Virtual Experiments to Predict Bolster Fatigue Lifetime Based on FEM Model Validated by Static Tests
-
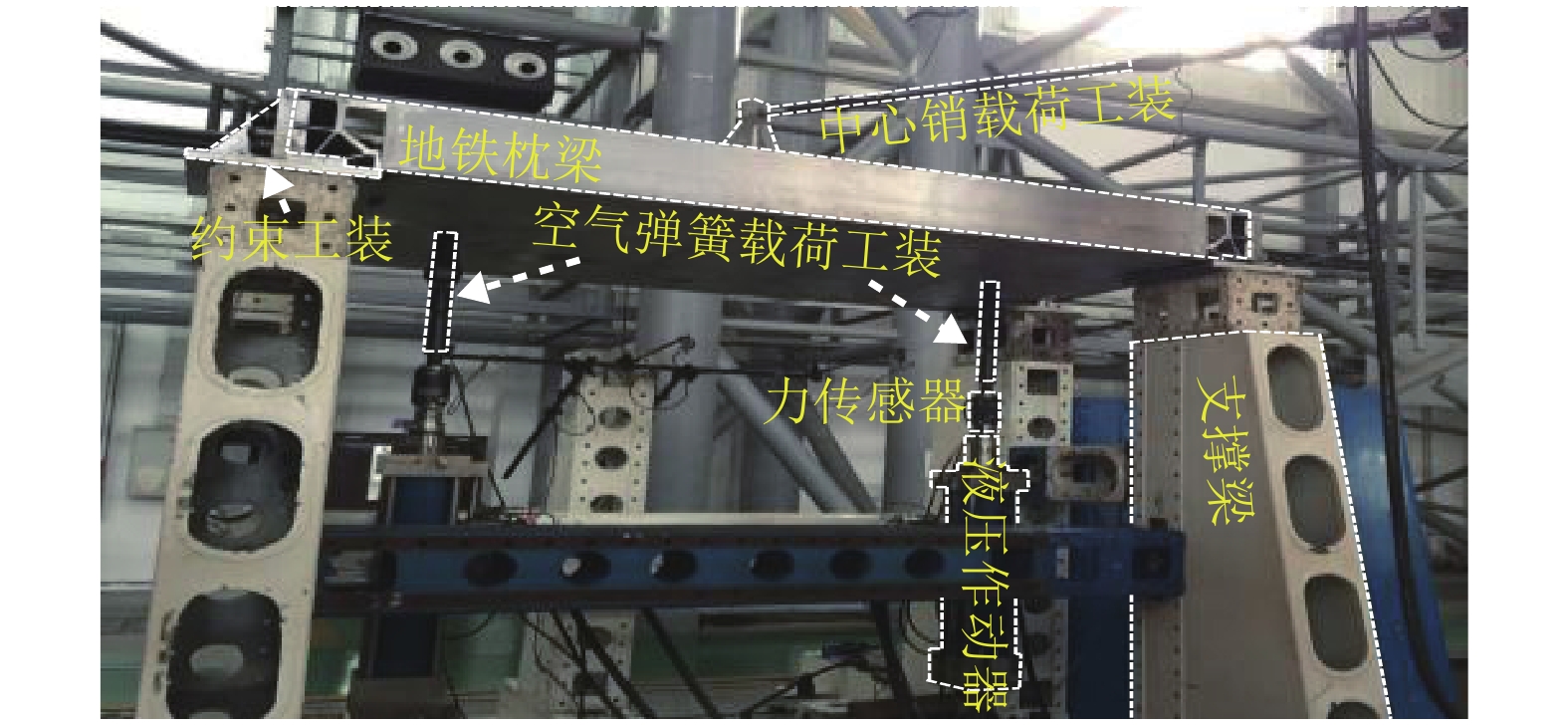
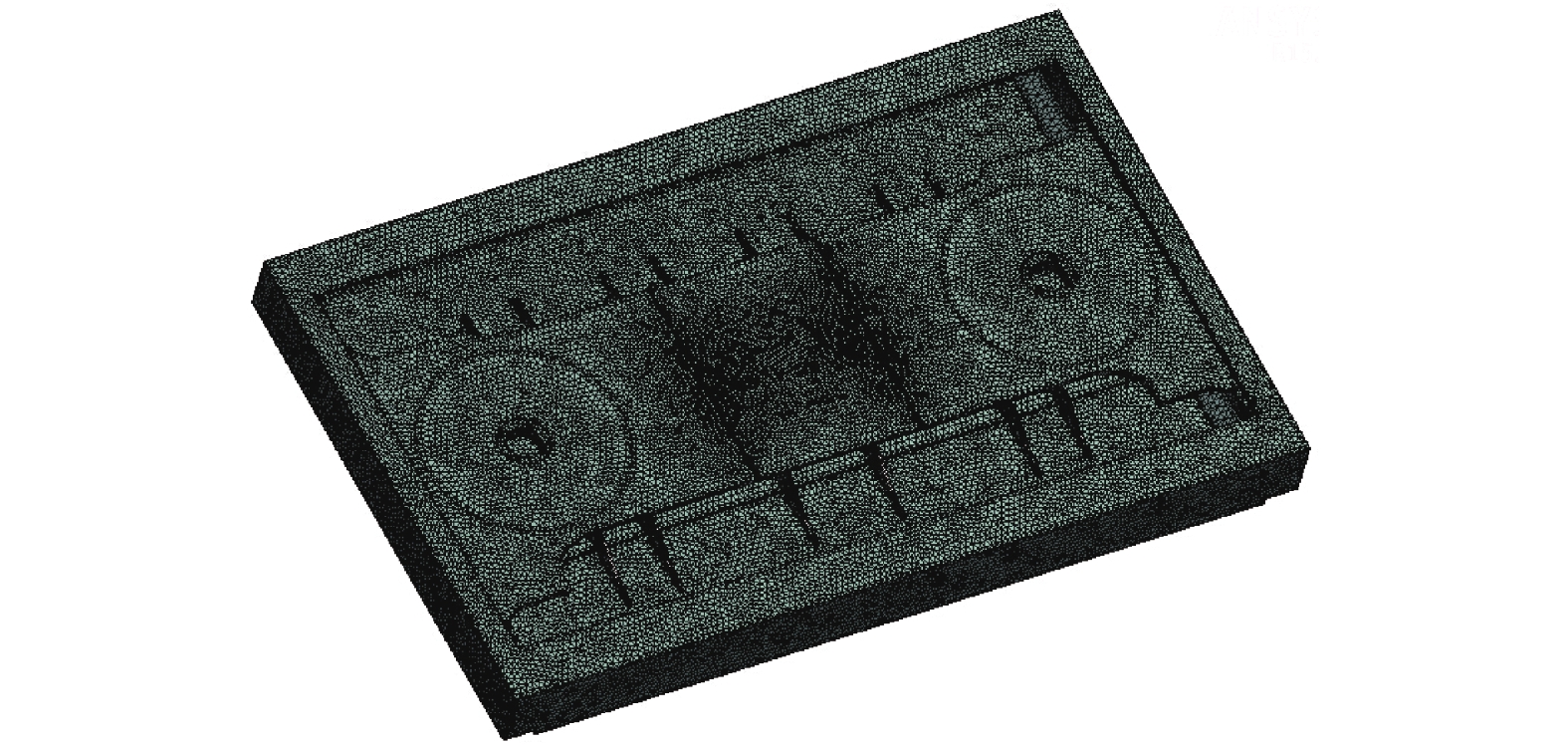
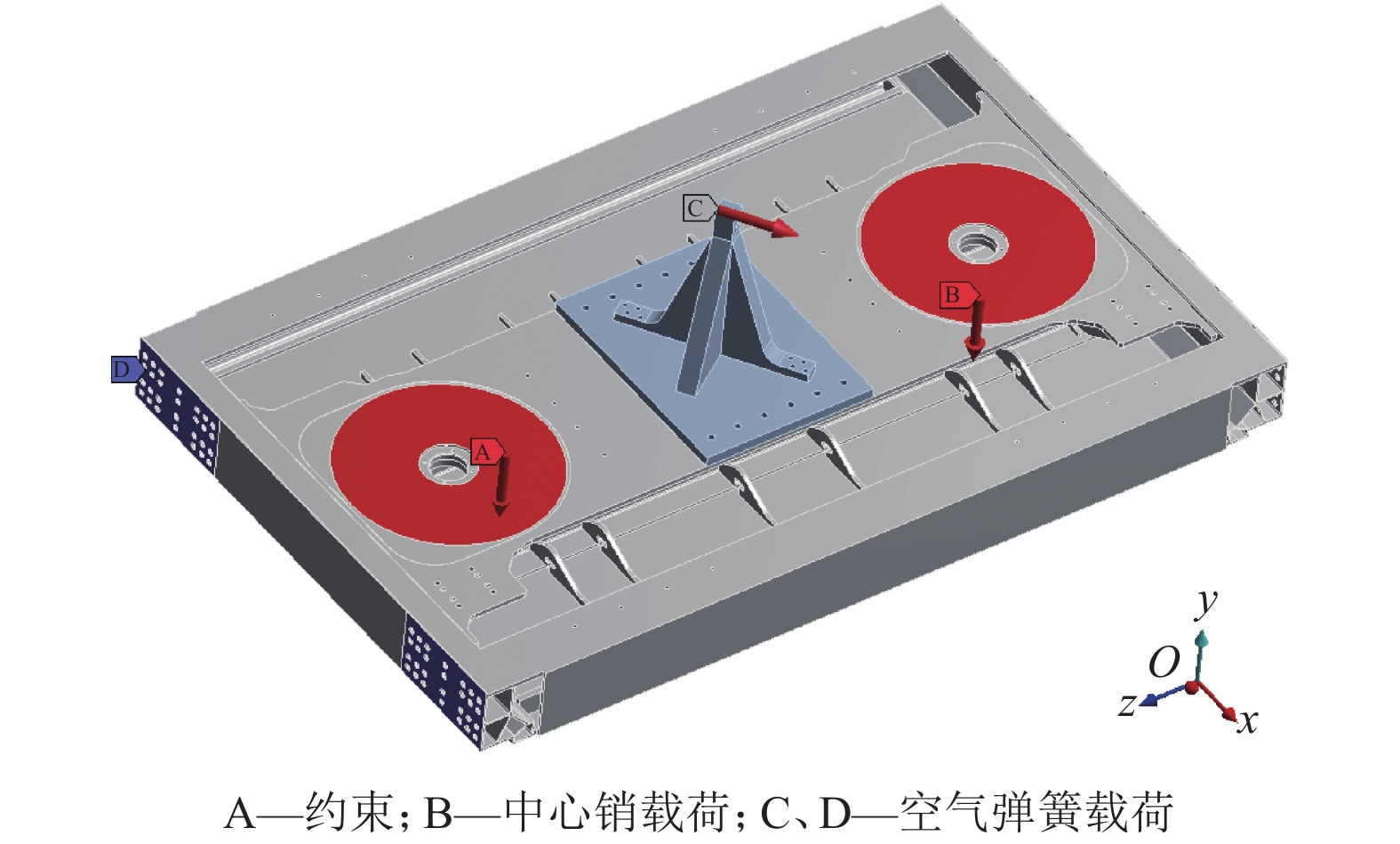
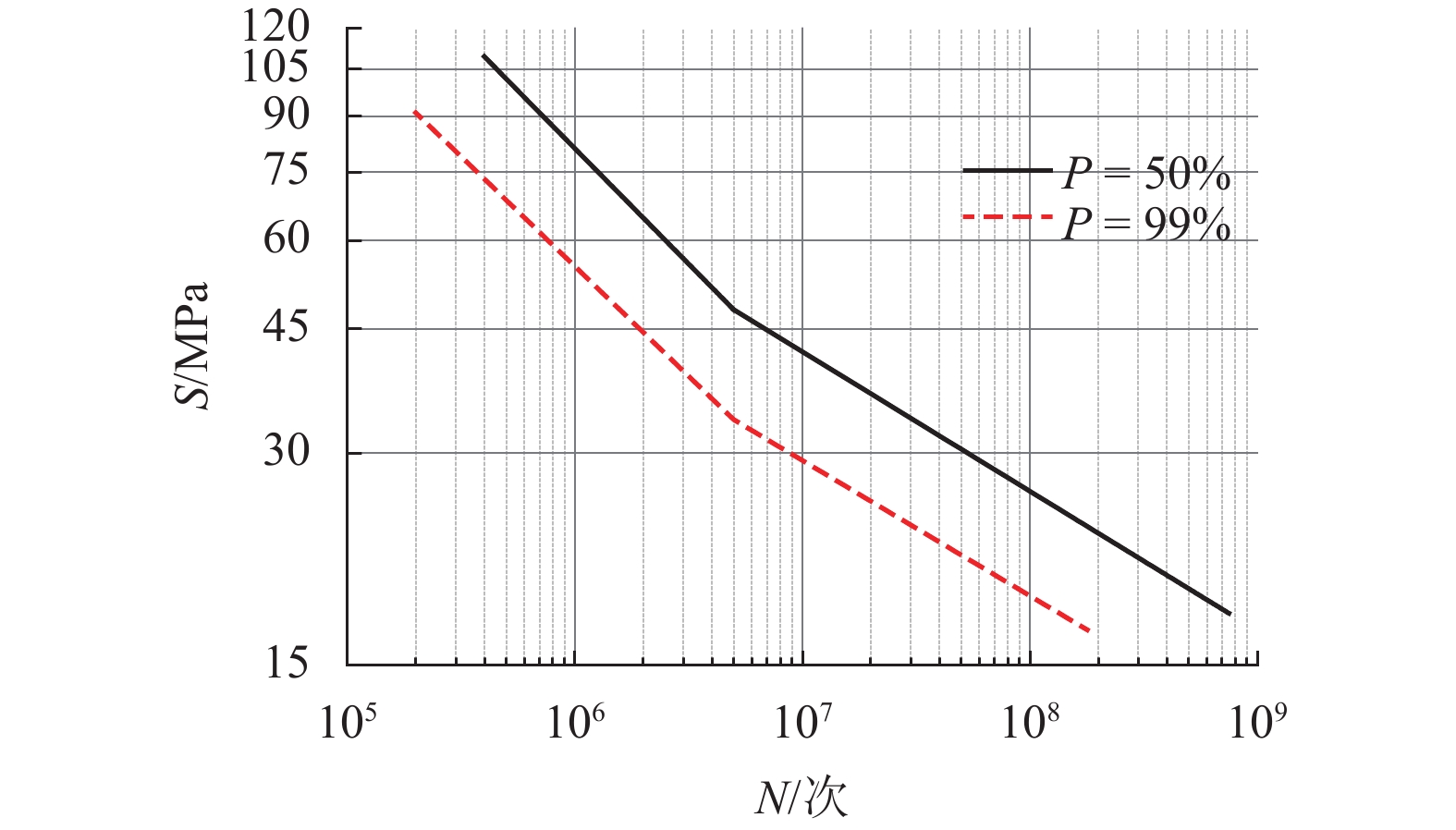
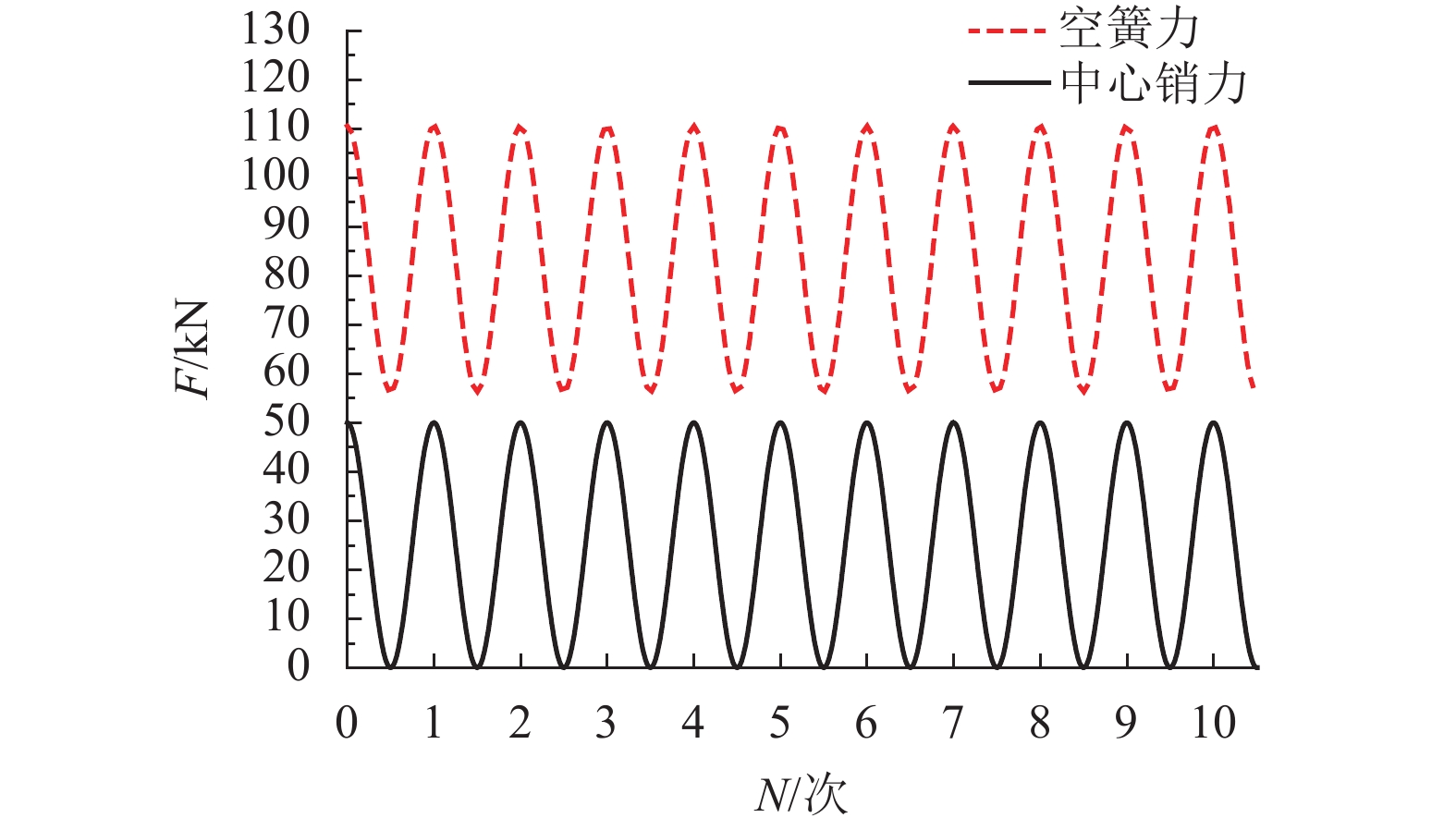
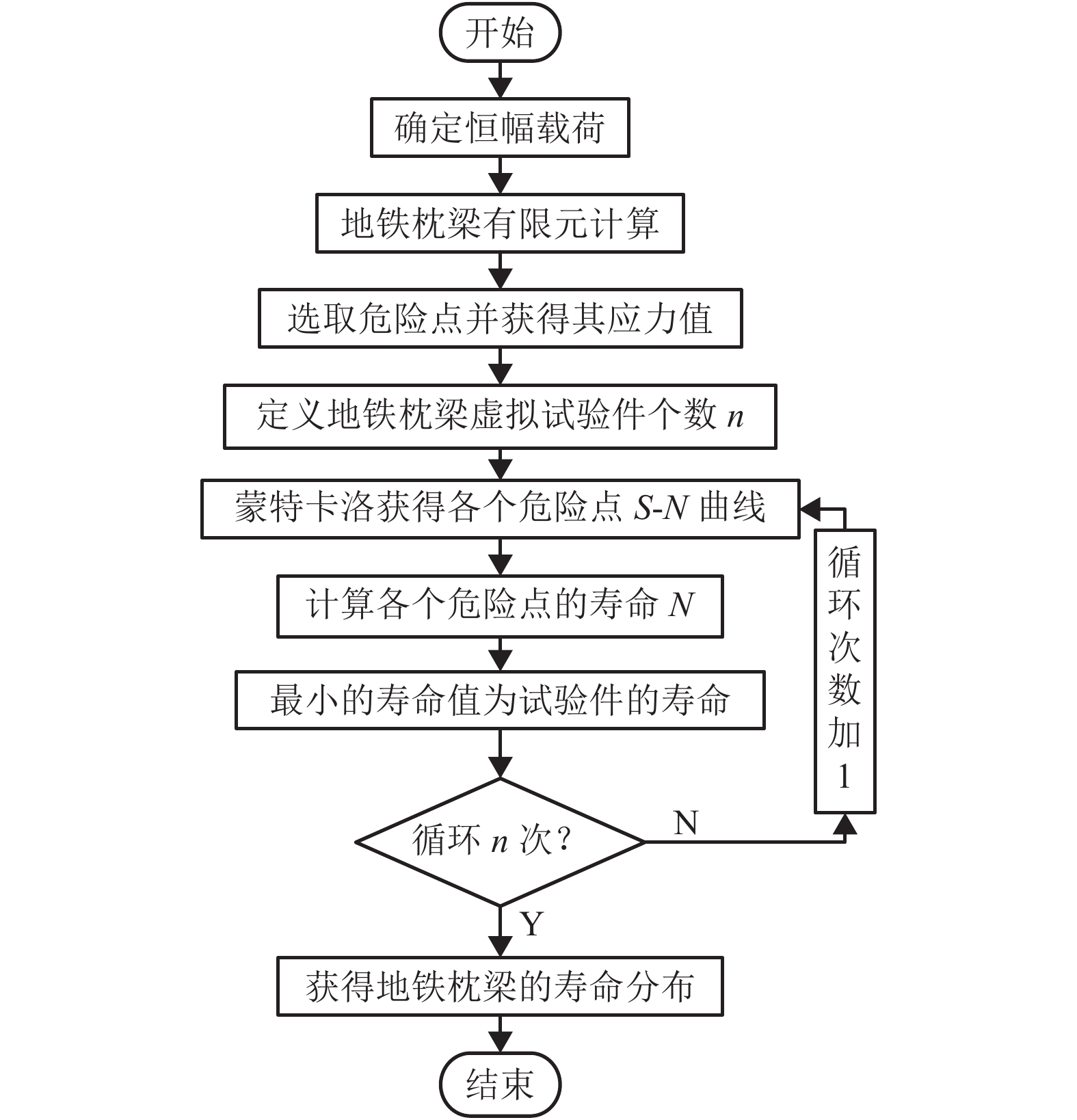
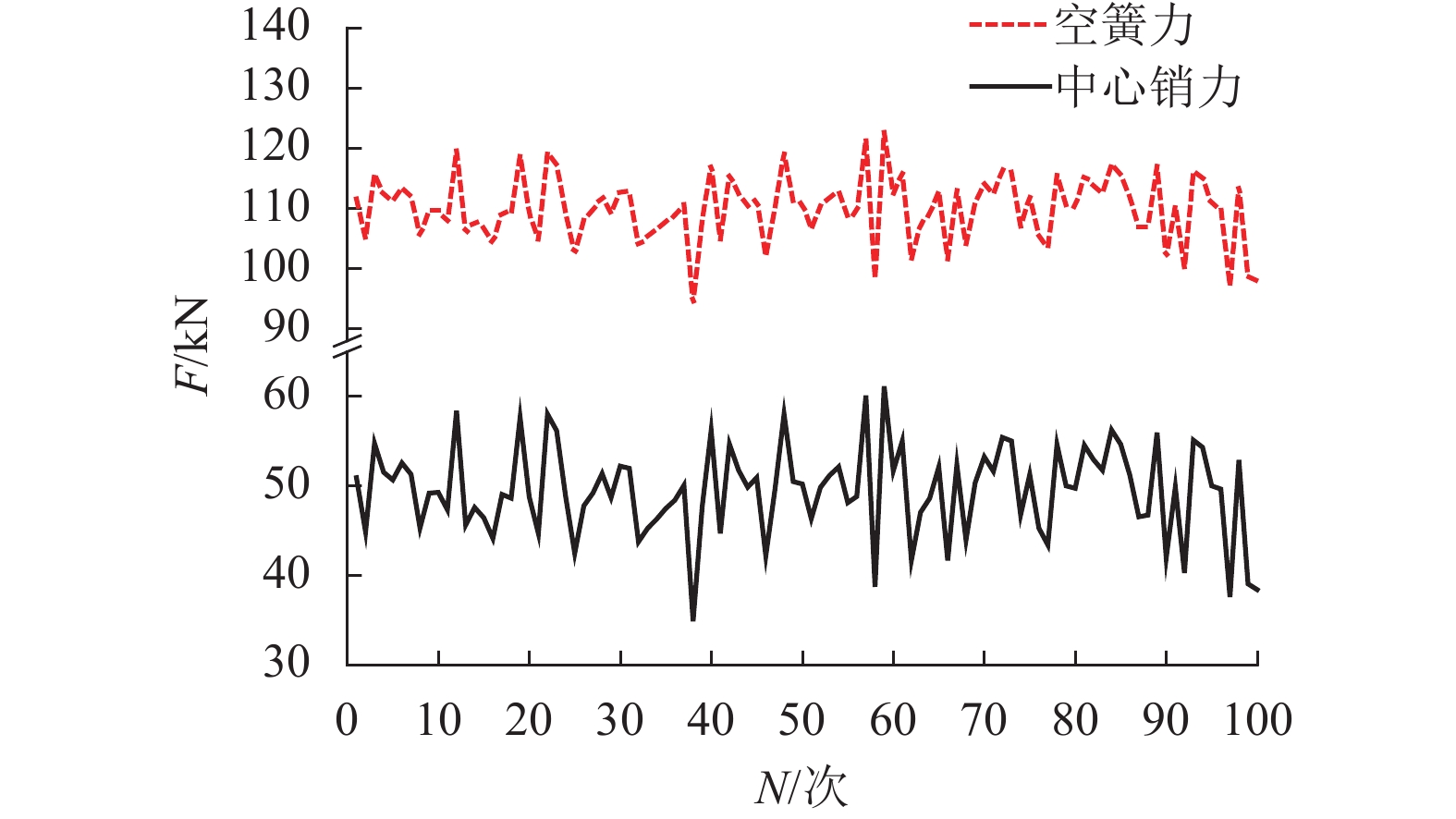
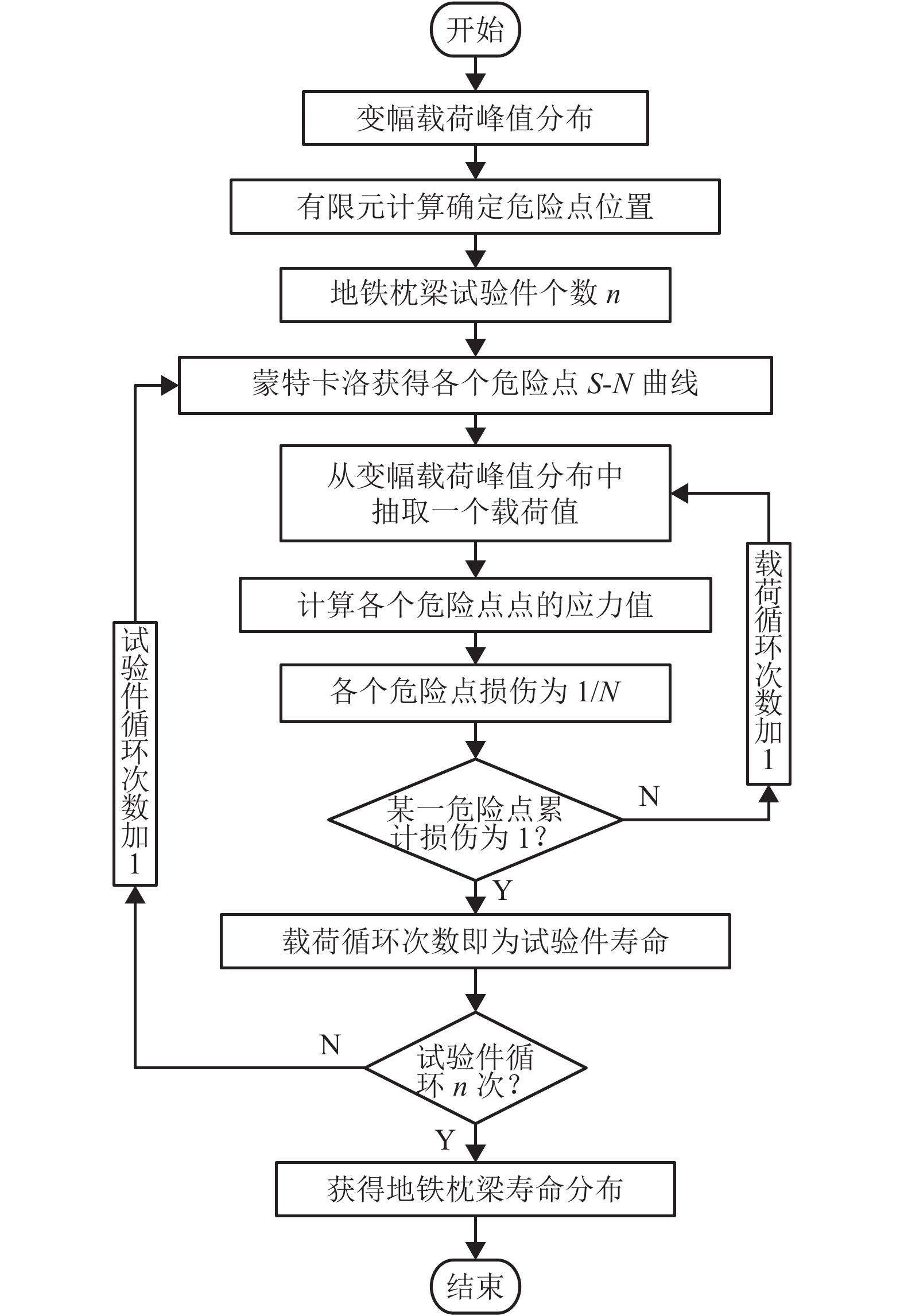
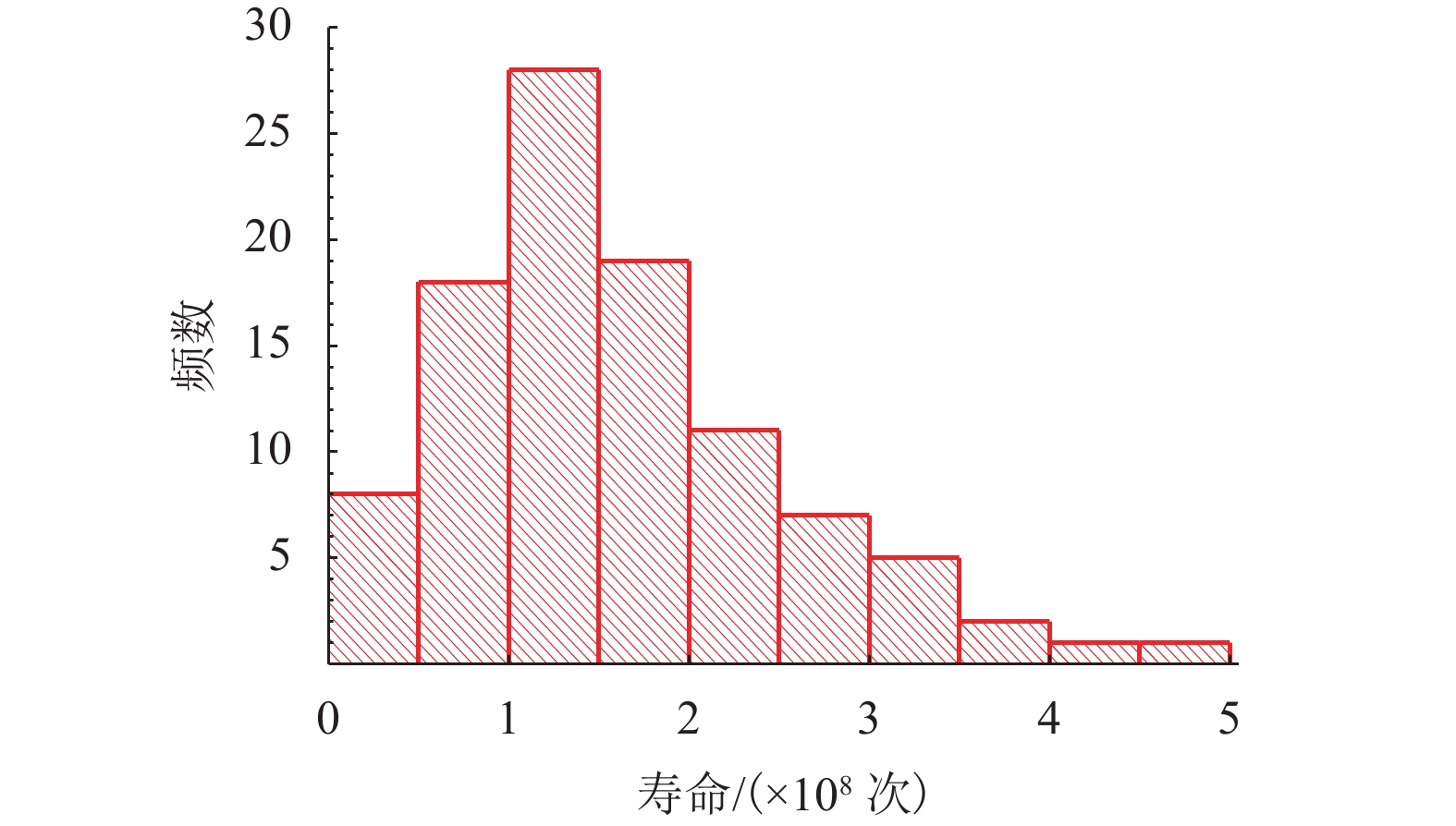
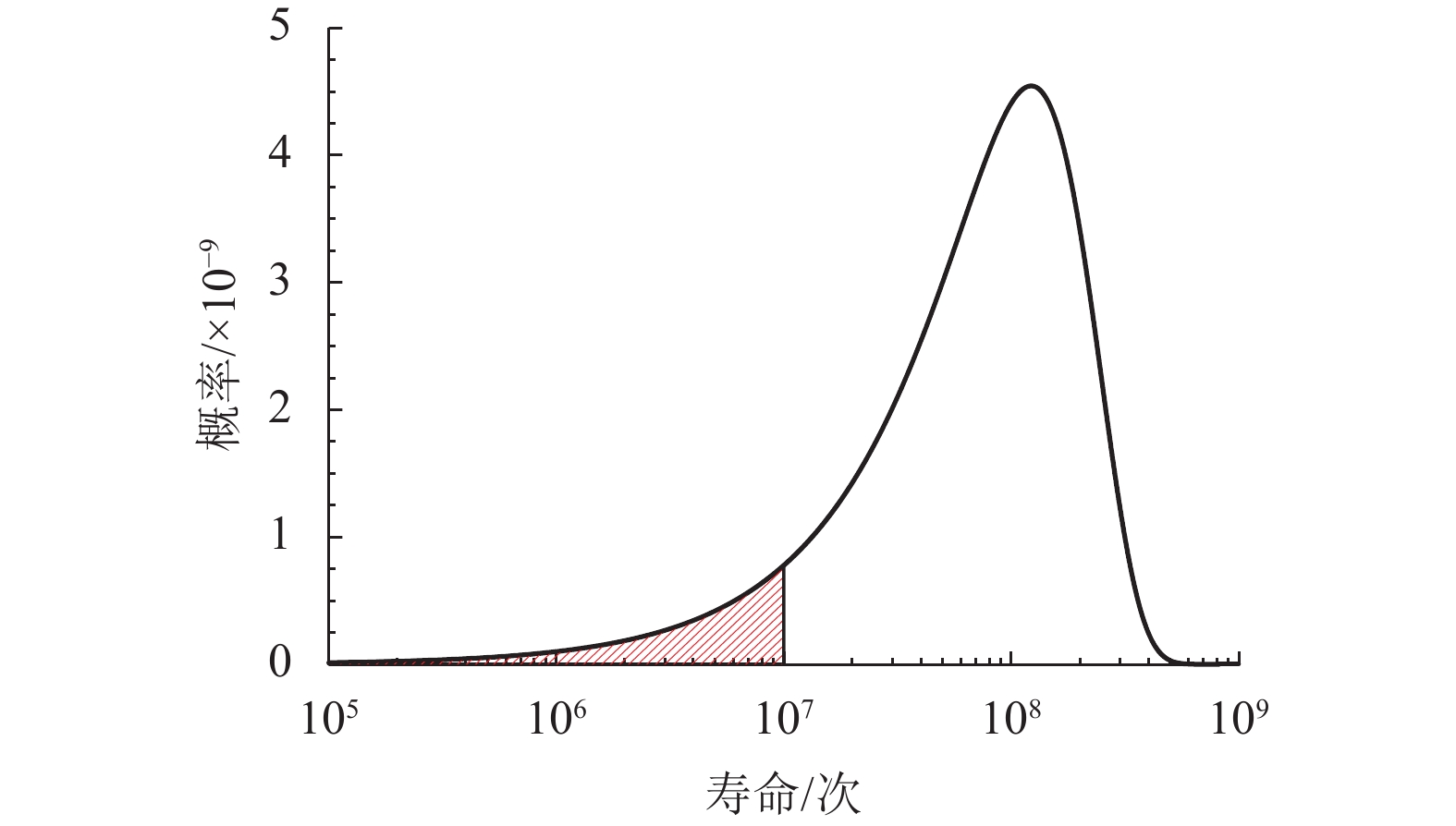
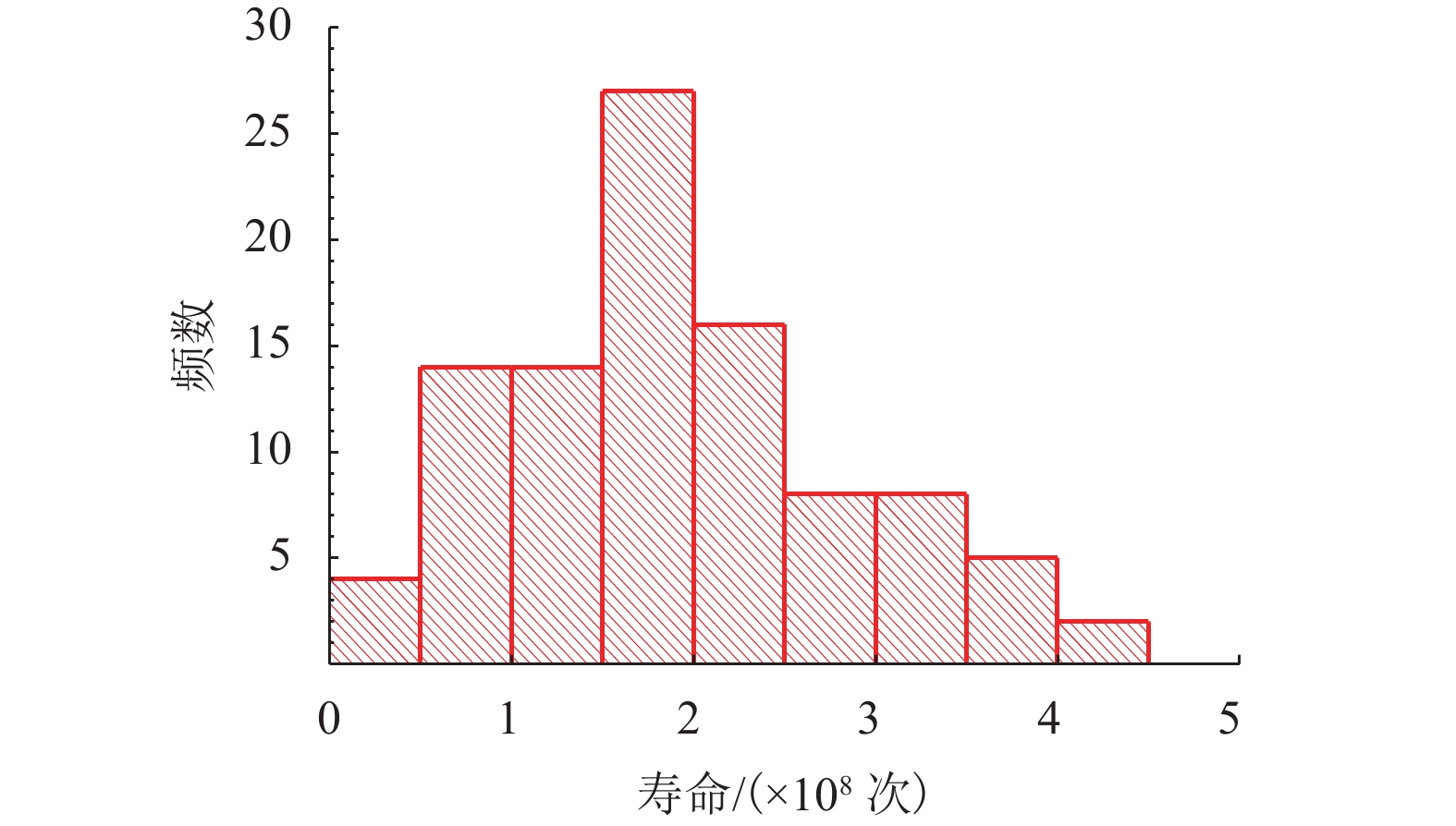
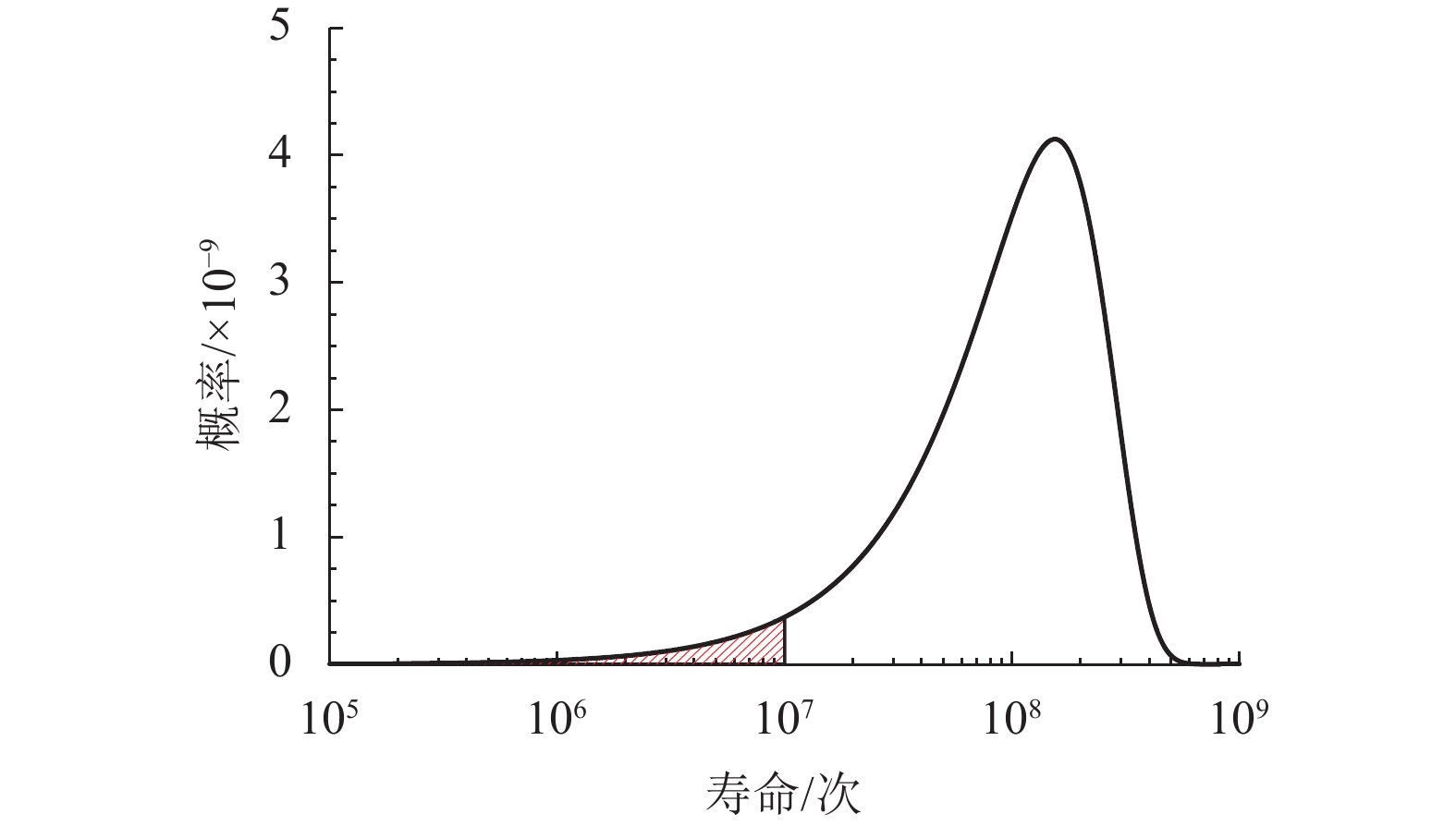
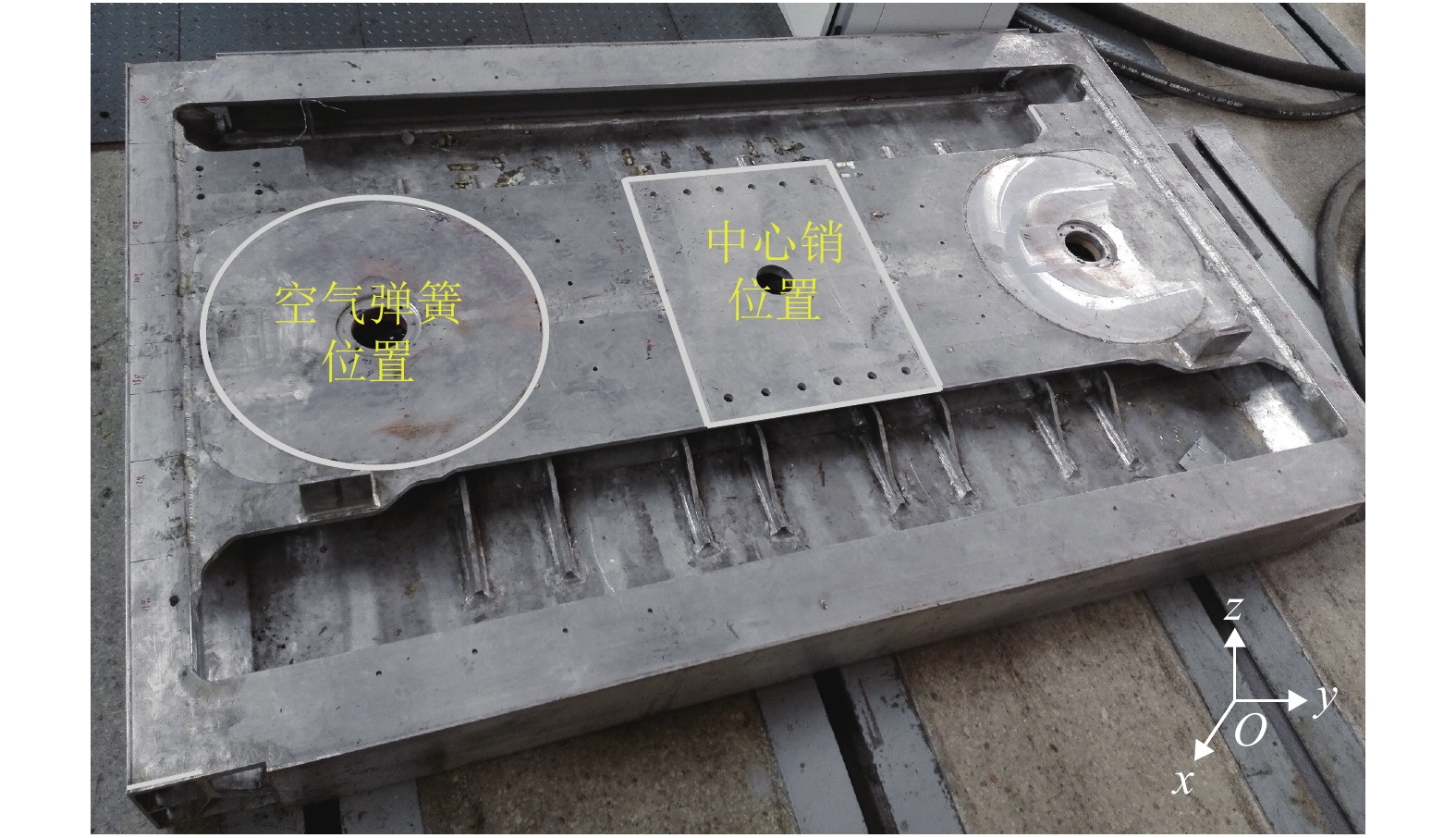
摘要: 为了研究地铁车辆枕梁服役安全性问题,考虑到大量疲劳实验耗时长且成本高,利用虚拟实验方法对枕梁结构疲劳寿命进行评估,根据EN12663-1标准设计枕梁静力实验,获得枕梁表面特征点的应力值和位移值;然后对枕梁进行有限元建模并仿真,对比静力实验结果,调整后获得与枕梁实际结构相符的有限元模型;最后利用Monte Carlo方法,进行地铁车辆枕梁在恒幅载荷与变幅载荷作用下的虚拟疲劳实验. 研究结果表明:在标准规定的恒幅载荷作用下,该地铁车辆枕梁寿命大于1 000万次载荷循环的可靠度约为0.73;在变幅载荷作用下,寿命大于1 000万次载荷作用的可靠度约为0.81;因此,该地铁车辆枕梁完全满足设计与使用要求.Abstract: To study the service safety of a metro train bolster, a virtual experiment method was used to evaluate fatigue lifetime, avoiding time-consuming and expensive fatigue tests. A static test of the bolster was designed based on the EN12663-1 standard, and the stresses and displacements on its surface were measured. An FEM model of the bolster was then established and analysed for comparison with the static test results; an FEM model that is consistent with the actual structure was thus determined. Finally, virtual experiments of the bolster under constant amplitude loads and variable amplitude loads were conducted using a Monte Carlo method. It is concluded that the fatigue reliability of this bolster with 107 loads cycles is 0.73 under constant amplitude loads and 0.81 under variable amplitude loads. This metro train bolster therefore meets the design and service requirements.
-
Key words:
- static test /
- finite element method /
- virtual experiments /
- reliability /
- lifetime prediction
-
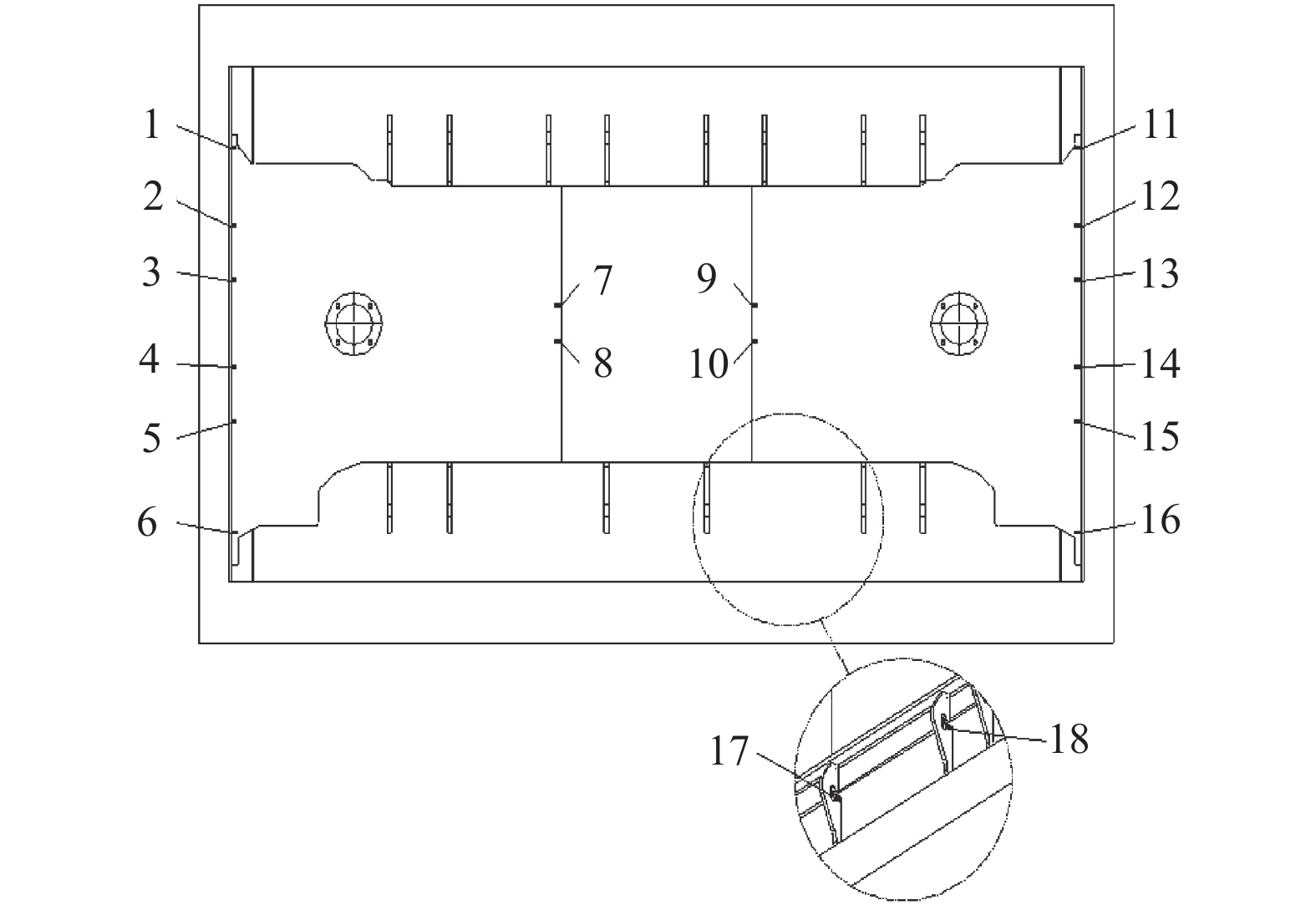
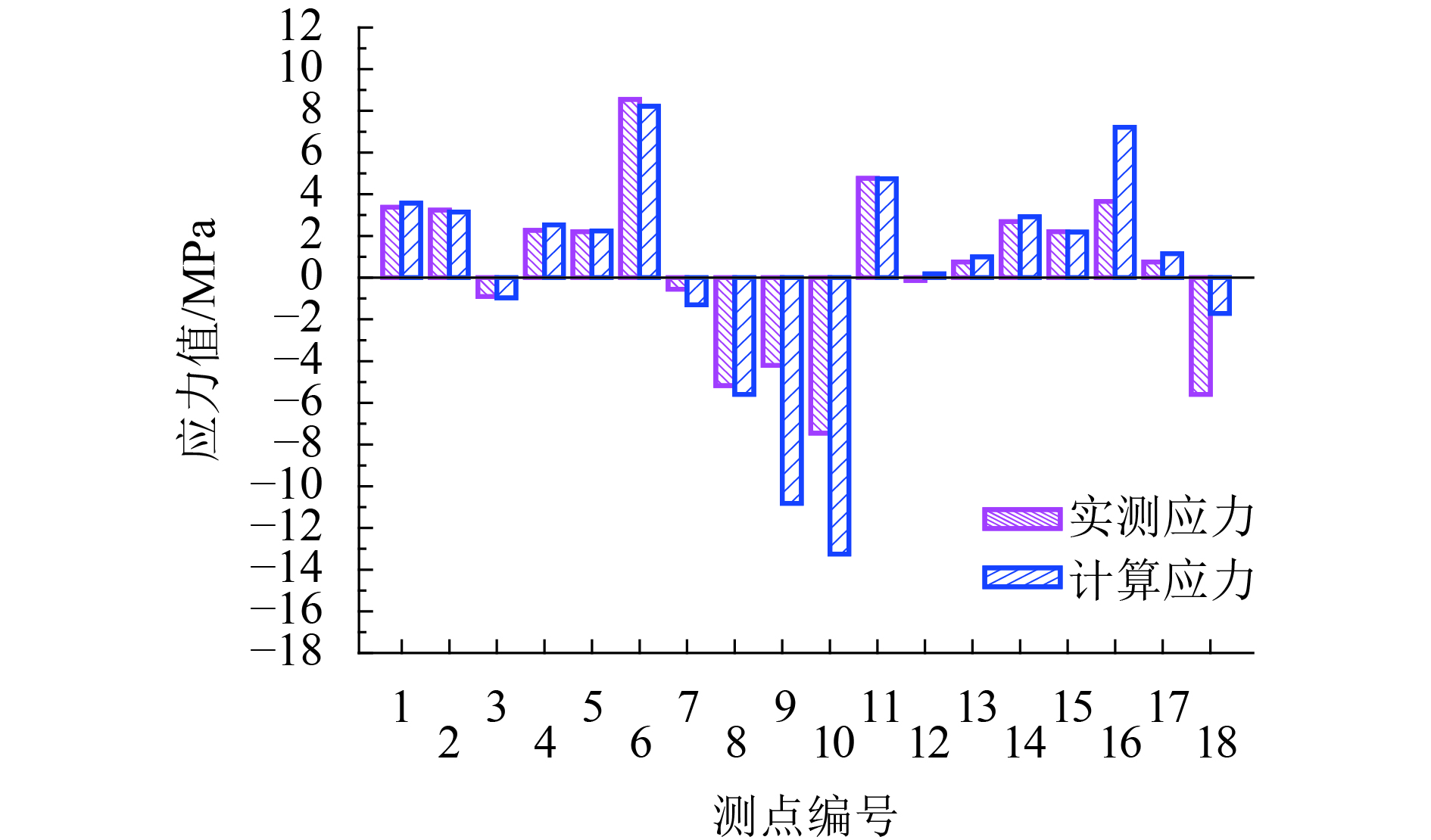
表 1 应力测点测量数据
Table 1. Results of the stress measurement sites
测点 应力值 测点 应力值 测点 应力值 1 3.381 7 – 0.552 13 0.759 2 3.243 8 – 5.175 14 2.691 3 – 0.897 9 – 4.209 15 2.208 4 2.277 10 – 7.452 16 3.657 5 2.208 11 4.761 17 0.759 6 8.556 12 – 0.138 18 – 5.589 表 2 位移测点测量数据
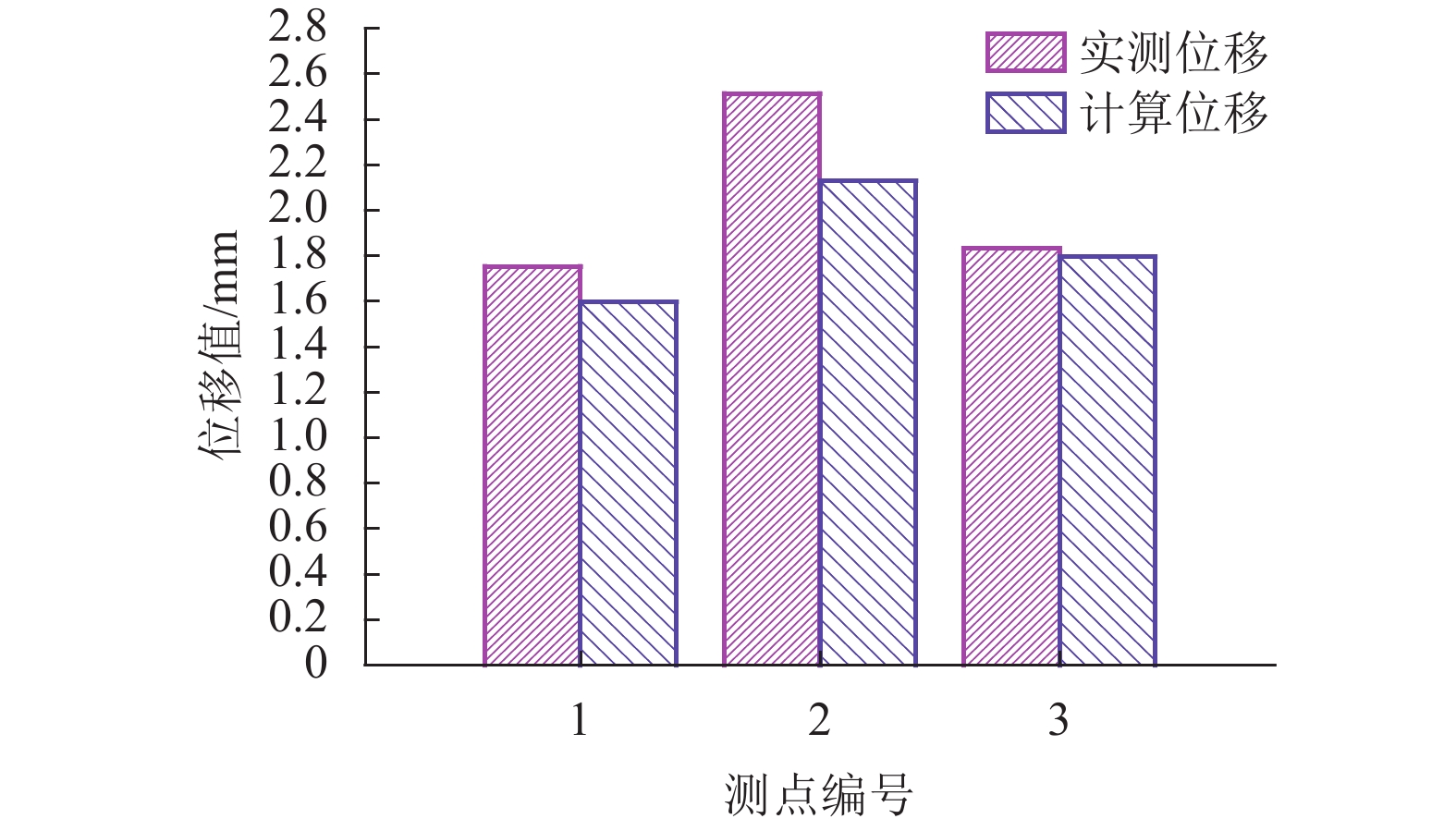
Table 2. Results of the displacement measurement sites
测点 位移值/mm 1 1.752 2 2.513 3 1.832 表 3 应力计算结果
Table 3. Stress calculation results
测点 应力值 测点 应力值 测点 应力值 1 3.580 7 –1.300 13 1.004 2 3.151 8 –5.590 14 2.924 3 –0.971 9 –10.814 15 2.191 4 2.536 10 –13.253 16 7.210 5 2.240 11 4.7454 17 1.148 6 8.220 12 0.184 18 –1.717 表 4 位移计算结果
Table 4. Displacement calculation results
测点 位移值 1 1.595 2 2.128 3 1.796 -
KIM J S, KIM N P. Evaluation of structural safety of a tilting bolster[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2007, 14(1): 63-72 张冉. 地铁铝合金枕梁焊接结构寿命评估[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2015 SONG Zhanxun, FANG Shaoxuan, ZHANG Yan, et al. Cracking analysis of bolster cover plate in C70 freight wagons[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2013, 30(2): 43-60 徐赐军. 挖泥船抓斗机滚筒虚拟实验分析[J]. 机械传动,2015,39(3): 126-128XU Cijun. Analysis of the virtual experiment of the roller in dredger grab machin[J]. Journal of Mechanical Transmission, 2015, 39(3): 126-128 李辉群,张鹏. 某专用校车顶部结构强度分析[J]. 客车技术与研究,2014,36(6): 9-11LI Huiqun, ZHANG Peng. Strength analysis of top structure for a special school bus[J]. Bus & Coach Technology and Research, 2014, 36(6): 9-11 杨帆,王红岩,尚其刚,等. 基于虚拟样机技术的坦克传动箱箱体结构强度分析[J]. 装甲兵工程学院学报,2008,22(2): 35-38YANG Fan, WANG Hongyan, SHANG Qigang, et al. Analysis on structure strength of tanks,gear box based on virtual prototyping technology[J]. Journal of Academy of Armored Force Engineering, 2008, 22(2): 35-38 LEI Liangyu, YANG Xiufang, LIU Jianjun. Virtual simulation method based reliability analyses on vehicular driving axle[J]. Intelligent Control & Automation, 2010, 20(1): 4019-4023 LI Ying, LIU Wenyuan. Dynamic dragline modeling for operation performance simulation and fatigue life prediction[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2013, 34(6): 93-101 YUAN Hengyi, HE Mingwang. Based on 3d virtual prototype technology and finite element analysis of the optimization of the automobile front axle[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 684: 330-334 许伟,杨济匡. 用于交通伤评估的头部有限元模型的虚拟实验验证[J]. 汽车工程,2008,30(2): 105,151-155XU Wei, YANG Jikuang. Virtual test validation of human head model for injury assessment in traffic accidents[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2008, 30(2): 105,151-155 许伟,杨济匡. 行人与汽车碰撞中颅骨骨折损伤机理的虚拟实验研究[J]. 汽车工程,2008,30(4): 291-296XU Wei, YANG Jikuang. A virtual experimental study on skull fracture injury mechanisms in car-pedestrian impact[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2008, 30(4): 291-296 LEE Dongchan, HAN Changsoo. CAE (computer aided engineering) driven durability model verification for the automotive structure development[J]. Finite Elem Anal Design, 2009, 45(5): 324-332 谢里阳, 王正, 周金宇. 机械可靠性基本理论与方法[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012: 120-133 何如. 高速列车铝合金焊接接头疲劳性能研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2008 SCHIJVE J. Fatigue of structures and materials[M]. Second Edition. Dordrecht: Springer, 2009: 249-255 -




 下载:
下载: