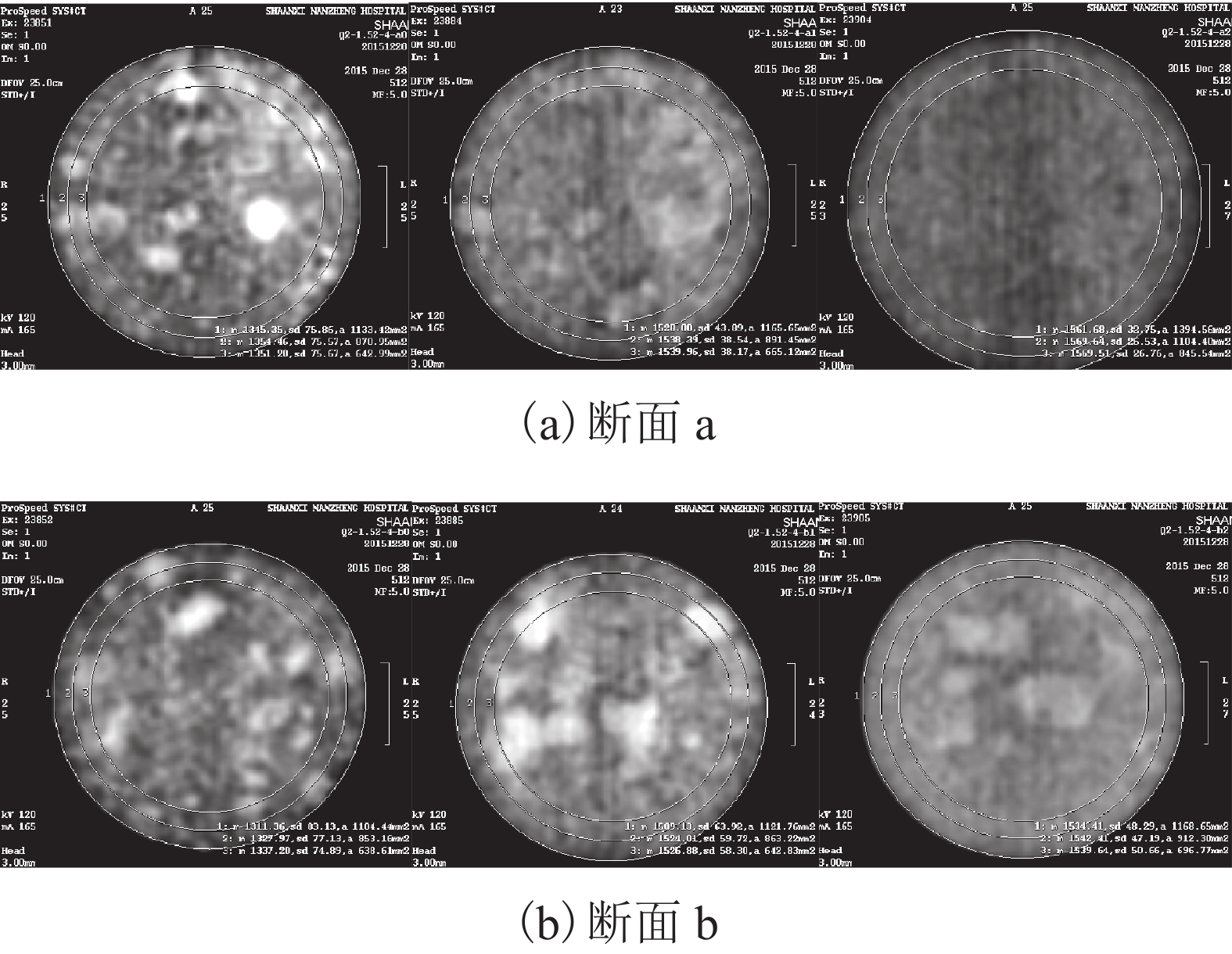
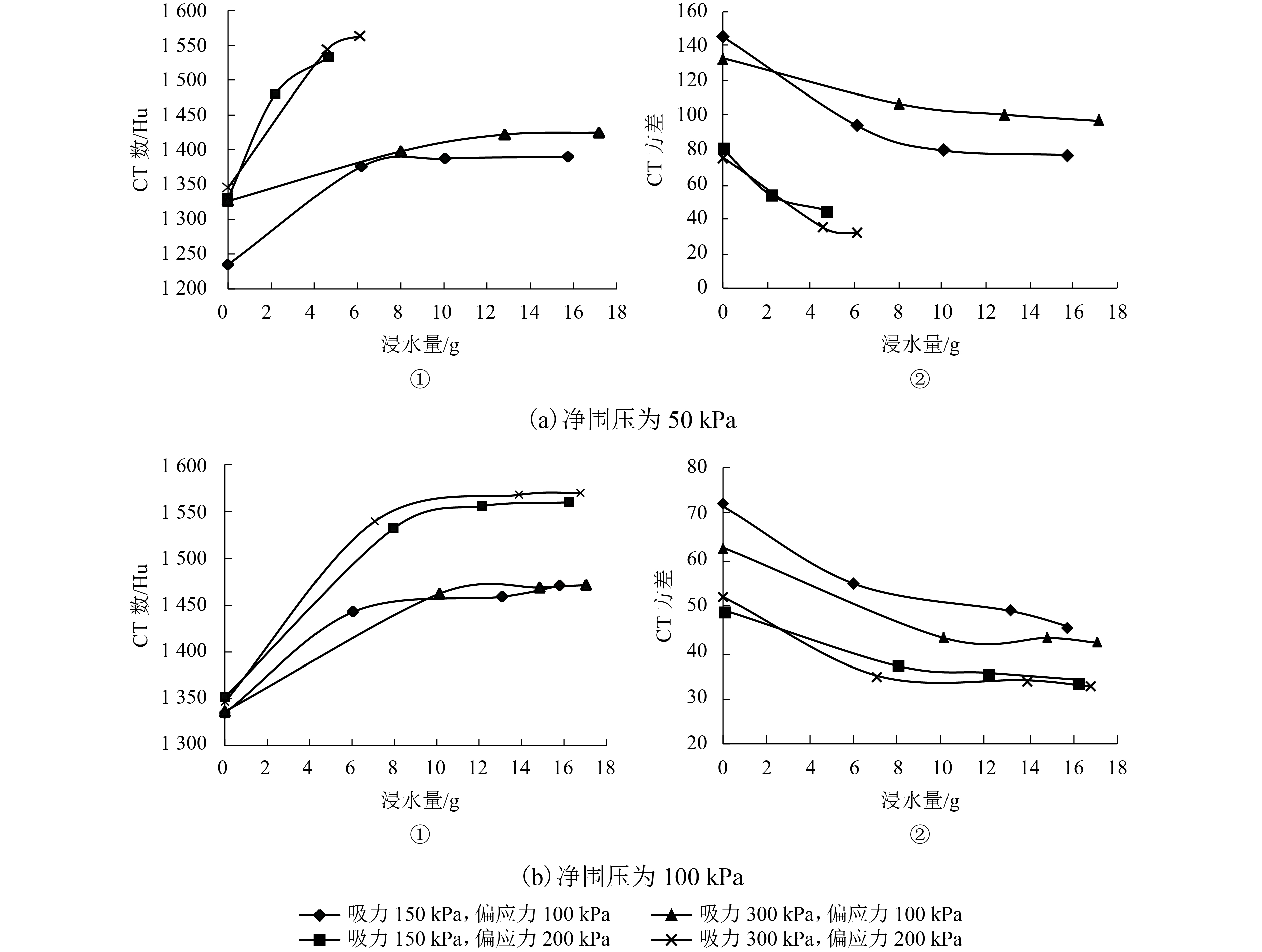
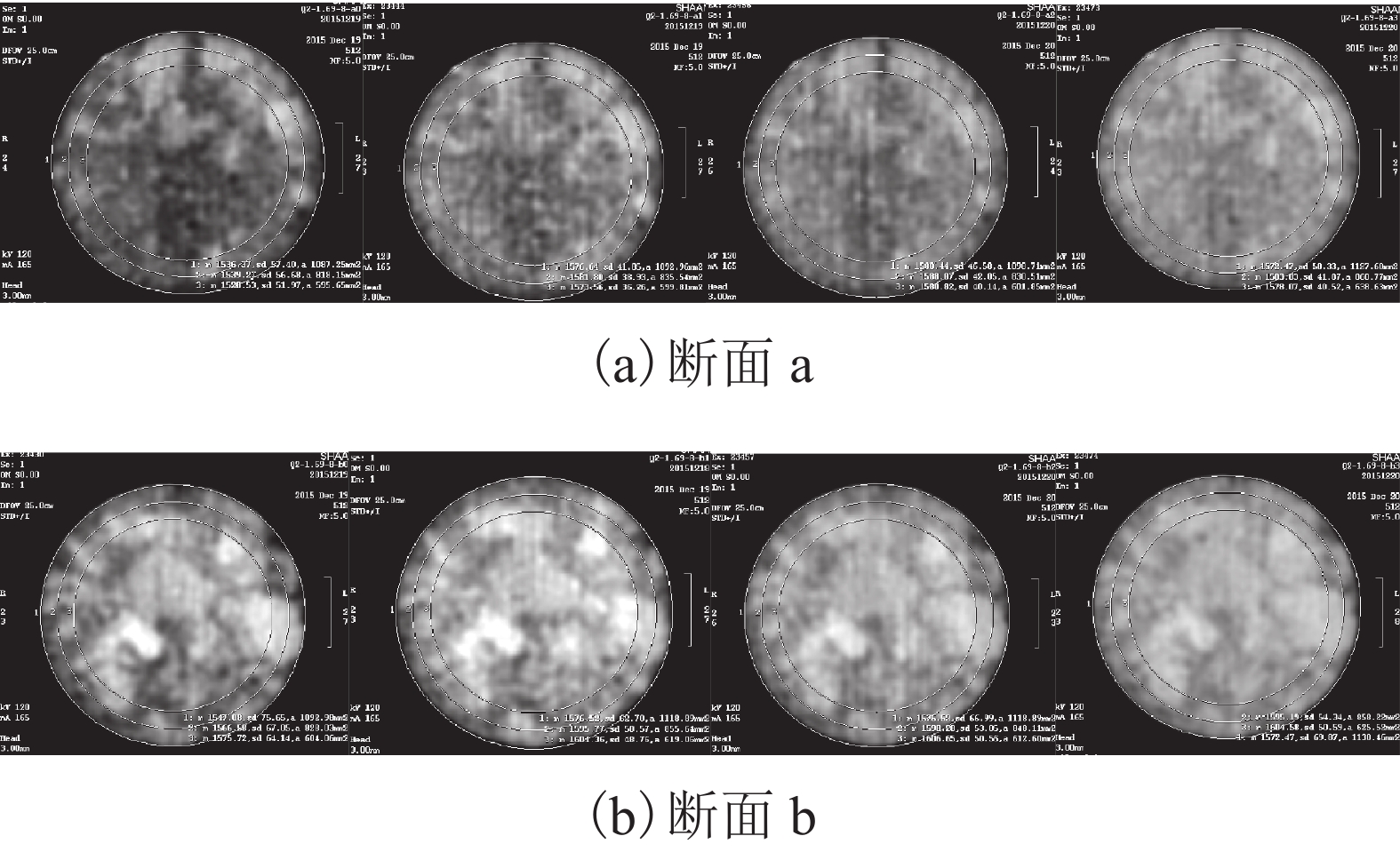
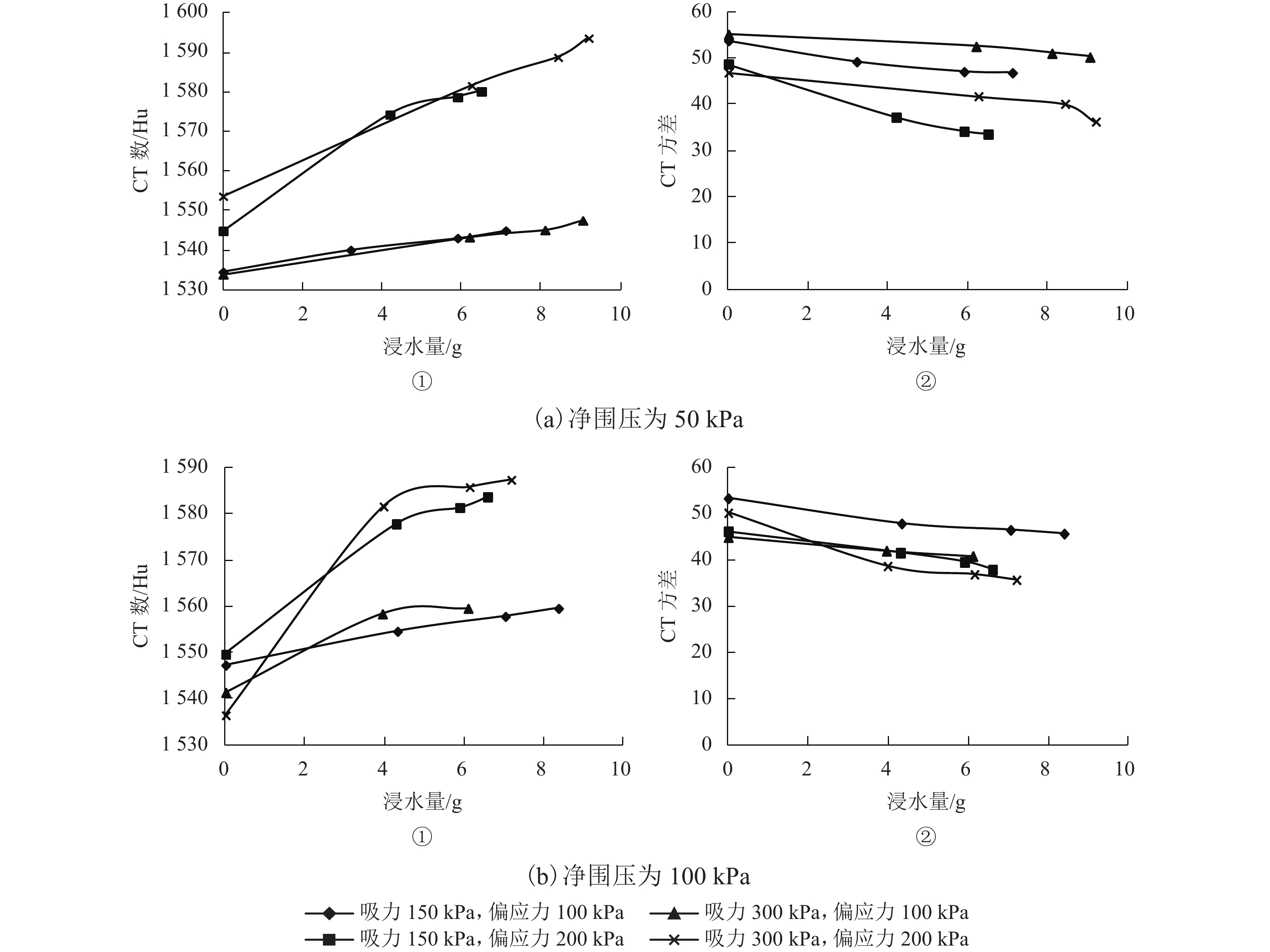
Research on Wetting-Deformation Regularity and Microstructure Evolution Characteristics of Remoulded Loess in Triaxial Soaking Tests
-
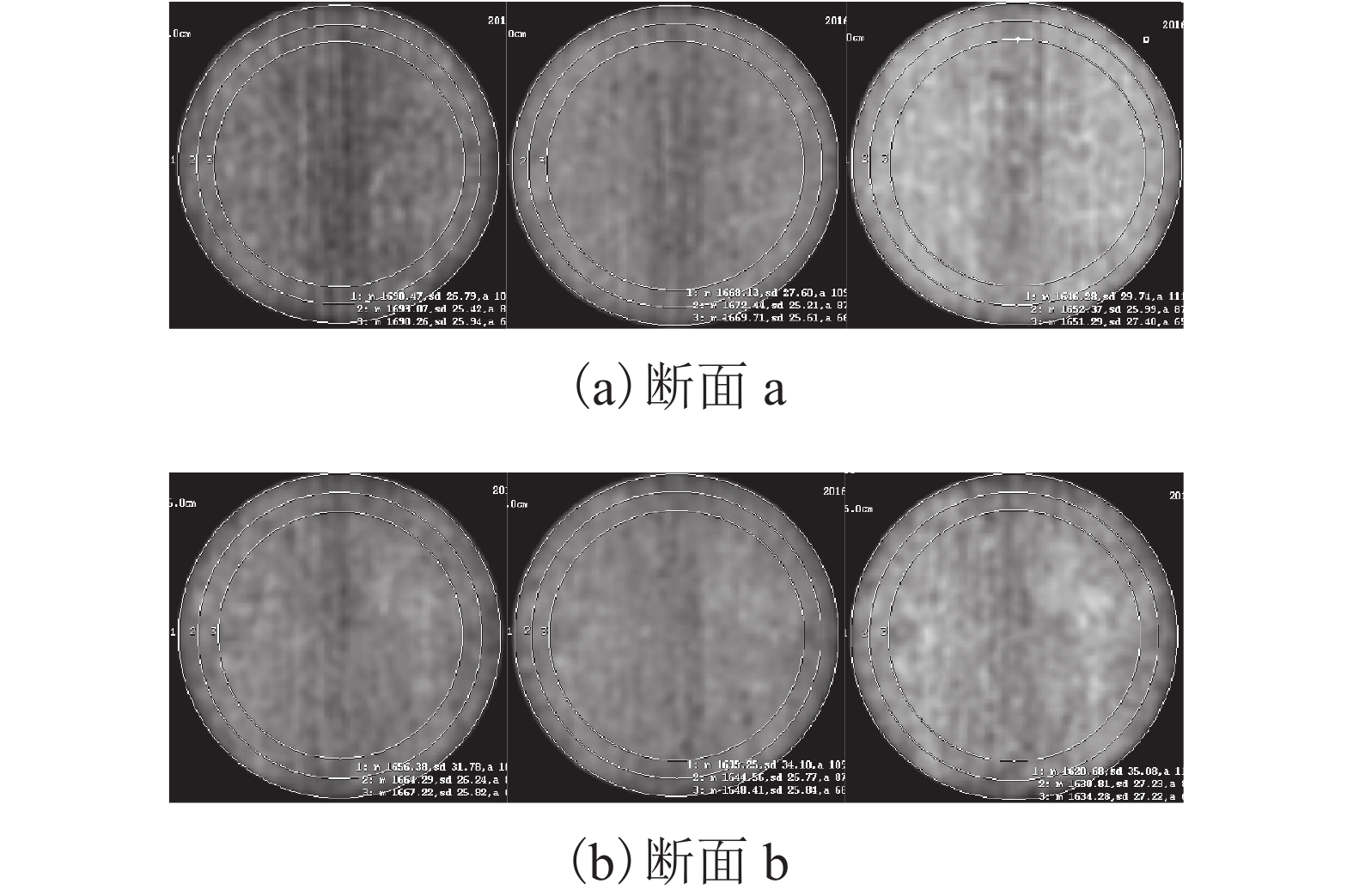
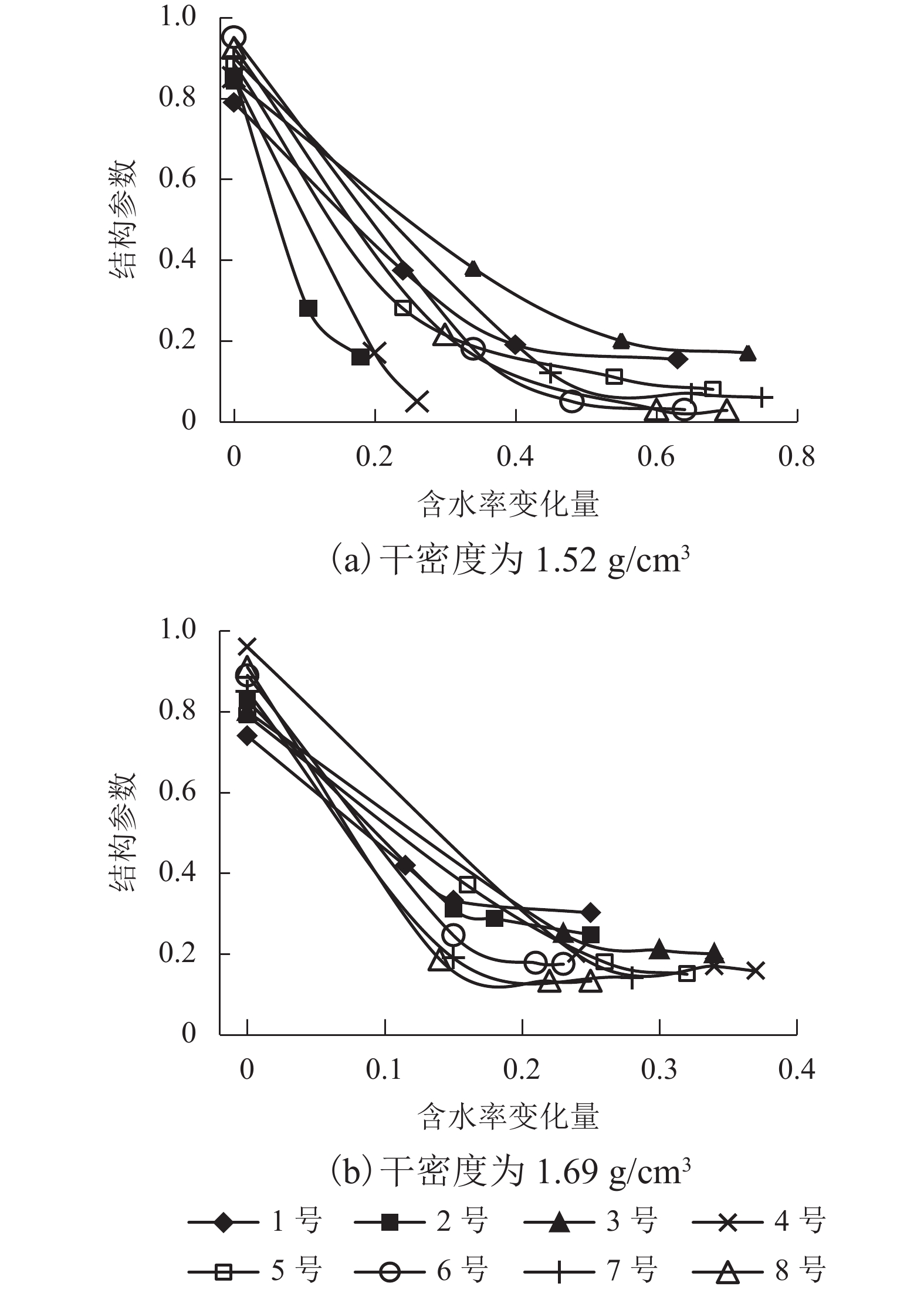
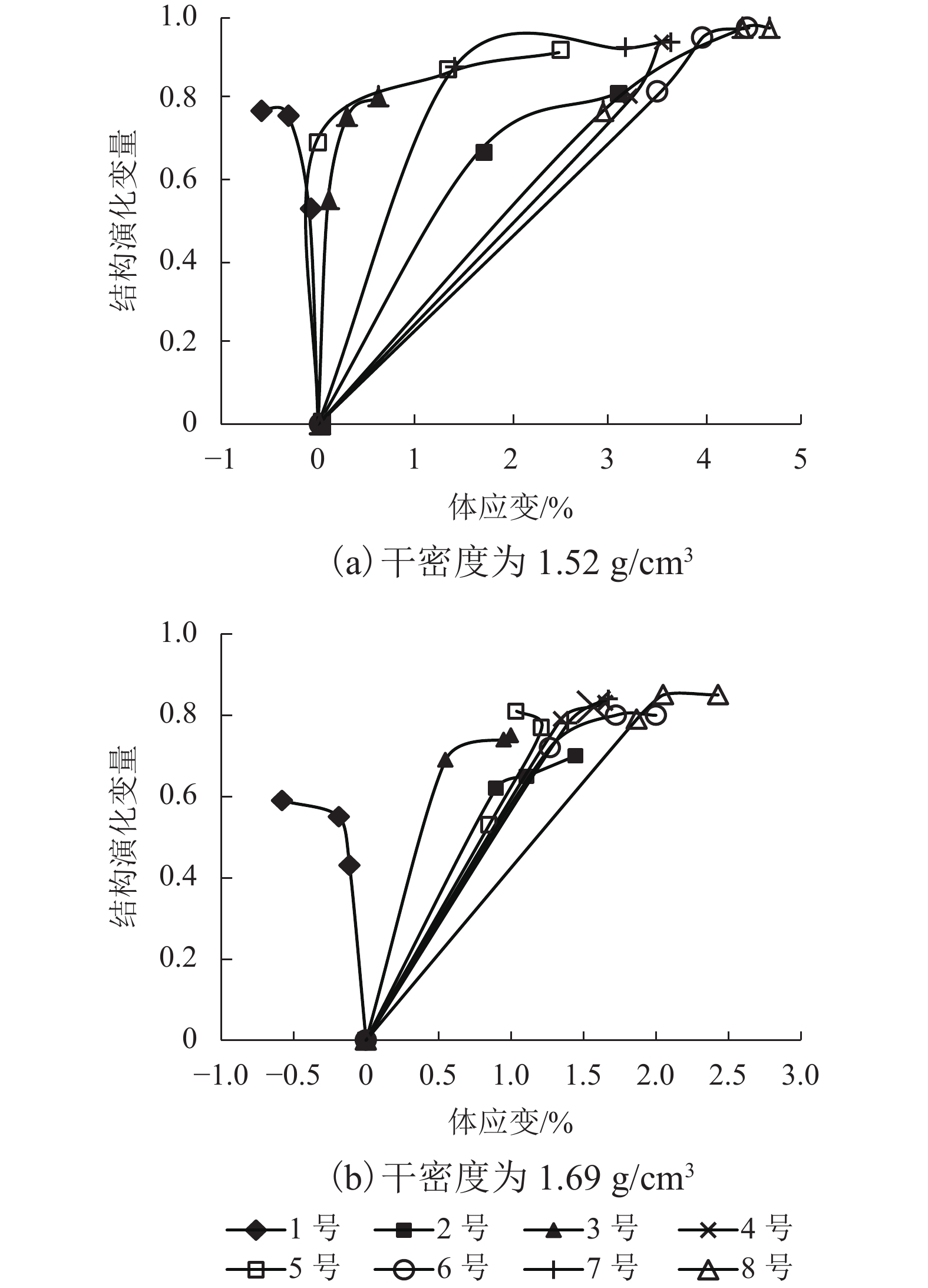
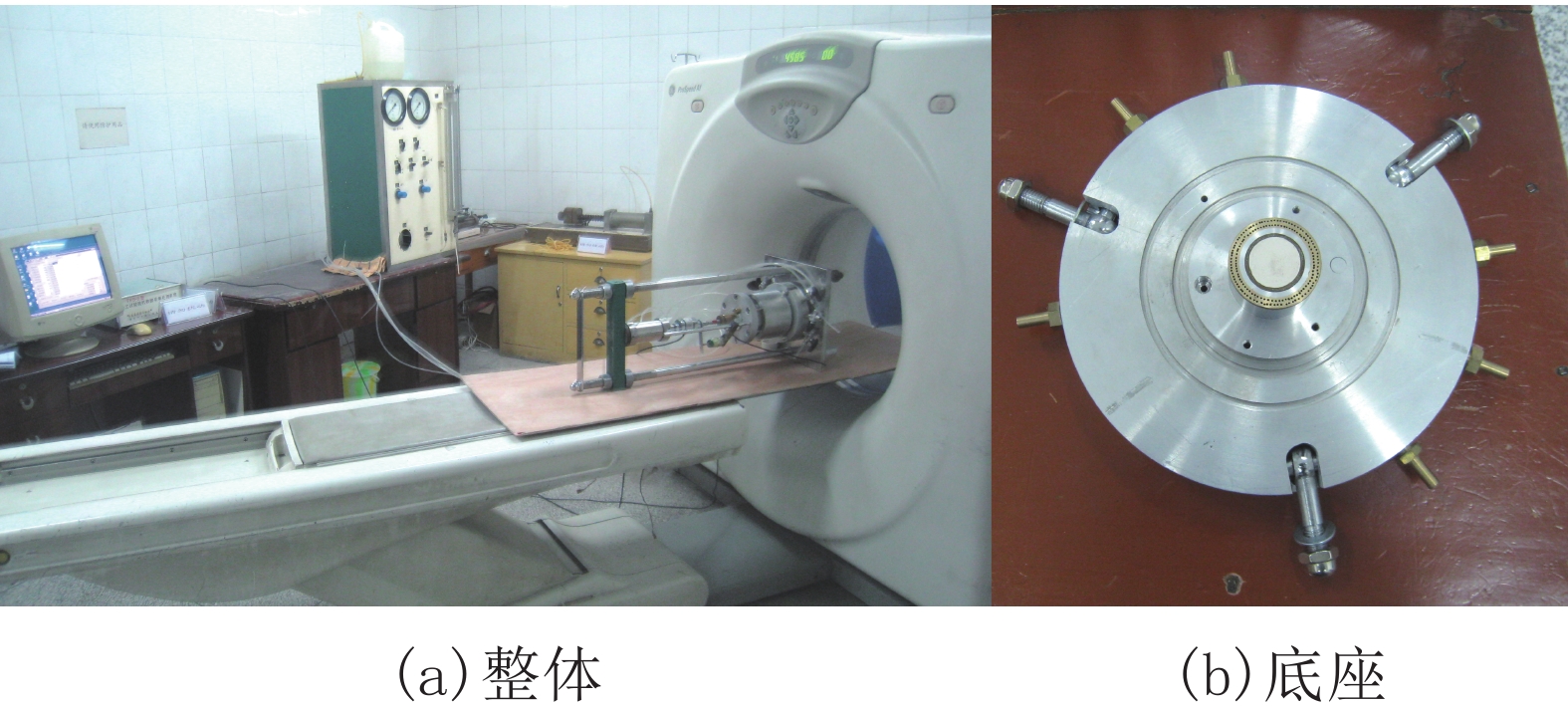
摘要: 为了研究填土在三轴浸水过程中的湿化变形规律及其细观结构演化特性,用改进的非饱和土CT-三轴仪对延安新区的重塑Q2黄土做了3组共17个偏压固结浸水试验. 在三轴浸水过程中对试样的两个断面进行了多次CT扫描,得到了固结和湿化过程中土样的宏观变形以及土样内部细观结构演化的CT图像和相应的CT数据,基于CT数定义了土的结构性参数和结构演化变量. 研究结果表明:干密度、净围压、基质吸力和偏应力均对试样的湿化变形特性有显著影响;提高干密度可有效减小湿化变形量和降低湿剪破坏的风险(干密度1.52、1.69 g/cm3的试样浸水过程中体应变分别为–0.58%~4.66%、–0.58%~2.43%,干密度1.79 g/cm3的试样体应变为0.019%);湿化过程中试样越来越密实,试样的CT数均增大;浸水初期,试样原有结构发生破坏,CT数变化较剧烈,均能达到总变化量的60%;同时干密度、净围压、基质吸力、偏应力及含水率对土的结构性参数和结构演化变量有显著影响. 研究成果对填土工程的设计具有重要参考价值,为建立非饱和重塑黄土的结构损伤演化方程与结构性模型提供了科学依据.Abstract: To explore the wetting-deformation regularity and microstructure evolution characteristics of filled soil, three groups, 17 samples, of immersed anisotropic consolidation tests of reshaped Q2 loess in the Yan’an new district were studied using the improved unsaturated soil triaxial apparatus with computed tomography (CT). The CT scanning was applied to the two sections of the samples in the triaxial soaking studies. The macroscopic deformations, soil samples’internal mesoscopic structure evolution CT images and the corresponding CT data were obtained in the consolidation and the wet process of the soil sample. Structural parameters and structural evolution variables of the soil were defined based on the CT data. The results show that the dry density, net confining pressure, matrix suction, and deviatoric stress have a significant influence on the wetting deformation characteristics. Increased dry density can effectively reduce the wetting deformations and the risk of wet shear failure. (The strains of the dry density specimen at 1.52 g/cm3 and 1.69 g/cm3 during immersion were –0.58% to 4.66% and –0.58% to 2.43%, respectively, and the strain of the dry density specimen of 1.79 g/cm 3 was 0.019%.)The CT data of all samples increased, indicating that the specimens become more and more compacted due to humidification deformation. In the early stage of immersion, the original structures of the soil samples were destroyed, and the change of CT data was more severe, reaching 60% of the total change. Meanwhile, the result is affected by the dry density, net confining pressure, suction, deviatoric stress, and moisture content. These results are valuable for the design of filled soil engineering and provide a scientific basis to establish the structure of the unsaturated remoulded loess damage evolution equation and the structural model.
-
表 1 扫描参数
Table 1. Scanning parameters
电压
/kV电流
/mA时间
/s层厚
/mm重建矩阵 空间分辨率
/mm120 165 3 3 512 × 512 0.38 表 2 土样的基本物理指标
Table 2. Physical parameters of soil samples
相对密度 ${d_{\rm{s}}}$ 塑限
${w_{\rm{p}}} $/%液限
${w_{\rm{L}}} $/%最大干密度
${\rho _{_{\rm{d}\max} }}$/(g•cm–3)最优含水率 ${w_{{\rm{op}}}} $/% 2.71 17.3 31.1 1.92 12.9 表 3 试验研究方案
Table 3. Experimental programs
试验分
组编号干密度ρd/(g•cm–3) 试样 净围压/kPa 基质吸力/kPa 偏应力/kPa Ⅰ 1.52 1号 50 150 100 2号 50 150 200 3号 50 300 100 4号 50 300 200 5号 100 150 100 6号 100 150 200 7号 100 300 100 8号 100 300 200 Ⅱ 1.69 9号 50 150 100 10号 50 150 200 11号 50 300 100 12号 50 300 200 13号 100 150 100 14号 100 150 200 15号 100 300 100 16号 100 300 200 Ⅲ 1.79 17号 100 300 100 表 4 干密度为1.52 g/cm3的试样在试验过程中的参数
Table 4. Control conditions of test sample with
$\rho_{\rm d}$ = 1.52 g/cm3试样 固结过程 浸水过程 轴向应变 饱和度 轴向应变 饱和度 体应变 1号 0.19 59.3 0.08 97.7 –0.58 2号 1.22 60.1 11.80 71.1 3.08 3号 0.26 55.5 0.73 96.2 0.64 4号 3.38 54.3 10.92 68.8 3.30 5号 0.25 57.9 0.51 97.2 2.49 6号 0.62 59.6 4.99 97.9 4.45 7号 0.49 53.8 1.63 94.1 3.62 8号 1.31 57.0 23.30 96.6 4.66 表 5 干密度为1.69 g/cm3的试样在试验过程中的参数
Table 5. Control conditions of test sample with
$\rho_{\rm d} $ = 1.69 g/cm3试样 固结过程 浸水过程 轴向应变 饱和度 轴向应变 饱和度 体应变 9号 0.19 78.9 0.03 98.6 –0.58 10号 0.24 79.6 21.87 99.2 1.8 11号 0.14 74.4 0.08 99.2 1.18 12号 0.89 68.5 0.88 93.3 1.65 13号 0.13 72.3 0.05 96.6 1.04 14号 0.16 79.5 0.09 97.7 1.78 15号 0.20 78.3 0.05 95.4 1.67 16号 0.53 79.0 0.10 98.5 2.43 -
中国民航机场建设集团公司空军工程设计研究局. 延安新区一期综合开发工程地基处理与土石方工程设计[R]. 北京: 空军工程设计研究局, 2012 兰州理工大学. 低丘缓坡未利用地开发技术规程: DB62/T25–3108—2016[S]. 兰州: 甘肃建筑标准图发行站, 2016 朱才辉,李 宁,刘明振,等. 吕梁机场黄土高填方地基工后沉降时空规律分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(2): 293-301ZHU Caihui, LI Ning, LIU Mingzhen, et al. Spatiotemporal laws of post-construction settlement of loess-filled foundation of Lüliang airport[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(2): 293-301 程海涛,刘保健,谢永利. 重塑黄土变形特性[J]. 长安大学学报 (自然科学版),2008,28(5): 31-34CHENG Haitao, LIU Baojian, XIE Yongli. Deformation characteristics of remolded loess[J]. Journal of Chang’an University (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 28(5): 31-34 关 亮,陈正汉,黄雪峰,等. 非饱和填土(黄土)的湿化变形研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2011,30(8): 1698-1704GUAN Liang, CHEN Zhenghan, HUANG Xuefeng, et al. Study of wetting deformation of unsaturated remolded loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(8): 1698-1704 梅源. 湿陷性黄土高填方地基处理技术及稳定性试验研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2013 沈珠江. 土体结构性的数学模型——21世纪土力学的核心问题[J]. 岩土工程学报,1996,18(1): 95-97 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1996.01.015SHEN Zhujiang. Mathematical model of the core issues of the 21st century soil structural soil mechanics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1996, 18(1): 95-97 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1996.01.015 任建喜,葛修润,杨更社. 单轴压缩岩石损伤扩展细观机理CT实时试验[J]. 岩土力学,2001,22(2): 130-133 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2001.02.003REN Jianxi, GE Xiurun, YANG Gengshe. CT Real-time testing on damage propagation microscopic mechanism of rock under uniaxial compression[J]. Rock and Soil mechanics, 2001, 22(2): 130-133 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2001.02.003 陈正汉. 非饱和土与特殊土力学的基本理论研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(2): 201-272CHEN Zhenghan. On basic theories of unsaturated soils and special soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(2): 201-272 陈正汉,卢再华,蒲毅彬. 非饱和土三轴仪的CT机配套及其应用[J]. 岩土工程学报,2001,23(4): 387-392 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.04.001CHEN Zhenghan, LU Zaihua, PU Yibin. The matching of computerized tomograph with triaxial test apparatus for unsaturated soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2001, 23(4): 387-392 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.04.001 朱元青,陈正汉. 原状Q3黄土在加载和湿陷过程中细观结构动态演化的CT-三轴试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2009,31(8): 1219-1228 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.08.011ZHU Yuanqing, CHEN Zhenghan. Experimental study on dynamic evolution of meso-structure of intact Q3 loess during loading and collapse using CT and triaxial apparatus[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 31(8): 1219-1228 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.08.011 方祥位,申春妮,陈正汉,等. 原状Q2黄土CT-三轴浸水试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2011,44(10): 98-106FANG Xiangwei, SHEN Chunni, CHEN Zhenghan, et al. Triaxial wetting tests of intact Q2 loess by computed tomography[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2011, 44(10): 98-106 朱宝龙,巫锡勇,李晓宁,等. 合肥地区重塑黏性土细观结构演化三轴CT试验[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(1): 144-149ZHU Baolong, WU Xiyong, LI Xiaoning, et al. Triaxial CT Tests of meso-structure evolution of remodeled cohesive soil in Hefei[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(1): 144-149 雷胜友,唐文栋. 黄土在受力和湿陷过程中微结构变化的CT扫描分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(24): 4166-4167 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.24.013LEI Shengyou, TANG Wendong. Analysis of microstructure change for loess in the process of loading and collapse with CT scanning[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(24): 4166-4167 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.24.013 罗爱忠,邵生俊. 湿载耦合作用下黄土结构性损伤演化及本构关系[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(4): 841-847LUO Aizhong, SHAO Shengjun. Structural damage evolution and constitutive relation of loess under coupling of stress and moisture[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(4): 841-847 谢定义. 试论我国黄土力学研究中的若干新趋向[J]. 岩土工程学报,2001,23(1): 3-13 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.01.002XIE Dingyi. Exploration of some new tendencies in research of loess soil mechanics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2001, 23(1): 3-13 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.01.002 李晓军,张登良. 路基填土单轴受压细观结构CT监测分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2000,22(2): 205-209 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2000.02.012LI Xiaojun, ZHANG Dengliang. Monitoring change of structure of road foundation soil in uniaxial compression test with CT[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2000, 22(2): 205-209 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2000.02.012 -




 下载:
下载: