Failure and Parametric Analysis of Shield Tunnel Bolts under Impact Load
-
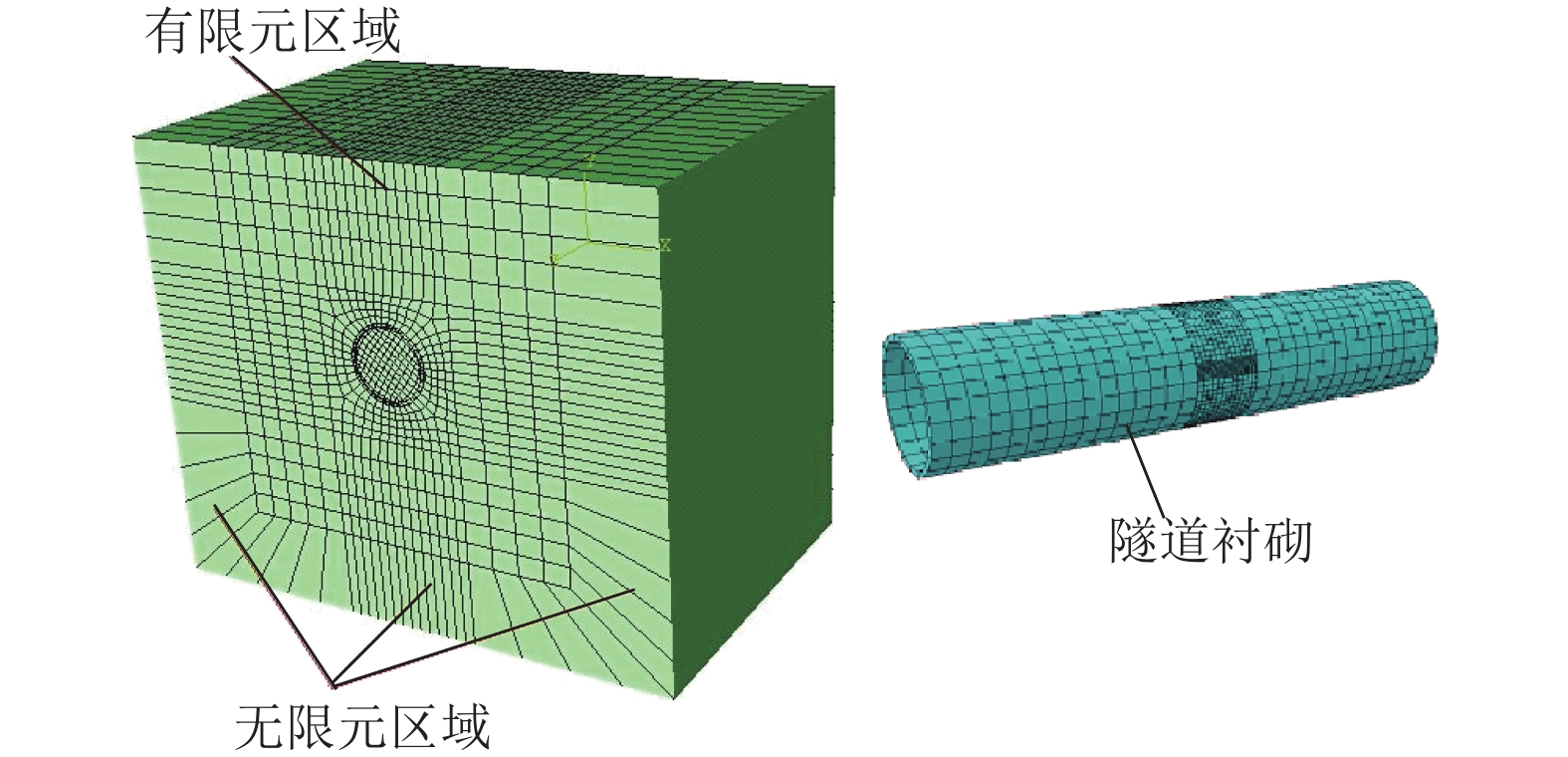
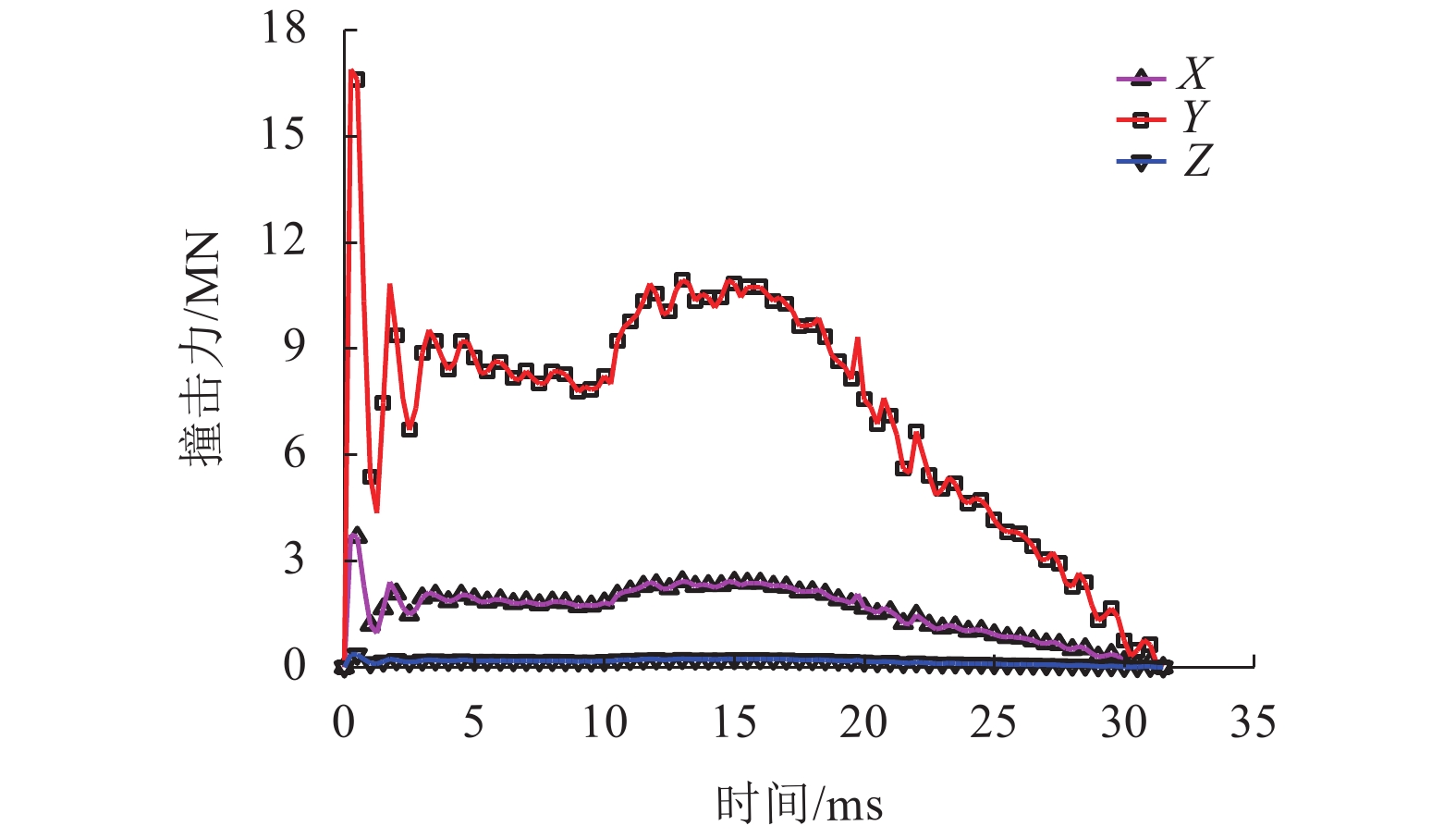
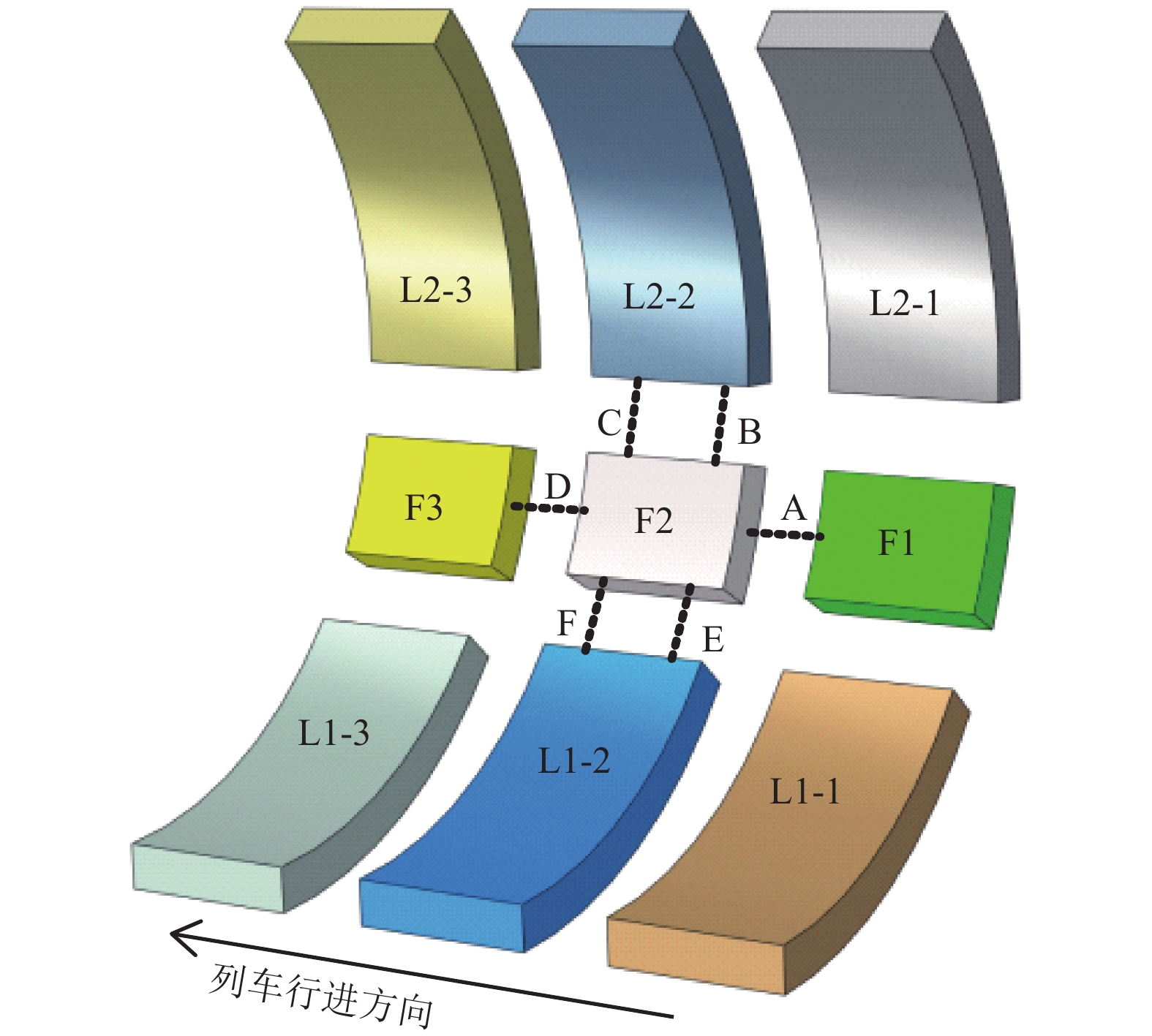
摘要: 为了研究高速列车脱轨撞击盾构隧道时接头螺栓参数对螺栓失效和管片的影响. 基于ABAQUS有限元软件,建立了盾构隧道管片衬砌分块拼装式模型,利用时速200 km/h列车12.5° 斜向撞击荷载曲线,通过设置接触面单元和具有抗拉、抗剪、抗弯3种刚度组合的连接单元,近似模拟了盾构隧道接缝混凝土接触效应和螺栓连接效应,开展了不同螺栓直径和不同螺栓强度级别下管片接头螺栓的失效研究. 研究结果表明:在列车撞击荷载作用下,接头螺栓主要发生拉伸失效和剪切失效两种失效状态,失效后螺栓拉力和剪力降低为0,并且螺栓失效一般是相对列车行进方向相继出现的;拉伸失效通常出现在被撞块后端纵向螺栓,而被撞块环向螺栓和前端纵向螺栓一般发生剪切失效;各螺栓发生失效的时间随着接头螺栓强度级别的提高或螺栓直径的增大有所延后;不同螺栓参数下被撞块管片位移极大值均在6 cm左右,提高接头螺栓的强度级别和增大螺栓直径,将减小被撞块管片最终位移较大值区域面积以及最终位移极大值的数值,但管片最终位移极大值数值的减幅在10%以内,说明改变螺栓参数无法明显减小管片最终位移.Abstract: In order to study the influence of bolt parameters on bolt failures and segments when a derailed high-speed train impacts a shield tunnel, a numerical model of division assembling the segmental lining of a shield tunnel was established using the finite element software ABAQUS. The contact effect of joint concrete and the connecting effect of joint bolts were simulated approximately by the contact element and the connector element, the latter of which characterises the tensile, shear and flexural stiffness. The failure of bolts with different diameters and strengths was investigated using the impact load curve of a train with speed of 200 km/h and oblique angle of 12.5°. The results show that joint bolts mainly underwent tensile failure and shear failure, and the tension and shear forces of the bolt decreased to zero after the failure. Bolt failures generally appeared in succession according to the direction of train travel. Tensile failure usually occurred at the rear longitudinal bolt of the impacted segment, while shear failure usually occurred at the circumferential bolt and the front longitudinal bolt of the impacted segment. The failure time of the bolt was delayed as the bolt strength grade or diameter increased. The maximum displacement of the impacted segments under different bolt parameters was approximately 6 cm. Increasing the strength grade and the diameter of the bolt would reduce the area and the maximum value of the final displacement of the impacted segment. However, the reduction of the maximum value of the final displacement was within 10%, which means that changing the parameters of the bolt cannot significantly reduce the final displacement of the segment.
-
Key words:
- shield tunnel /
- train collision /
- parametric analysis /
- numerical simulation /
- bolt failure
-
表 1 基本材料参数
Table 1. Basic material parameters
材料名称 密度/(kg•m–3) 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 摩擦角/(°) 内聚力/MPa 粉砂岩 2 460 19.5 0.205 38 3.75 砂岩 2 580 25.0 0.159 42 2.50 衬砌
混凝土2 400 34.5 0.200 表 2 分析工况及相应螺栓物理力学参数
Table 2. Analysis conditions and physical and mechanical parameters of corresponding bolts
分析
工况型号 直径/mm 强度
级别弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 抗拉刚
度/MN抗剪刚
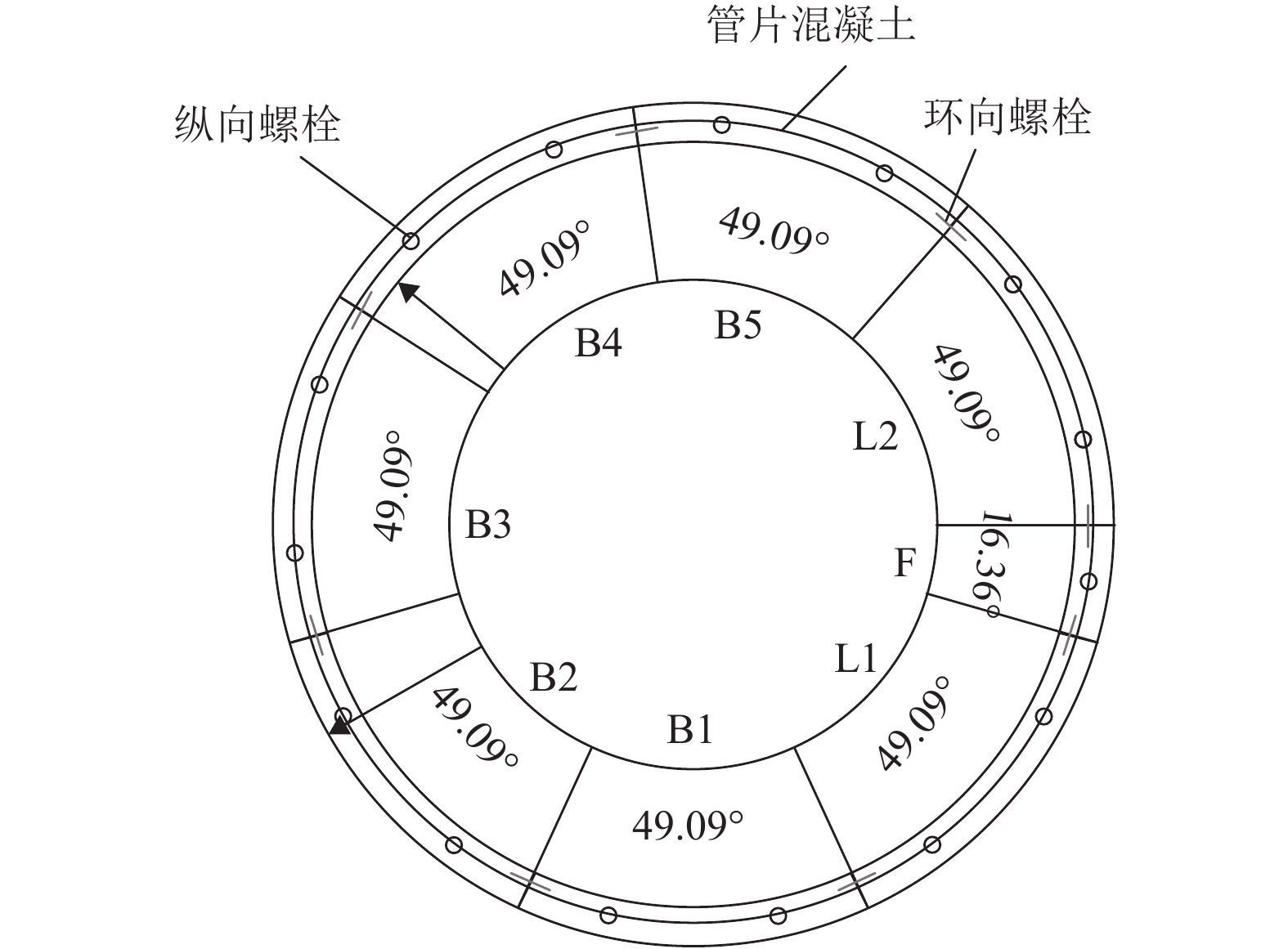
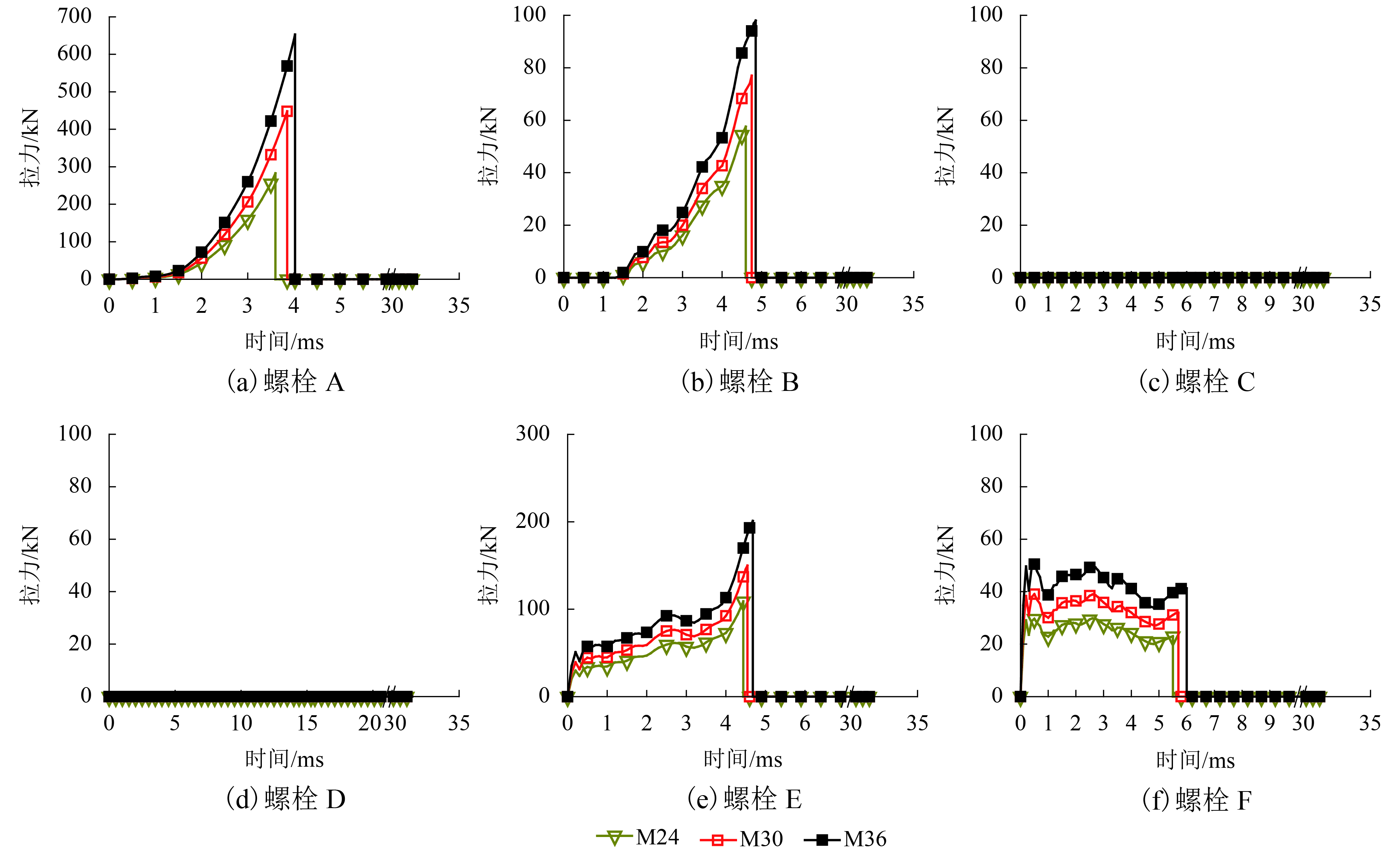
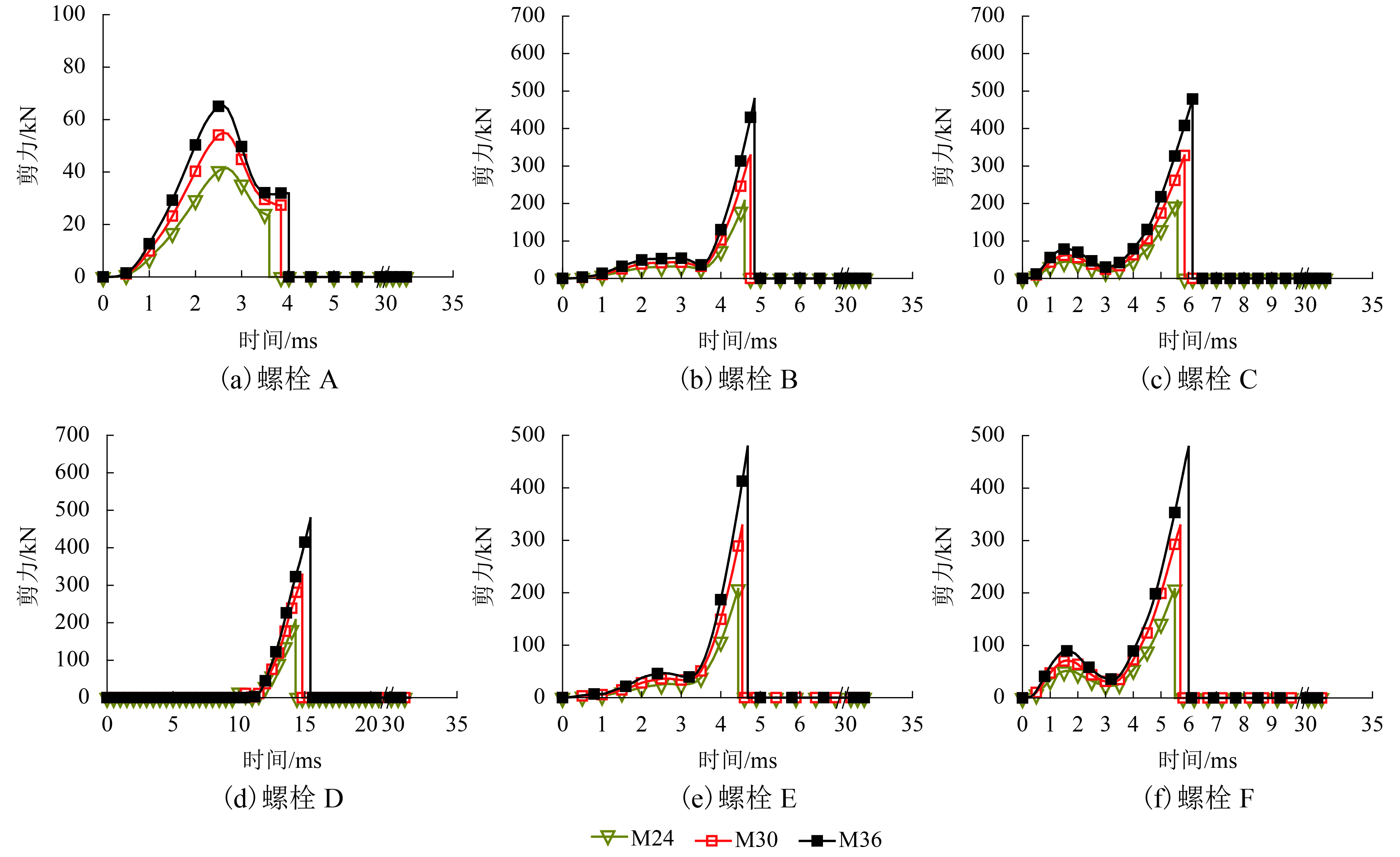
度/MN抗弯刚度/(N•m2) 截面积/mm2 抗拉极限强度/MPa 抗剪极限强度/MPa 极限拉力/kN 极限剪力/kN 1 M24 24.0 8.8 206.0 0.3 72.7 28.0 3 353.2 353.0 800.0 586.4 282.4 207.0 2 M30 30.0 8.8 206.0 0.3 115.4 44.4 8 186.6 560.0 800.0 586.4 448.0 328.4 3 M36 36.0 8.8 206.0 0.3 168.1 64.7 16 975.7 816.0 800.0 586.4 652.8 478.5 4 M36 36.0 6.8 206.0 0.3 168.1 64.7 16 975.7 816.0 600.0 439.8 489.6 358.9 5 M36 36.0 5.6 206.0 0.3 168.1 64.7 16 975.7 816.0 500.0 336.5 408.0 299.1 表 3 8.8级螺栓在不同直径下的失效情况
Table 3. Failure conditions for 8.8-grade bolts with different diameters
螺栓编号 失效类型 失效时间/ms 失效次序 M24 M30 M36 M24 M30 M36 M24 M30 M36 A 拉伸 拉伸 拉伸 3.59 3.85 4.02 1 1 1 B 剪切 剪切 剪切 4.60 4.75 4.85 3 3 3 C 剪切 剪切 剪切 5.60 5.84 6.14 5 5 5 D 剪切 剪切 剪切 14.28 14.8 15.45 6 6 6 E 剪切 剪切 剪切 4.42 4.53 4.68 2 2 2 F 剪切 剪切 剪切 5.49 5.71 6.01 4 4 4 表 4 M36螺栓在不同强度级别下的失效情况
Table 4. Failure conditions for M36 bolts with different strength grades
螺栓编号 失效类型 失效时间/ms 失效次序 5.6级 6.8级 8.8级 5.6级 6.8级 8.8级 5.6级 6.8级 8.8级 A 拉伸 拉伸 拉伸 3.46 3.67 4.02 1 1 1 B 剪切 剪切 剪切 4.47 4.61 4.85 3 3 3 C 剪切 剪切 剪切 5.36 5.63 6.14 5 5 5 D 剪切 剪切 剪切 13.96 14.48 15.45 6 6 6 E 剪切 剪切 剪切 4.29 4.43 4.68 2 2 2 F 剪切 剪切 剪切 5.27 5.51 6.01 4 4 4 表 5 不同螺栓参数下管片最终位移极大值及变化率
Table 5. Maximum value and change rate of final displacement of the segment under different bolt parameters
项目 强度级别 直径型号 5.6级 6.8级 8.8级 M24 M30 M36 位移极值/cm 6.86 6.61 6.21 6.79 6.43 6.21 相对变化率/% 0 –3.6 –9.5 0 –5.3 –8.5 -
叶飞,朱合华,丁文其. 基于螺栓接头受力性能的盾尾注浆压力控制[J]. 同济大学学报 (自然科学版),2009,37(3): 312-316YE Fei, ZHU Hehua, DING Wenqi. Pressure control analysis based on mechanical properties of bolts during grouting at shield tail[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2009, 37(3): 312-316 LI Z, SOGA K, WANG F, et al. Behaviour of cast-iron tunnel segmental joint from the 3D FE analyses and development of a new bolt-spring model[J]. Tunneling and Underground Space Technology, 2014, 41: 176-192 doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2013.12.012 WANG L Z, WANG Z, LI L L, et al. Construction behavior simulation of a hydraulic tunnel during standpipe lifting[J]. Tunneling and Underground Space Technology, 2011, 26: 675-685 卢岱岳,徐国文,王士民. 加卸载对盾构隧道材料损伤和结构特性的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(6): 1104-1112LU Daiyue, XU Guowen, WANG Shimin. Effects of material damage and structural characteristics on tunnel shield during loading and unloading[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(6): 1104-1112 田红旗. 客运列车耐冲击吸能车体设计方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2001,1(1): 110-114TIAN Hongqi. Crashworthy energy absorbing car-body design method for passenger train[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2001, 1(1): 110-114 谢素超,田红旗,姚松. 车辆吸能部件的碰撞实验与数值仿真[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2008,8(3): 1-5XIE Suchao, TIAN Hongqi, YAO Song. Impacting experiment and numerical simulation of energy-absorbing component of vehicles[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2008, 8(3): 1-5 高广军,田红旗,姚松,等. 列车多体耦合撞击分析[J]. 中国铁道科学,2005,26(4): 93-97GAO Guangjun, TIAN Hongqi, YAO Song, et al. Multi-car coupling collision analysis[J]. China Railway Science, 2005, 26(4): 93-97 肖守讷,张志新,阳光武,等. 列车碰撞仿真中钩缓装置模拟方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(5): 831-836XIAO Shouna, ZHANG Zhixin, YANG Guangwu, et al. Simulation method for couplers and buffers in train collision calculations[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(5): 831-836 丁叁叁,李强,卢毓江,等. 防爬吸能装置的碰撞动力学性能[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(4): 732-739DING Sansan, LI Qiang, LU Yujiang, et al. Dynamic performance of anti-climber device for trains in crash[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(4): 732-739 赵雅娜, 刘艳辉, 赵世春. 高速脱轨列车作用下铁路客站结构反应分析[J]. 建筑结构, 2012, 42(增刊1): 242-245ZHAO Yana, LIU Yanhui, ZHAO Shichun. Reactions of railway-station under the impact of derailed high-speed train[J]. Building Structure, 2012, 42(S1): 242-245 谢素明,兆文忠,闫雪冬. 高速车辆大变形碰撞仿真基本原理及应用研究[J]. 铁道车辆,2001,39(8): 1-4XIE Suming, ZHAO Wenzhong, YAN Xuedong. Fundamental principles and application research on simulation of collision with large deformation of high speed cars[J]. Rolling Stock, 2001, 39(8): 1-4 陈秉智, 张向海, 马纪军等. 高速动车组被动安全性和耐撞性研究[J]. 计算力学学报, 2011, 28(增刊1): 152-158CHENU Bingzhi, ZHANG Xianghai, MA Jijun, et al. High-speed EMUs passive safety and crashworthiness study[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2011, 28(S1): 152-158 晏启祥,李彬,张蒙,等. 列车撞击荷载的有限元数值分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(1): 1-7YAN Qixiang, LI Bin, ZHANG Meng, et al. Numerical analysis of train impact load with finite element method[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(1): 1-7 艾辉军,彭立敏,施成华. 基于三维非连续接触模型的管片接头静动力特性分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(11): 2023-2029AI Huijun, PENG Limin, SHI Chenghua. Static and dynamic characteristic analysis of segment joints based on three-dimensional discontinuous contact model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(11): 2023-2029 李宇杰,何平,秦东平. 盾构隧道管片纵缝错台的影响分析[J]. 工程力学,2012,29(11): 277-282LI Yujie, HE Ping, QIN Dongping. Influence analysis on longitudinal dislocation for shield tunnel segment[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 29(11): 277-282 Working Group on General Approaches to the Design of Tunnels. Guidelines for the design of the shield tunnel lining[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2000(3): 303-331 -




 下载:
下载: