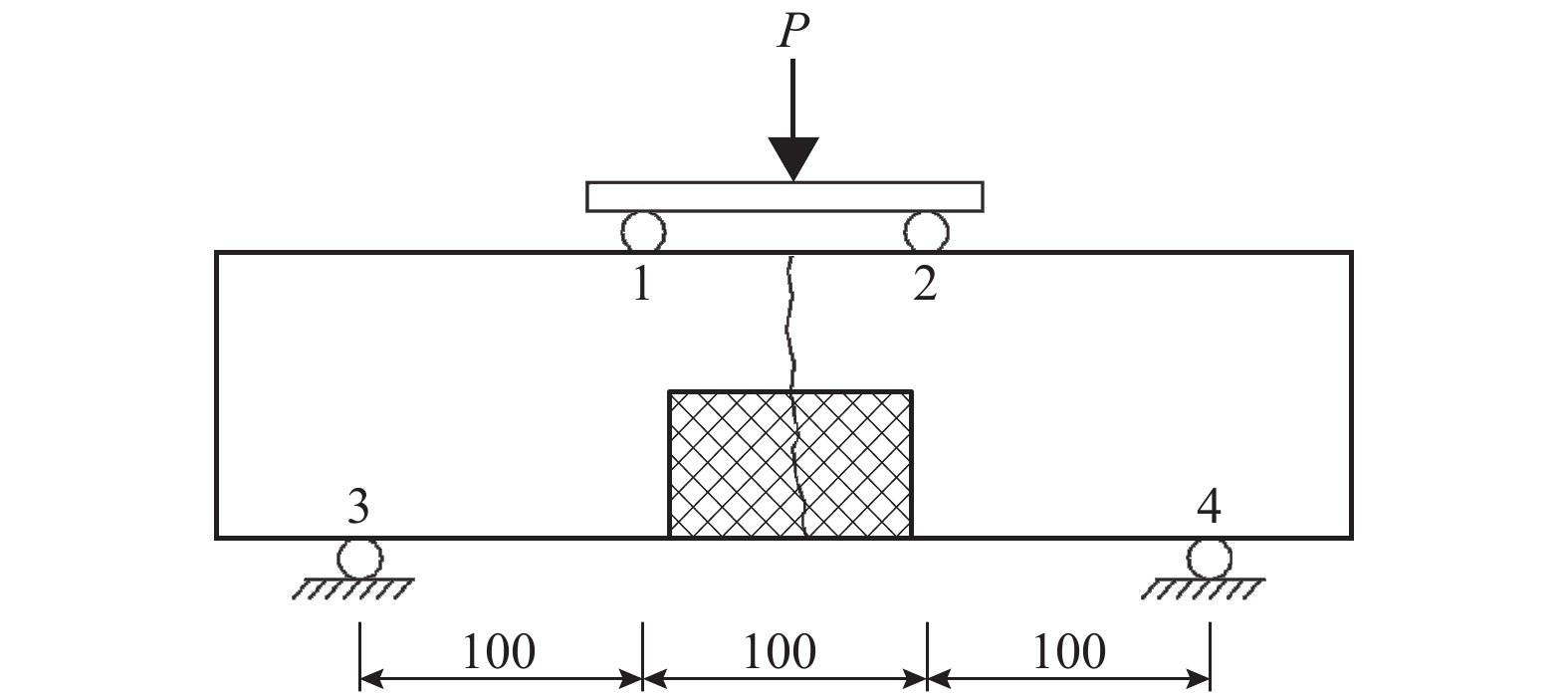
mm28 d强度/MPa 90 d强度/MPa 180 d强度/MPa 抗折 抗压 抗折 抗压 抗折 抗压 1# 340 1 307 666 136 3.74 35 4.1 43.0 5.0 54.1 6.0 62.4 2# 340 1 307 666 136 3.4 37 4.3 48.9 4.8 53.1 5.4 60.7 表 4 混凝土样品28、90 d的疲劳试验结果
Table 4. Fatigue lives of 28、90 d concrete
样品 应力水平 0.90 0.85 0.80 1#(28 d) 207.8 523.6 9 585.4 2#(28 d) 132.2 476.0 1 753.0 1#(90 d) 352.8 2 171.4 10 316.6 2#(90 d) 58.2 1 245.5 5 042.1 表 5 混凝土样品180 d的疲劳试验结果
Table 5. Fatigue lives of 180 d concrete
样品 应力水平 0.85 0.80 0.75 1# 398.0 2 418.6 20 226.8 2# 355.5 1 515.5 17 676.1 表 6 DTA-TG曲线上各样品对应吸热峰的失重比例
Table 6. Weight loss of cement pastes calculated through DTA-TG curve
样品 28 d 90 d 180 d 120℃ 450℃ 120℃ 450℃ 120℃ 450℃ PC1 8.00 2.46 10.83 2.51 11.32 2.89 PC2 9.27 3.73 10.89 3.98 11.21 4.57 -
郑克仁. 矿物掺合料对混凝土疲劳性能的影响及机理[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2007 郑克仁,孙伟,赵庆新,等. 基于混凝土基体和界面过渡区性质的疲劳方程[J]. 硅酸盐学报,2007,35(2): 236-241. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2007.02.022ZHENG Keren, SUN Wei, ZHAO qingxin. Fatigue equation based on properties of concrete matrix and interfacial transition zone[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2007, 35(2): 236-241. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2007.02.022 LI Pingguo, WEI Sun. Study on the flexural fatigue performance and fractal mechanism of concrete with high proportions of ground granulated blast-furnace slag[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2007, 37(2): 242-250. SUN Wei. Fatigue performance and equations of roller compacted concrete with fly ash[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1998, 28(2): 309-315. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(97)00211-1 孙伟,严云. 高强混凝土与钢纤维高强混凝土冲击和疲劳特性机理的研究[J]. 土木工程学报,1994,27(5): 20-27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.1994.05.001SUN Wei, YAN Yun. Study on the mechanism of impact and fatigue behavior of high-strength concrete and steel fiber reinforced high-strength concrete[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 1994, 27(5): 20-27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.1994.05.001 张小辉. 钢纤维混凝土弯曲疲劳及其损伤特性和细观强度研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2001 姜丽伟,肖福贵. 辅特维纤维水泥混凝土抗折疲劳性能试验研究[J]. 森林工程,2006,22(6): 47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2006.06.017JIANG Liwei, XIAO Fugui. Experimental studies of the flexural fatigue-resistant performance of the forta-ferro fiber cement concrete[J]. Forest Engineering, 2006, 22(6): 47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2006.06.017 LEE M K, BARR B I G. An overview of the fatigue behaviour of plain and fibre reinforced concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2004, 26(4): 299-305. doi: 10.1016/S0958-9465(02)00139-7 徐铜鑫,吴笑梅,樊粤明. 不同熟料矿物含量的水泥对混凝土部分性能的影响[J]. 水泥,2013(4): 4-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3922.2013.04.003XU Tongxin, WU Xiaomei, FAN Yueming. Influence of different mineral composition of clinker on partial performance of concrete[J]. Cement, 2013(4): 4-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3922.2013.04.003 王可良,隋同波,许尚杰,等. 高贝利特水泥混凝土的断裂韧性[J]. 硅酸盐学报,2012,40(8): 1139-1142.WANG Keliang, SUI Tongbo, XU Shangjie, et al. Fracture toughness of high belite cement concrete[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2012, 40(8): 1139-1142. 王可良,隋同波,刘玲,等. 高贝利特水泥混凝土的抗拉性能[J]. 硅酸盐学报,2012,40(8): 1139-1142.WANG Keliang, SUI Tongbo, LIU Ling, et al. Tensile properties of high belite cement concrete[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2012, 40(8): 1139-1142. 中国建筑科学研究院. JGJ63—89混凝土拌和用水标准[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2002 付智, 罗翥, 王大鹏,等. 公路水泥混凝土路面施工技术细则: JTG F30—2014[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2014 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 普通混凝土拌合物性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50080—2016[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2016 沈威, 黄文熙, 闵盘荣. 水泥工艺学[M]. 武汉: 武汉工业大学出版社. 1999: 291-323 -




 下载:
下载: