Experimental Study on Permeability of Mining-Cracked N2 Laterite
-
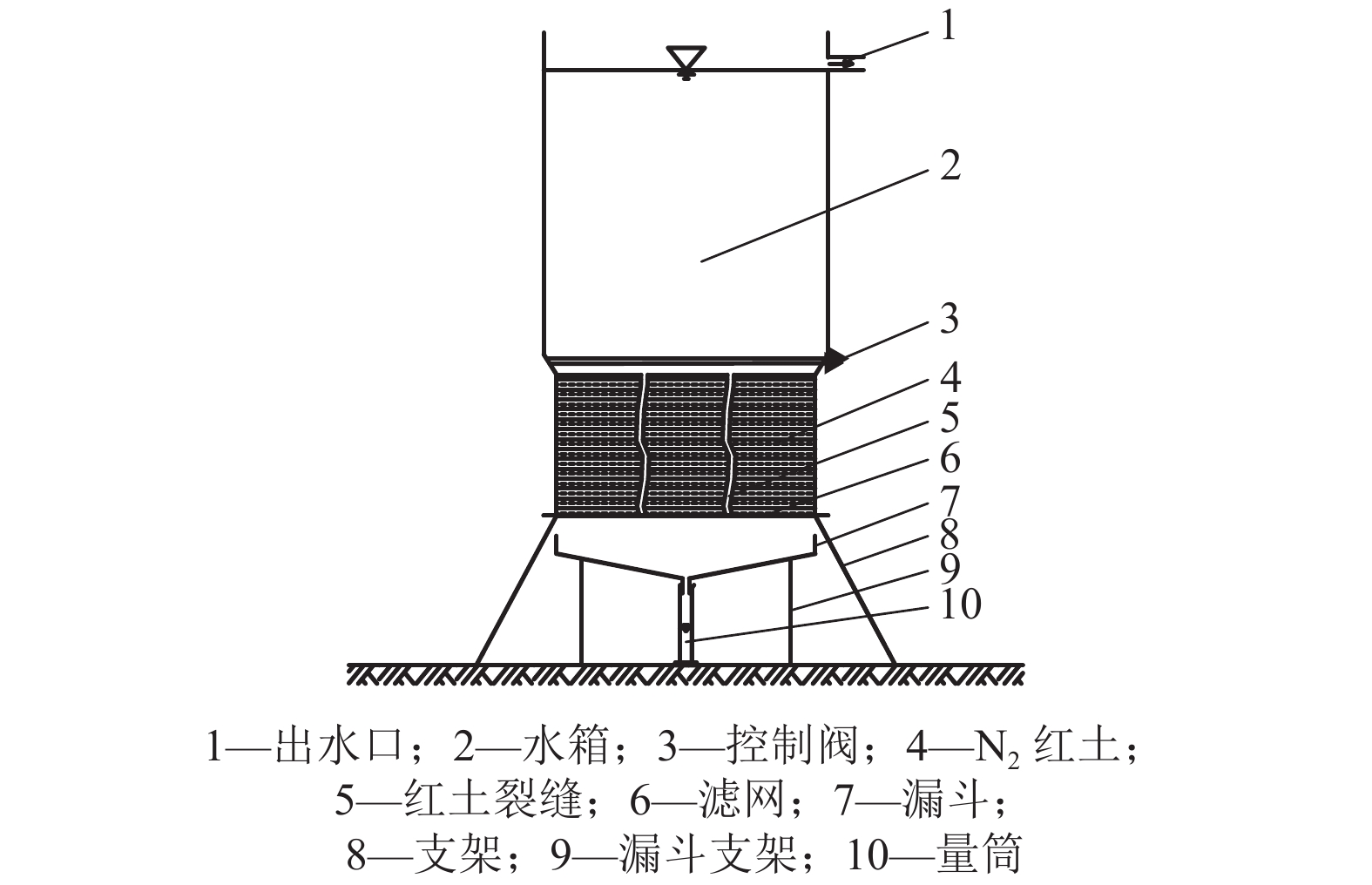
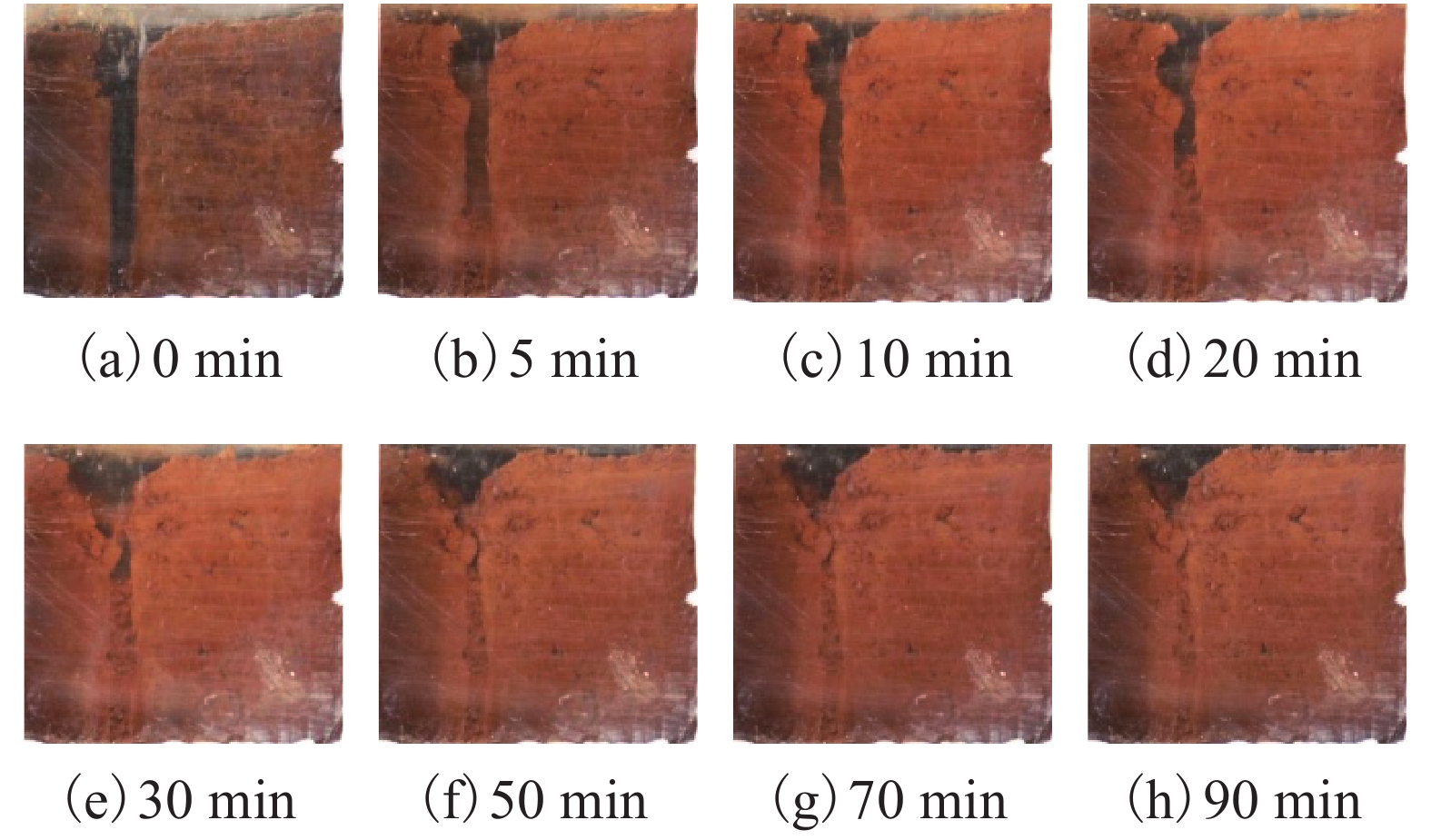
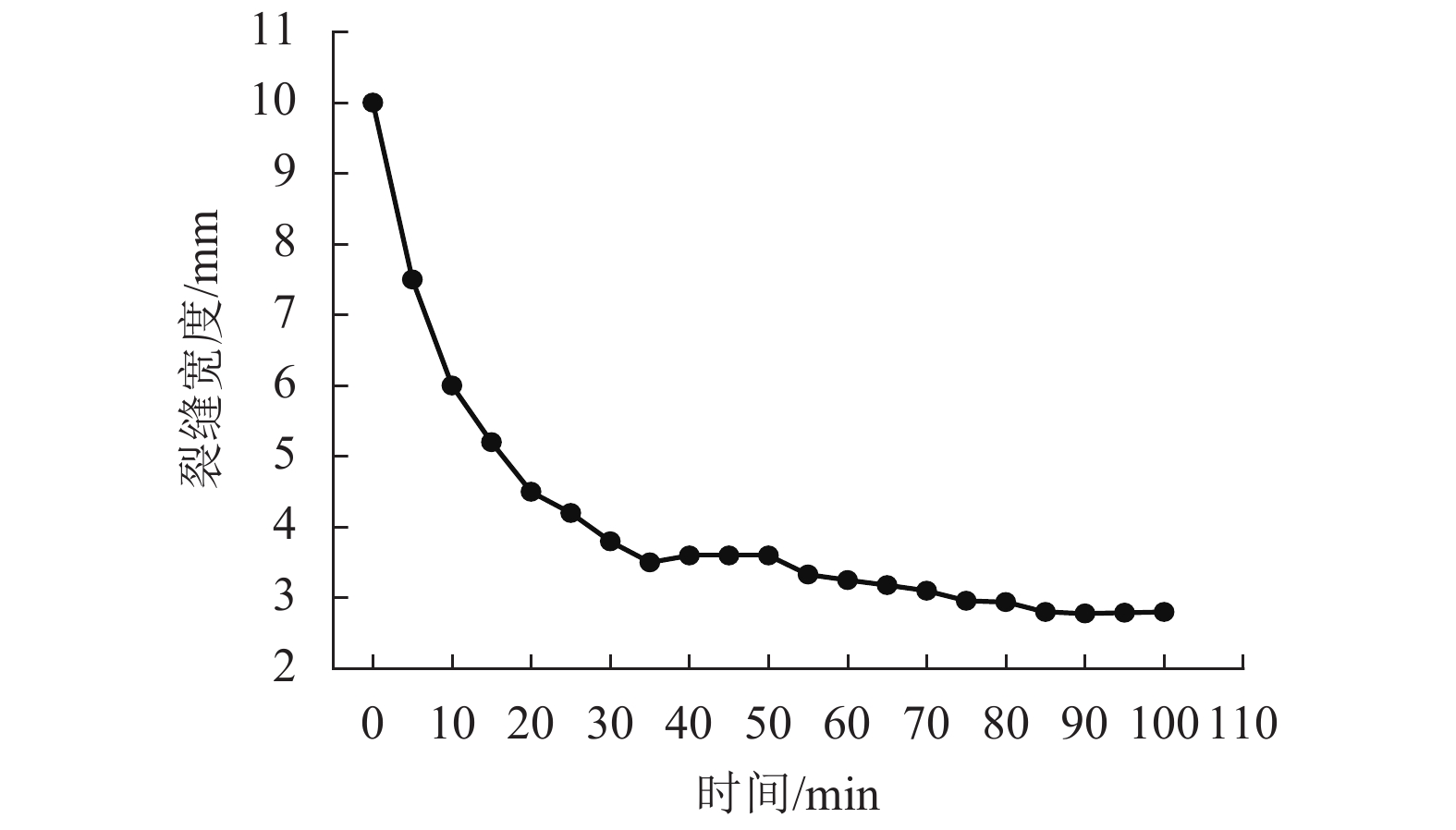
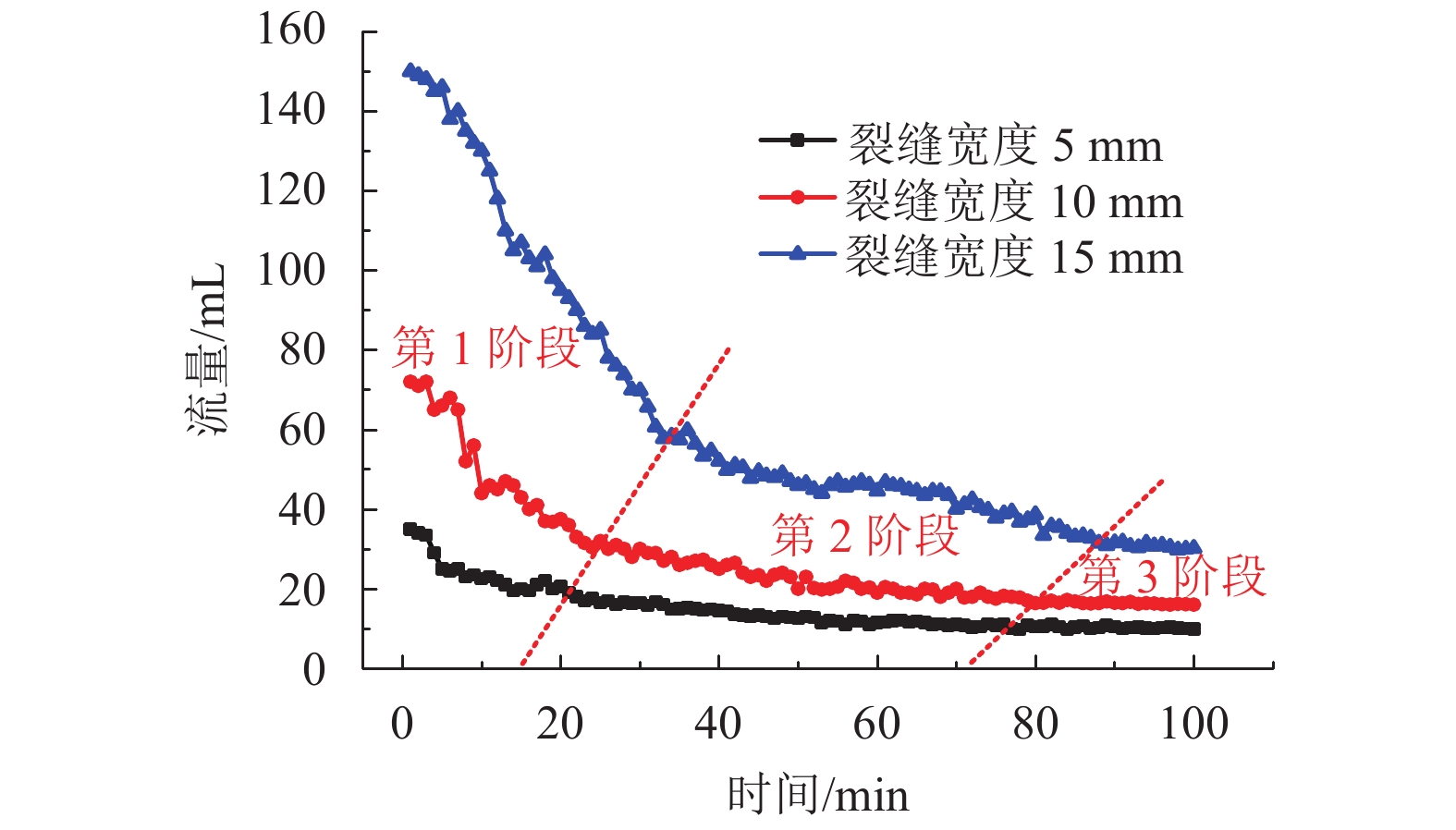
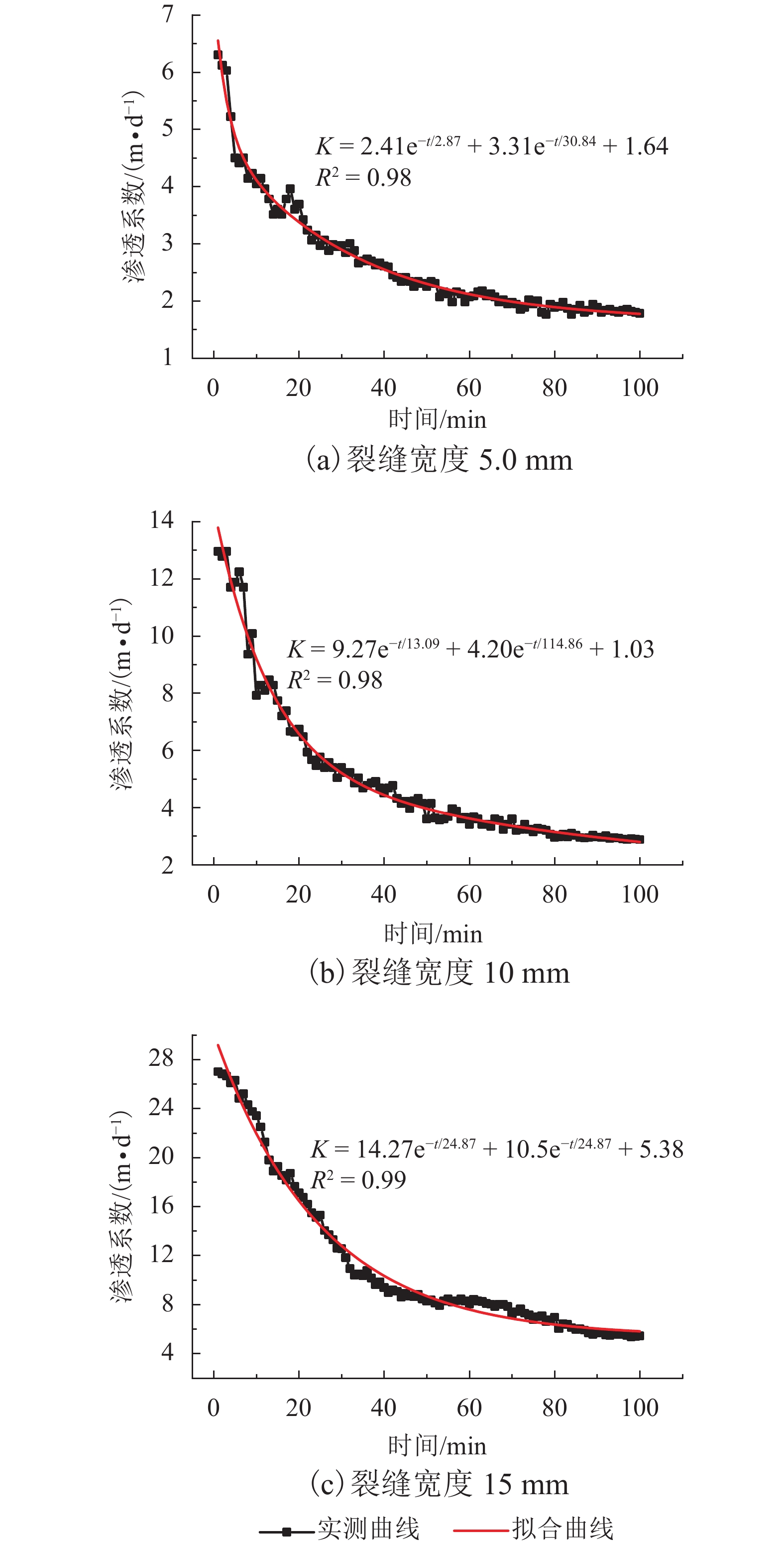
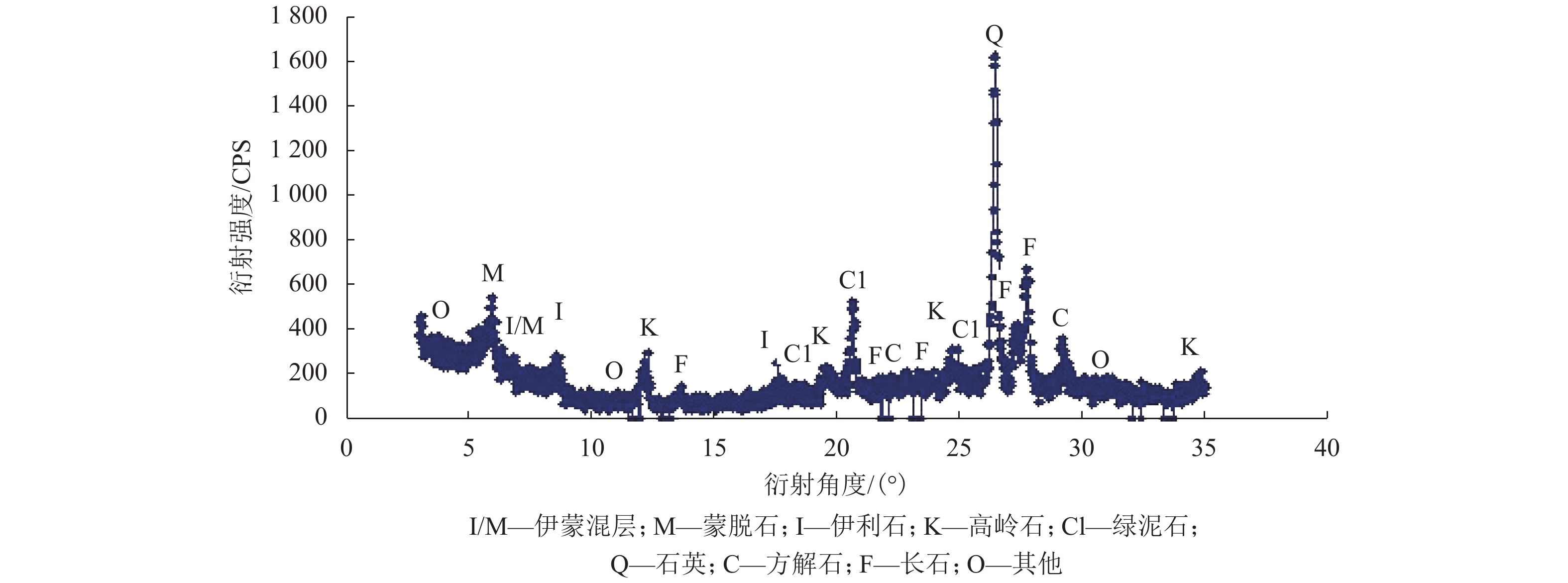
摘要: N2红土层是我国西北干旱-半干旱矿区广泛存在的、对保水采煤起关键作用的隔水层,为了研究釆动破裂N2红土水土相互作用渗透性变化规律,在分析N2红土矿物成分及膨胀性的基础上,采用自制的水土相互作用突水过程试验装置,定量化地研究了不同釆动破裂宽度N2红土水土相互作用突水演化过程. 研究结果表明:N2红土的黏土矿物中亲水性矿物蒙脱石(含量达36%)、伊利石/蒙脱石混层(含量达18%)含量高,亲水性强,具有较强的膨胀性;釆动破裂N2红土水土相互作用的初期裂缝周边松散颗粒堆积、裂缝边缘溃塌较为剧烈,裂缝闭合量较大,突水试验100 min中前15 min裂缝闭合量约占总闭合量的60%;突水量的变化可分为典型的3个阶段,即初期水量快速下降阶段、中期水量缓慢下降阶段和后期水量稳定阶段,裂缝宽度越大,突水稳定时间越长;釆动破裂N2红土水土相互作用渗透性与时间呈负指数关系.Abstract: The laterite of Neogene pliocene series (N2), abbreviated as N2 laterite, over coal seams distributed widely in the mining area of western China is the key aquifuge soil for protecting the shallow water from being destroyed by coal mining. The permeability change induced by soil-water interactions of mining-cracked N2 laterite was studied. On the basis of analyzing the mineral composition and swelling properties of N2 laterite, the water inrush evolution process induced by soil-water interactions of mining-cracked N2 laterite was studied quantitatively using self-made experimental equipment. The results show that there is a high content of hydrophilic minerals in the clay minerals of N2 laterite, such as montmorillonite and illite/montmoduonite interstratified, therefore N2 laterite is more hydrophilic and has strong expansionary. During the early stages of soil-water interactions of mining-cracked N2 laterite, the accumulation of loose particles and the collapse of fracture edges were more intense, and the degree of fracture closure was larger. In the 100 minutes of the whole water inrush test, the amount of crack closure in the first 15 minutes accounts for about 60% of the total closure degree. In addition, the change of water inrush volume can be divided into three typical stages, namely, the rapid decline stage, the slow decline stage, and the stable stage. The greater the crack width is, the longer the water inrush stability time. The relationship between the permeability induced by soil-water interactions of mining-cracked N2 laterite and time is a negative exponential relationship.
-
Key words:
- N2 laterite /
- mining crack /
- soil-water interactions /
- permeability
-
表 1 自然条件下N2红土物理性质
Table 1. Physical properties of natural N2 laterite
含水率/% 密度/(g•cm–3) 比重 孔隙比 液限/% 塑限/% 塑性指数 液性指数 14.5~26.5 1.82~2.18 2.63~2.73 0.57~0.92 30.6~32.7 17.0~17.4 12.5~13.2 0.11~0.20 -
王双明. 鄂尔多斯盆地聚煤规律及煤炭资源评价[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 1996: 5–20 李文平,李涛,陈伟,等. 采空区储水——干旱区保水采煤新途径[J]. 工程地质学报,2015,22(5): 1003-1007LI Wenping, LI Tao, CHEN Wei, et al. Goaf water storage—a new way for water preserved mining in arid areas[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 22(5): 1003-1007 王征,马建喜. 能源战略转型视野下的煤炭利用前景探析[J]. 西南交通大学学报 (社会科学版),2015,16(4): 136-140WANG Zheng, MA Jianxi. Future of coal in the strategic transformation of energy[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University (Social Sciences), 2015, 16(4): 136-140 李文平,叶贵钧,张莱,等. 陕北榆神府矿区保水采煤工程地质条件研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2000,25(5): 449-454LI Wenping, YE Guijun, ZHANG Lai, et al. Study on the engineering geological condition of protected water resources during coal mining action in Yushenfu mine area in the north Shaanxi provice[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2000, 25(5): 449-454 马雄德,王文科,范立民,等. 生态脆弱矿区采煤对泉的影响[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2010,22(1): 32-36MA Xiongde, WANG Wenke, FAN Limin, et al. Coal mining impacting on springs in ecologically fragile mining area[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2010, 22(1): 32-36 韩树青,范立民,杨保国. 开发陕北侏罗纪煤田几个水文地质工程地质问题分析[J]. 中国煤田地质,1992,4(1): 49-52HAN Shuqing, FAN Limin, YANG Baoguo. Exploitation of north Shaanxi Jurassic coal field hydrogeologic and engineering geological problems for analysis[J]. Coal Geology of China, 1992, 4(1): 49-52 王力,卫三平,王全九. 榆神府煤田开采对地下水和植被的影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2008,33(12): 1408-1414WANG Li, WEI Sanping, WANG Quanjiu. Effect of coal exploitation on groundwater and vegetation in the Yushenfu Coal Mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2008, 33(12): 1408-1414 苗霖田. 榆神府矿区主采煤层赋存规律及煤炭开采对水资源影响分析[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2008 李涛. 陕北煤炭大规模开采含隔水层结构变异及水资源动态研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2012 范立民,蒋泽泉. 榆神矿区保水采煤的工程地质背景[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2004,32(5): 32-35FAN Limin, JIANG Zequan. Engineering geologic background of coal mining under water-containing condition in Yushen coal mining area[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2004, 32(5): 32-35 宋世杰. 榆神府矿区煤炭开采对生态环境损害的定量化评价[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2009 王启庆,李文平,李涛. 陕北生态脆弱区保水采煤地质条件分区类型研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(3): 515-521WANG Qiqing, LI Wenping, LI Tao. Division types of geological conditions at mining with water protection in ecological fragile area of northern shaanxi[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(3): 515-521 隋旺华,狄乾生. 开采沉陷土体变形与孔隙水压相互作用研究进展[J]. 工程地质学报,1999,7(4): 303-309SUI Wanghua, DI Qiansheng. Study on interaction between soil mass deformation and pore pressure during subsidence by mining[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 1999, 7(4): 303-309 HSI J, GUNASEKARA C, NGUYEN V. Characteristics of soft peats,organic soils and clays,Colombo-Katunayake expressway,Sri Lanka[J]. Elsevier Geo-Engineering Book Series, 2005, 3: 681-722 RAMANA K V. Humid tropical expansive soils of Trinidad:their geotechnical properties and areal distribution[J]. Engineering Geology, 1993, 34(1): 27-44 AL-RAWAS A A, GUBA I, MCGOWN A. Geological and engineering characteristics of expansive soils and rocks in northern Oman[J]. Engineering Geology, 1998, 50(3): 267-281 石振明,周圆媛,彭铭,等. 含盐量对蒙脱石黏土电渗影响试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(5): 1005-1013SHI Zhenming, ZHOU Yuanyuan, PENG Ming, et al. Experimental study on effect of soil salinity on electro-osmosis in montmorillonite clay[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 1005-1013 李龙起,罗书学,姜红,等. 非饱和红黏土土水特性及强度特征研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(3): 393-398LI Longqi, LUO Shuxue, JIANG Hong, et al. Soil-water and shear strength characteristics of unsaturated red clay[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(3): 393-398 李登峰,胡卸文,赵晓彦,等. 花岗岩残积土边坡水平拱高竖向变化规律[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(5): 1024-1032LI Dengfeng, HU Xiewen, ZHAO Xiaoyan, et al. Variation of horizontal arch height of granite residual soil slope in vertical direction[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 1024-1032 刘秀铭,安芷生,强小科,等. 甘肃第三系红黏土磁学性质初步研究及古气候意义[J]. 中国科学:D 辑,2001,31(3): 192-205LIU Xiuming, AN Zhisheng, QIANG Xiaoke, et al. A preliminary study on the magneric properties of the tertiary red earth in the Gansu province[J]. Science in China:Series D, 2001, 31(3): 192-205 张云翔,陈丹玲,薛祥煦,等. 黄河中游新第三纪晚期红黏土的成因类型[J]. 地层学杂志,1998,22(1): 10-15ZHANG Yunxiang, CHEN Danling, XUE Xiangxu, et al. The genetic types of the late neogene red clay in the middle reaches of the yellow river[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 1998, 22(1): 10-15 张永双,曲永新,周瑞光. 南水北调中线工程上第三系膨胀性硬黏土的工程地质特性研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2002,10(4): 367-377ZHANG Yongshuang, QU Yongxin, ZHOU Ruiguang. Engineering geological properties of neogene hard clay along the middle line of the north-south diversion water project in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2002, 10(4): 367-377 储文静,付新平,蔡云廷. 山西吕梁地区三趾马红土的工程地质特性及其工程环境效应研究[J]. 铁道勘察,2014(5): 35-38CHU Wenjing, FU Xinping, CAI Yunting. Study on engineering geology characteristics and engineering-environmental effects of hipparion laterite in Lüliang Sanxi province[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 2014(5): 35-38 石菊松,曲永新,李滨,等. 陕西宝鸡市新近系硬黏土工程地质特性与斜坡失稳效应[J]. 地质通报,2013,32(12): 1911-1917SHI Jusong, QU Yongxin, LI Bin, et al. Engineering geological properties of Neogene hard clays in Baoji City area,Shaanxi province,and their effect on slope failure[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(12): 1911-1917 李涛,李文平,常金源,等. 陕北浅埋煤层开采隔水土层渗透性变化特征[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2011,28(1): 127-131LI Tao, LI Wenping, CHANG Jinyuan, et al. Permeability features of water-resistant clay layer in northern Shaanxi province while shallowly buried coal mining[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2011, 28(1): 127-131 -




 下载:
下载: