Experimental Study of Stick-Slip Behaviour of Dry Granular Materials
-
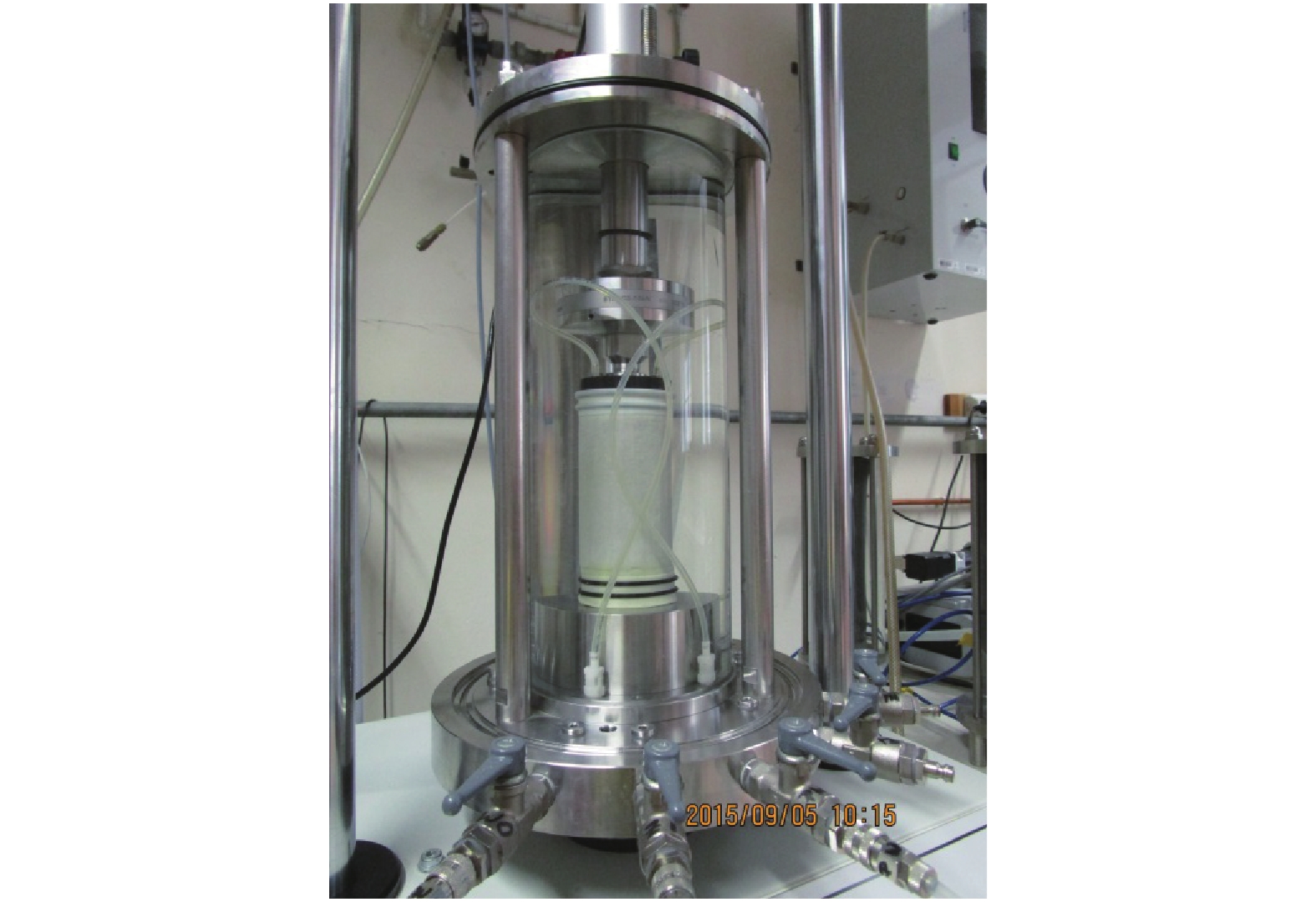
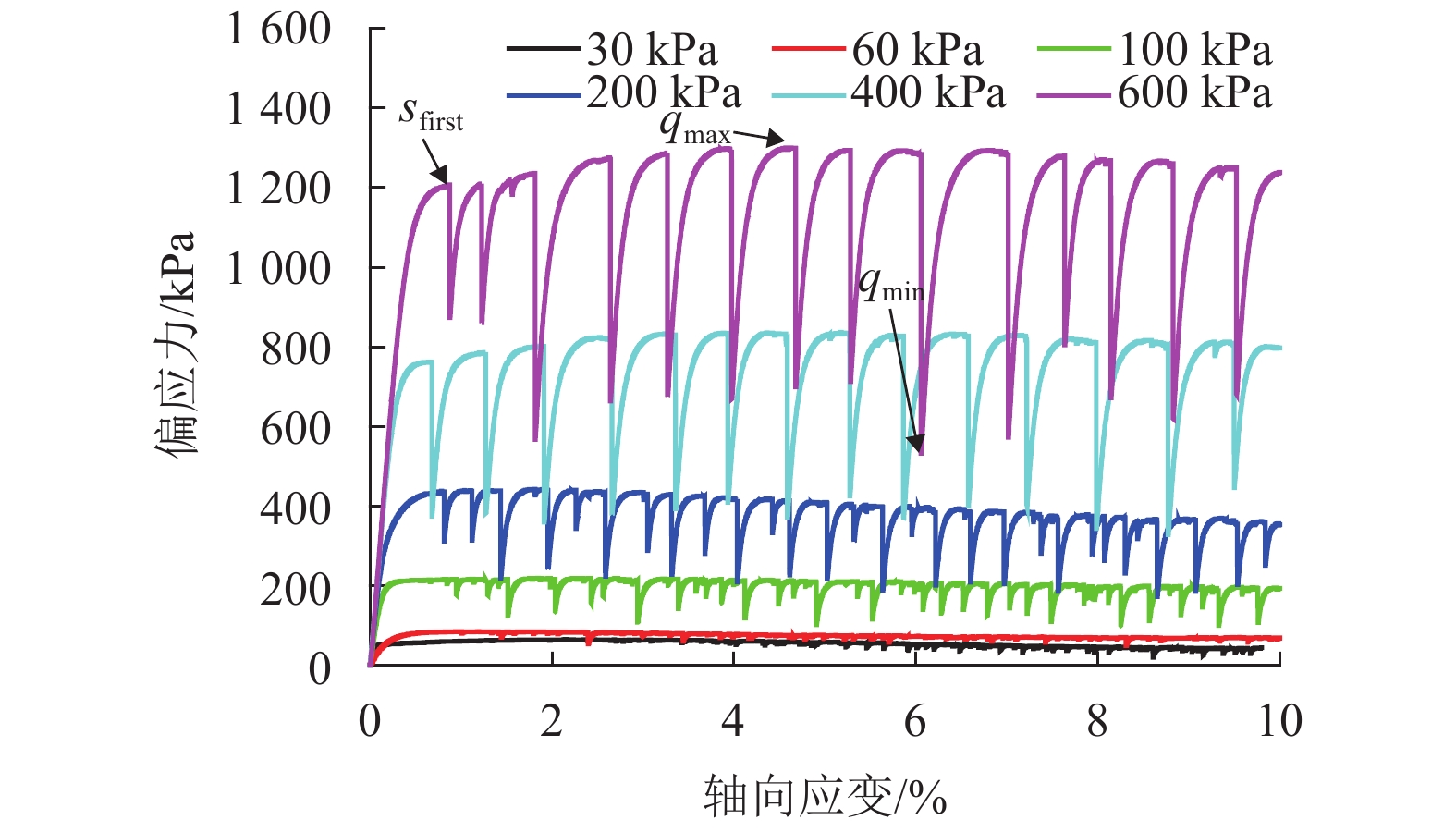
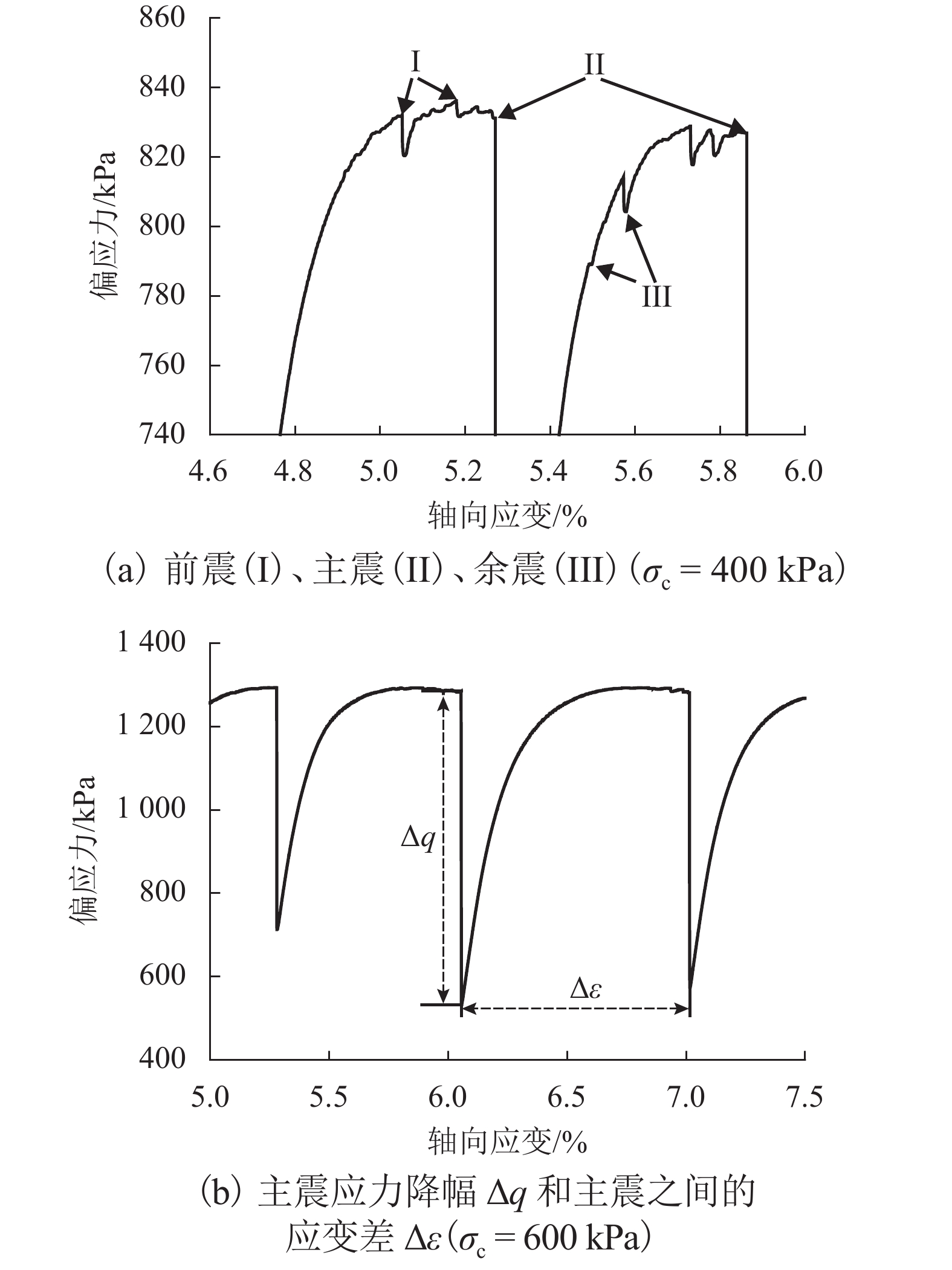
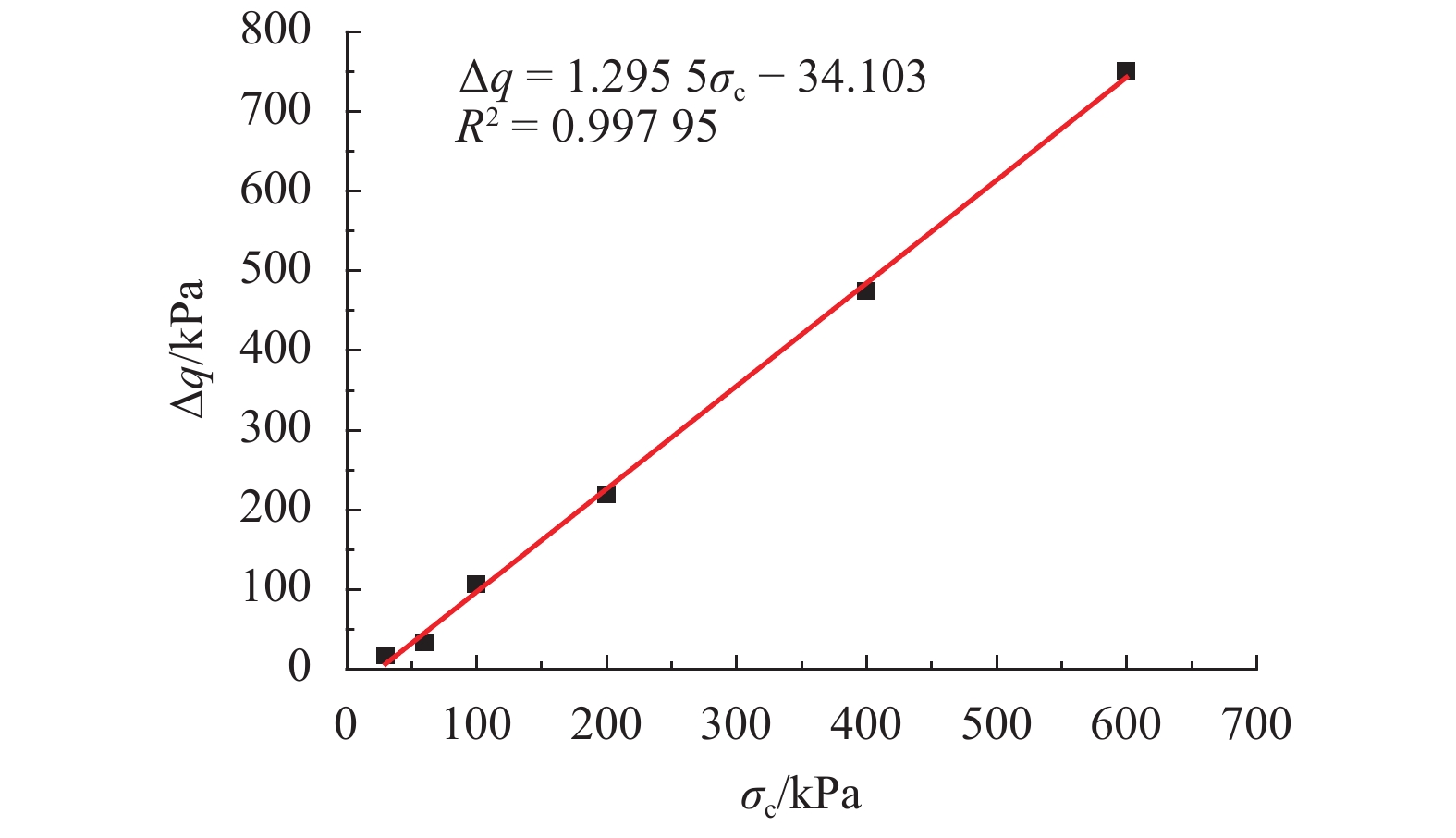
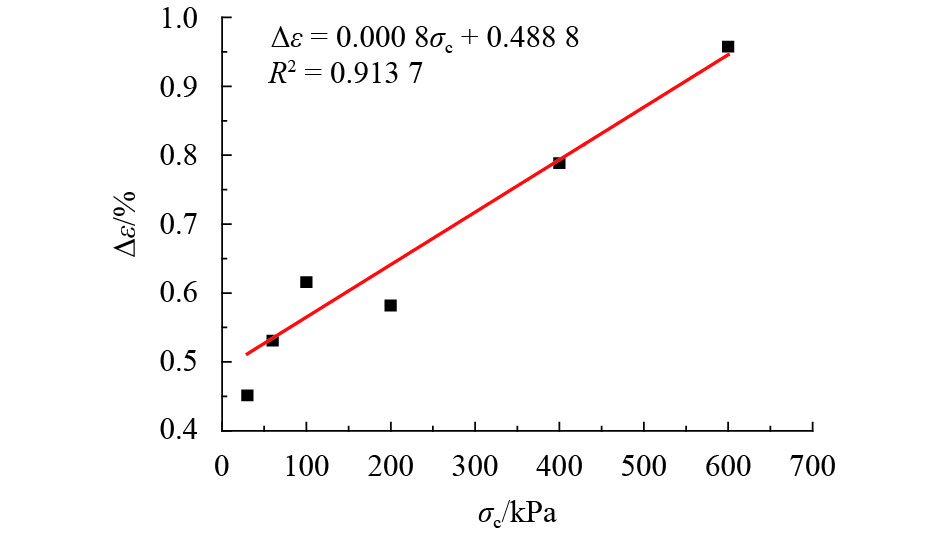
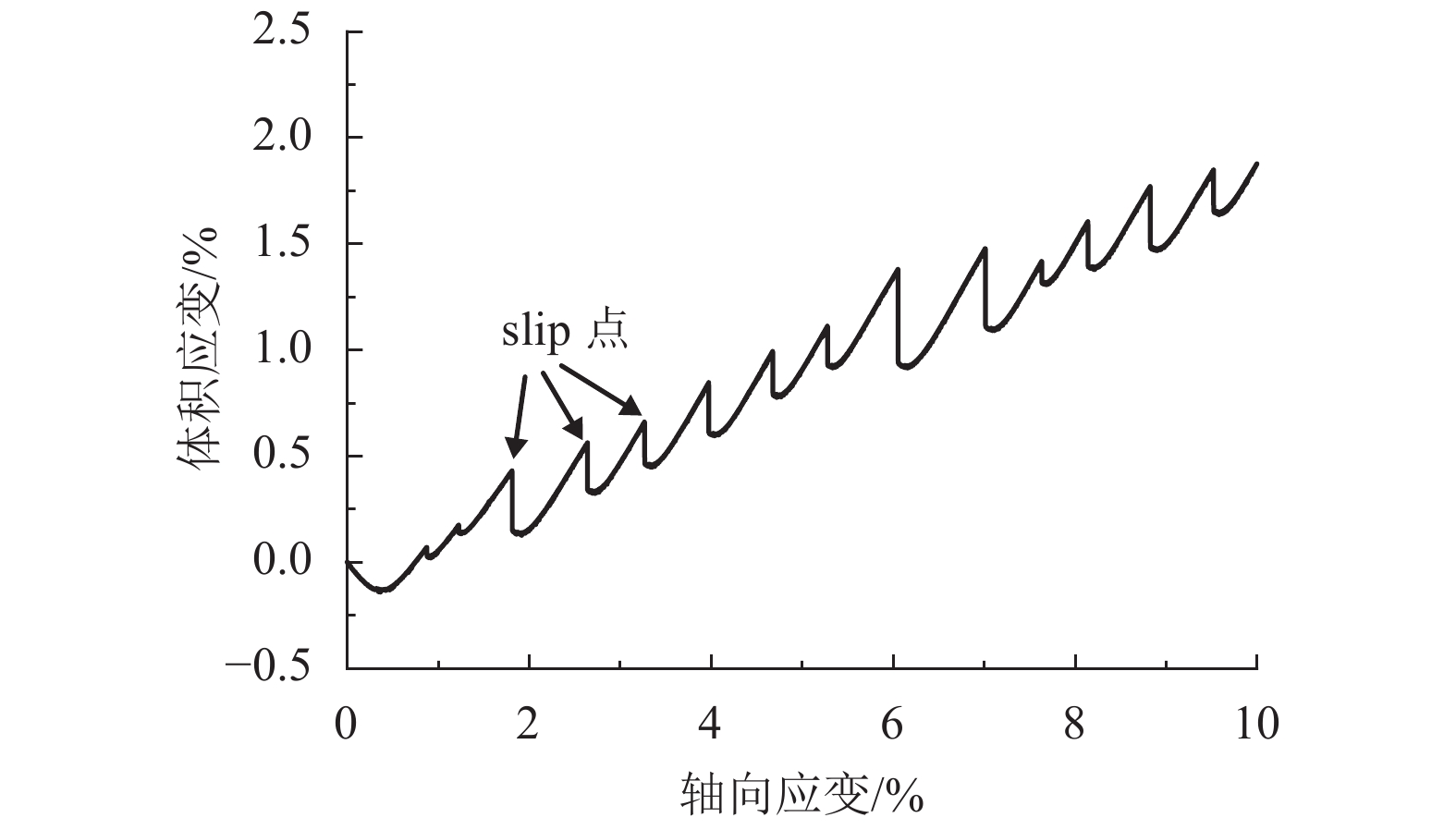
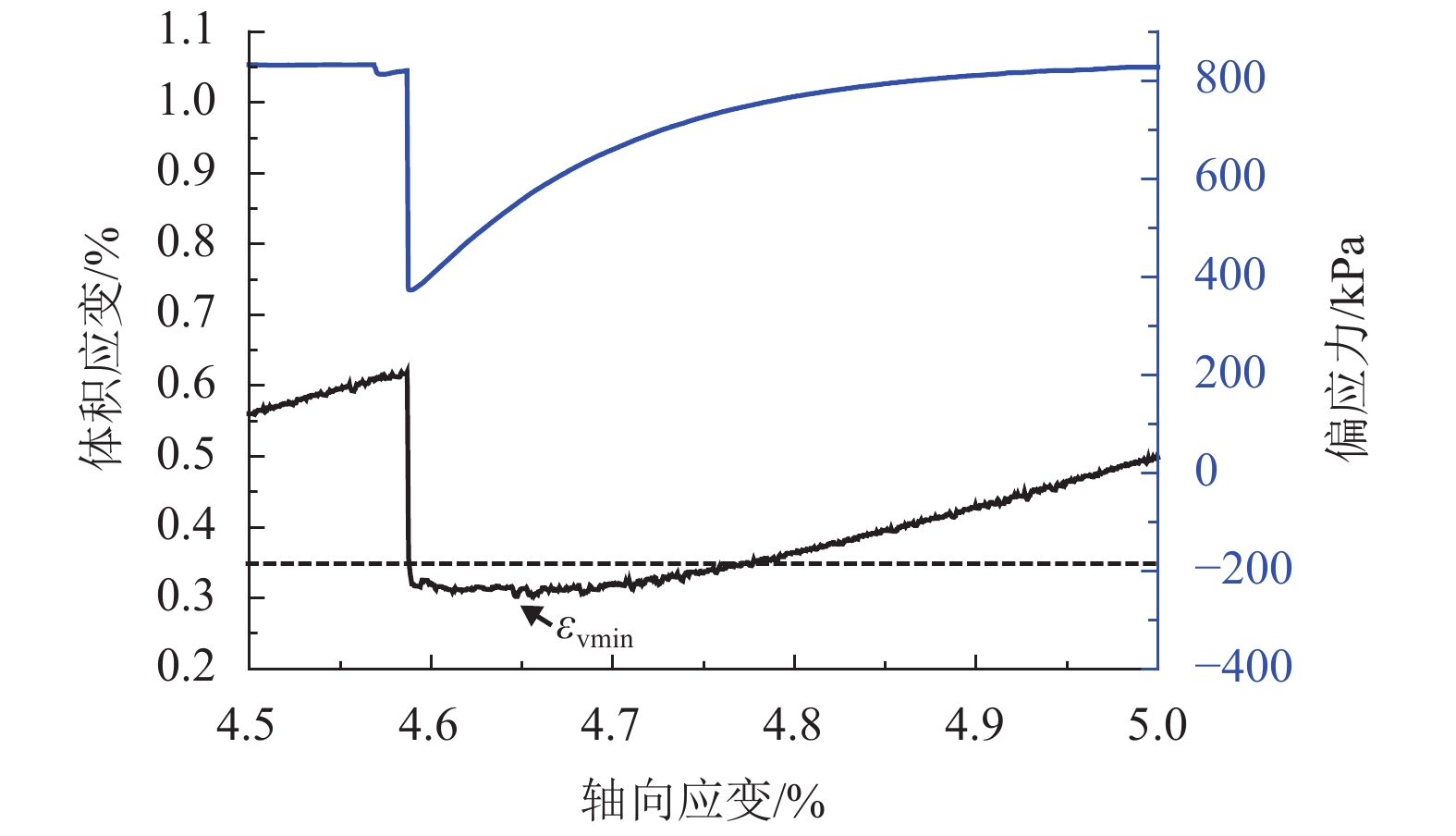
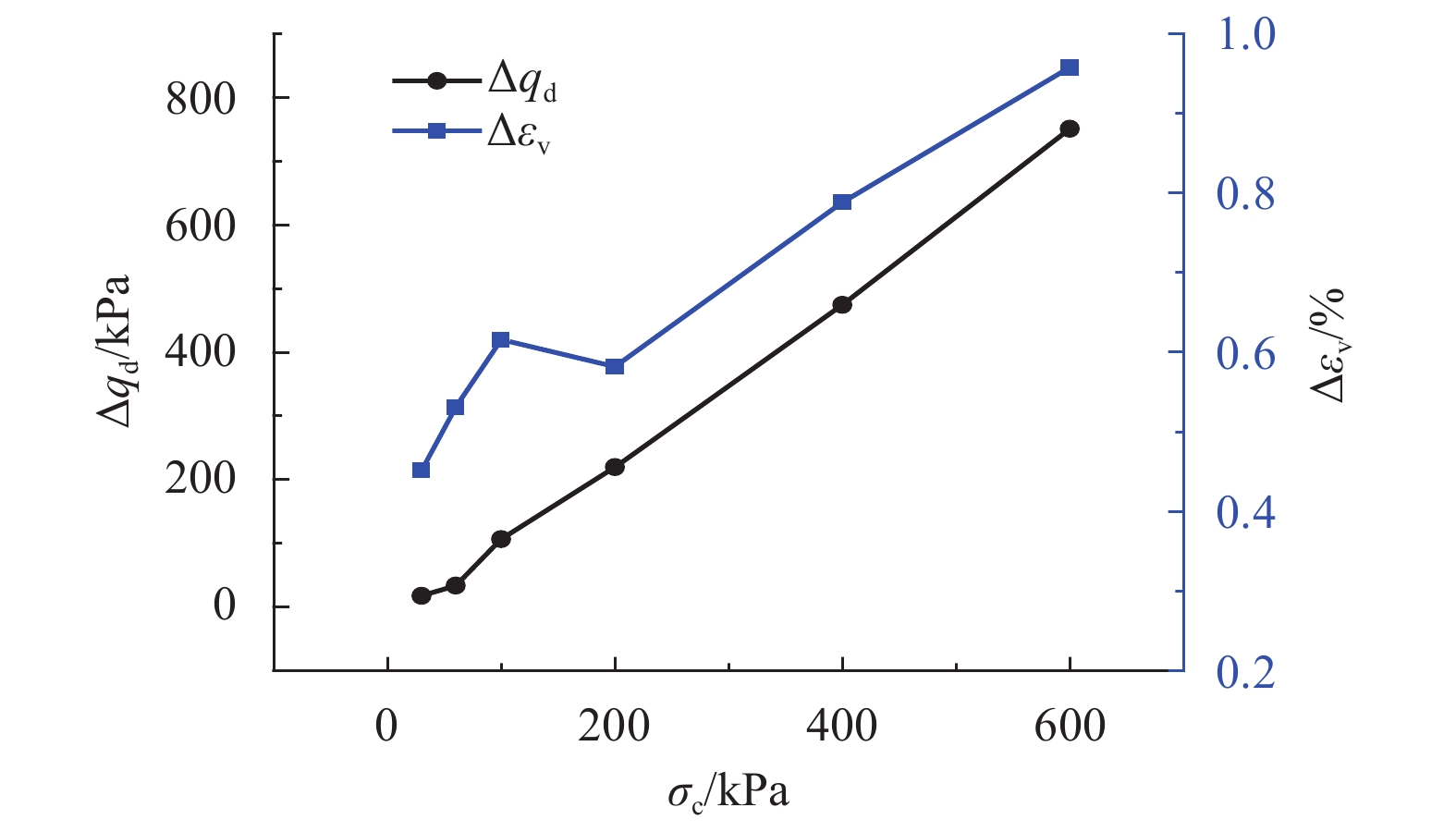
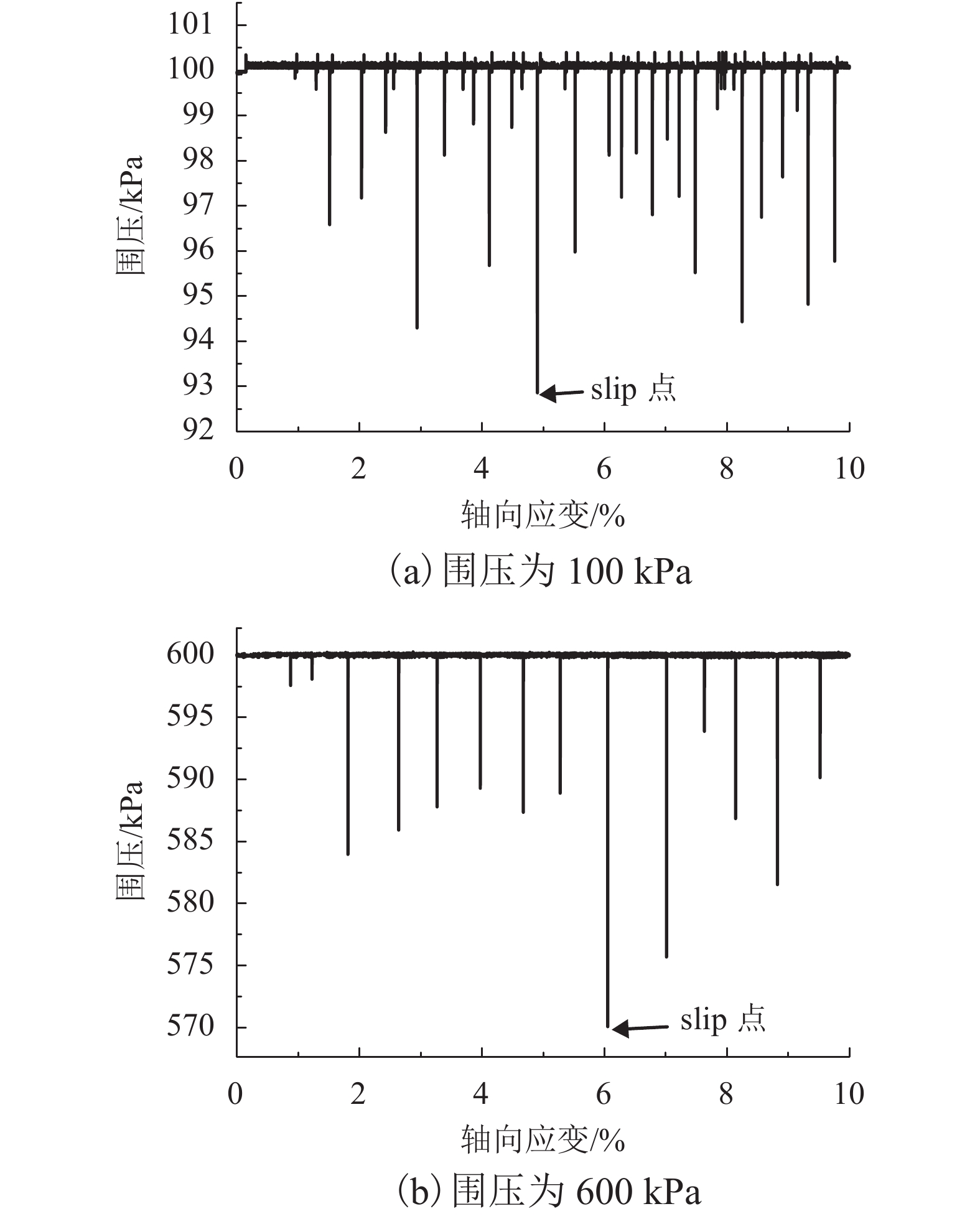
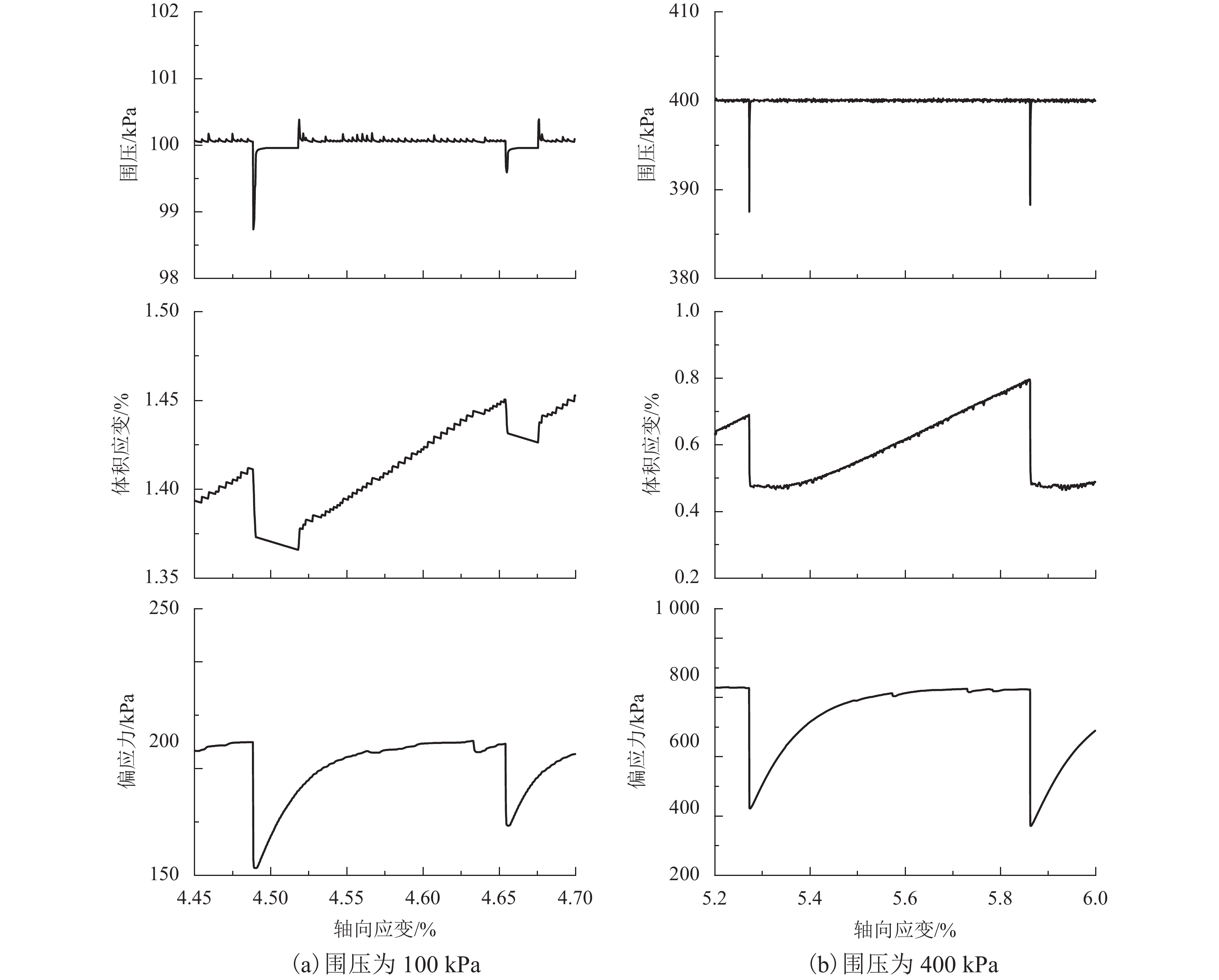
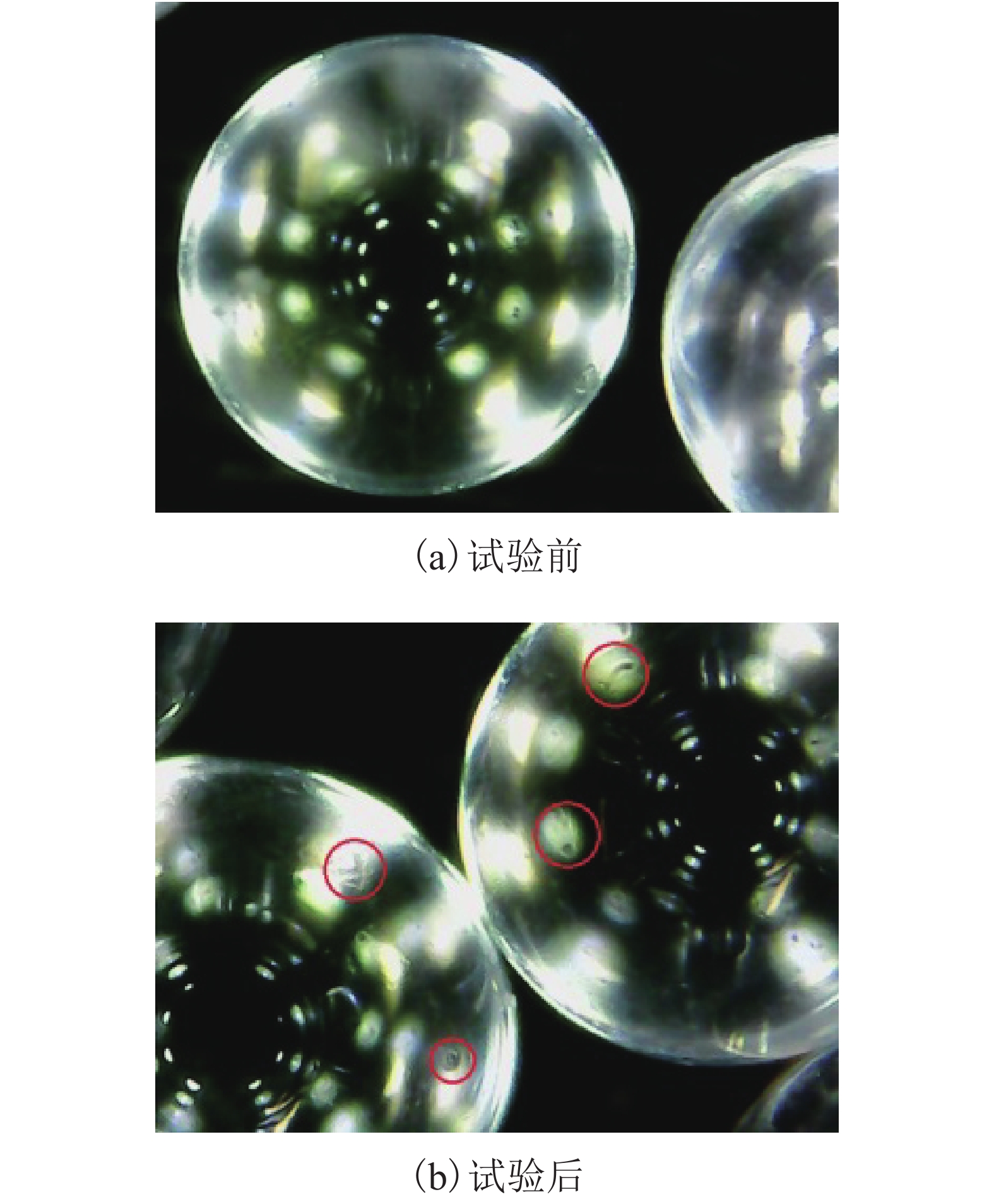
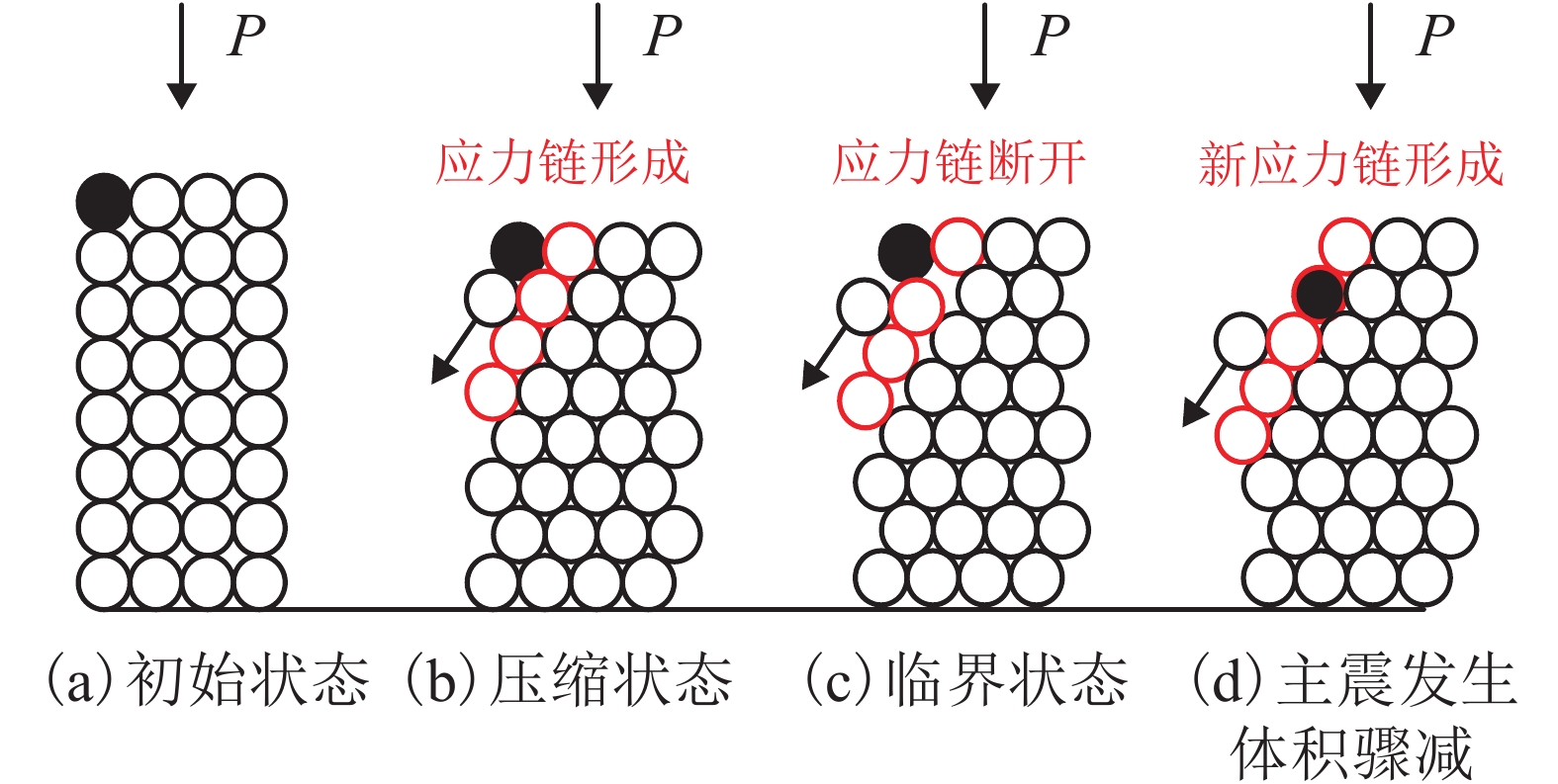
摘要: 为了研究浅源地震的诱发机制,基于室内三轴试验,对颗粒材料的粘滑震动特性进行了分析. 采用颗粒直径为0.6~0.8 mm的玻璃珠,在围压为30、60、100、200、400 kPa和600 kPa的条件下,以0.02 mm/min的轴向应变速率,开展干燥、密实玻璃珠的固结不排水三轴压缩试验,结果表明:试样偏应力主震和偏应力应变间距随着围压的增大而增大;除了初始压密阶段外,体变-应变曲线中所有体积的突然收缩均与粘滑震动有关;在30、60、100 kPa围压条件下,围压-应变曲线中出现较多尖而窄的波峰和波谷;在200、400 kPa和600 kPa围压条件下,围压-应变曲线中只有尖而窄的波谷;玻璃珠类颗粒材料发生粘滑震动过程中既有静摩擦也有转动摩擦;颗粒之间应力链的连续变形和破坏是引起颗粒粘滑震动的根本原因.Abstract: The stick-slip characteristics of glass beads were analysed based on an indoor triaxial test to investigate the mechanism of shallow vibration. Glass beads with diameters of 0.6–0.8 mm were used to conduct consolidated and undrained triaxial tests under cell pressures of 30, 60, 100, 200, 400, and 600 kPa at an axial strain rate of 0.02 mm/min. The results show that the deviator drop and the interval strain between the maximum deviator drops increase with cell pressure. In addition to the first compaction, the volumetric strain drops in the volumetric curve are related to the stick-slip. Under confining stresses of 30, 60, and 100 kPa, a large number of sharp and narrow peaks and valleys appear in the curve of cell pressure versus strain. Only sharp and narrow valleys are observed under confining stresses of 200, 400, and 600 kPa. It is found that static friction and sliding friction affect the stick-slip characteristics of the glass beads by observing the surface of the glass beads before and after the triaxial compression test. Finally, the continuous deformation and destruction of the force chain between the glass beads are the causes of stick-slip in the glass beads.
-
Key words:
- glass beads /
- stick-slip /
- vibration /
- deviatoric stress /
- force chain
-
表 1 不同围压条件下试样的偏应力峰值强度和摩擦角
Table 1. Peak strengths and friction angles of glass beads under different cell pressures
编号 高度/mm 直径/mm 围压/kPa 峰值强度/kPa 摩擦角/(°) CU_D1 100 50 30 64.62 31.23 CU_D2 100 50 60 130.67 31.42 CU_D3 100 50 100 218.45 31.47 CU_D4 100 50 200 442.43 31.68 CU_D5 100 50 400 836.18 30.73 CU_D6 100 50 600 1299.31 31.32 表 2 不同围压下第1次出现粘滑震动的应变与偏应力降幅
Table 2. Deviator drop and strain of the first stick-slip
项目 围压/kPa 30 60 100 200 400 600 应变/% 1.33 1.17 0.90 0.81 0.67 0.87 偏应力降幅/kPa 1.18 3.02 38.72 123.95 385.70 332.95 Δq/σc/% 3.93 5.03 38.72 61.98 96.42 55.49 表 3 不同围压下试样由压缩转为膨胀的应变点
Table 3. Volumetric strain turning point of glass beads under different cell pressures
项目 围压/kPa 30 60 100 200 400 600 最小压缩体变 –0.024 –0.120 –0.056 –0.053 –0.094 –0.140 轴向应变 0.069 0.305 0.145 0.148 0.210 0.340 -
马宗晋. 活动构造基础与工程地震 [M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1992: 82-83 李力刚,黄培华,傅容珊,等. 断层粘滑摩擦增温的理论分析及其对TL,ESR测龄的意义[J]. 地震地质,1999,21(4): 387-396LI Ligang, HUANG Peihua, Fu Rongshan, et al. Frictional heating by stick slip and its significance for TL,ESR dating[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1999, 21(4): 387-396 崔德山,项伟,陈琼,等. 细颗粒粘滑运动的能量耗散与释放试验[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2016,41(9): 1603-1610CUI Deshan, XIANG Wei, CHEN Qiong, et al. Experiment of energy dissipation and energy release during stick-slip within glass beads[J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2016, 41(9): 1603-1610 ADJEMIAN F, EVESQUE P. Experimental study of stick-slip behaviour[J]. International Journal for Numerical & Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2004, 28(6): 501-530 邵同宾,嵇少丞. 俯冲带地震诱发机制:研究进展综述[J]. 地质论评,2015,61(2): 245-268SHAO Tongbin, JI Shaocheng. Earthquake mechanisms of subduction zones:a state-of-the-art overview[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(2): 245-268 OKAZAKI K, KATAYAMA I. Slow stick slip of antigorite serpentinite under hydrothermal conditions as a possible mechanism for slow earthquakes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(4): 1099-1104 王绳祖,张流. 剪切破裂与粘滑——浅源强震发震机制的研究[J]. 地震地质,1984,6(2): 63-73WANG Shengzu, ZHANG Liu. Shear fracture and stick-slip:a study on shock-generation mechanism of strong shallow earthquakes[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1984, 6(2): 63-73 徐锡伟,于贵华,王峰. 1966年邢台地震群的发震构造模型——新生断层形成?先存活断层摩擦粘滑?[J]. 中国地震,2004,16(4): 364-378XU Xiwei, YU Guihua, WANG Feng, et al. Seismogenic model for the 1966 Xingtai earthquakes—nucleation of new-born fault or strick-slip of pre-existing fault?[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 2004, 16(4): 364-378 WILSON B, DEWERS T, RECHES Z E, et al. Particle size and energetics of gouge from earthquake rupture zones[J]. Nature, 2005, 434(7034): 749-52 ALBERT I, TEGZES P, ALBERT R, et al. Stick-slip fluctuations in granular drag[J]. Physical Review E: Statistical Nonlinear & Soft Matter Physics, 2001, 64(1): 031307 BOBRYAKOV A P. Stick-slip mechanism in a granular medium[J]. Journal of Mining Science, 2010, 46(6): 600-605 DOANH T, HOANG M T, ROUX J N, et al. Stick-slip behaviour of model granular materials in drained triaxial compression[J]. Granul Matter, 2013, 15(1): 1-23 JOHNSON P A, FERDOWSI B, KAPROTH B M, et al. Acoustic emission and microslip precursors to stick-slip failure in sheared granular material[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2013, 40(21): 5627-5631 LEEMAN J R, SCUDERI M M, MARONE C, et al. On the origin and evolution of electrical signals during frictional stick slip in sheared granular material[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 2014, 119(5): 4253-4268 ELKHOLY K N, KHONSARI M M. Experimental investigation on the stick-slip phenomenon in granular collision lubrication[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2008, 130(2): 021302-021308 张徐,赵春发,翟婉明. 铁路碎石道砟静态压碎行为数值模拟[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(1): 137-143ZHANG Xu, ZHAO Chunfa, ZHAI Wanming. Numerical analysis of static crushed behavior of railway ballast[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(1): 137-143 BRACE W F, BYERLEE J D. Stick-slip as a mechanism for earthquakes[J]. Science, 1966, 153(3739): 990-992 何昌荣,张流. 用负刚度及变刚度方法研究粘滑[J]. 地震地质,1996,18(3): 199-211HE Changrong, ZHANG Liu. A study on the mechanics of stick slip by controlling a linear combination of load and displacement[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1996, 18(3): 199-211 王学滨,马冰,吕家庆. 实验室尺度典型断层系统破坏,前兆及粘滑过程数值模拟[J]. 地震地质,2014,36(3): 845-861WANG Xuebin, MA Bing, LÜ Jiaqing. Numerical simulation of failures,precursors and stick-slip processes for typical fault sturctures at a laboratory scale[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2014, 36(3): 845-861 BRUNE J N, HENYEY T L, ROY R F. Heat flow,stress,and rate of slip along the San Andreas fault,California[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1969, 74(15): 3821-3827 王贤仁,卢艳清. 澜沧—耿马地震前FSQ仪记录到的粘滑和慢地震及对短临预报探讨[J]. 地震研究,1994,17(2): 157-163WANG Xianren, LU Yanqing. Stick-slip and slow shocks recorded on FSQ tiltmeters before Lancang-Gengma earthquake and primary study on short-impending earthquake prediction[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 1994, 17(2): 157-163 李普春,刘力强,郭玲莉,等. 粘滑过程中的多点错动[J]. 地震地质,2013,35(1): 125-137LI Puchun, LIU Liqiang, GUO Lingli, et al. Multi-point dislocation in stick-slip process[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2013, 35(1): 125-137 井国庆,黄红梅,施晓毅,等. 道砟尖角折断的三轴压缩试验与离散元数值分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(2): 216-221JING Guoqing, HUANG Hongmei, SHI Xiaoyi, et al. Triaxial test and dem analysis of ballast aggregate with angularity breakage[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(2): 216-221 崔德山,项伟,陈琼,等. 颗粒材料黏滑运动特征与颗粒黏结试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(9): 1924-1935CUI Deshan, XIANG Wei, CHEN Qiong, et al. Experimental study on stick-slip behaviour and sintering phenomenon of glass beads[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(9): 1924-1935 -





 下载:
下载: