Stability Analysis and Evaluation of a Tunnel Entrance Slope Under Complex Disaster-Prone Environments
-
摘要:
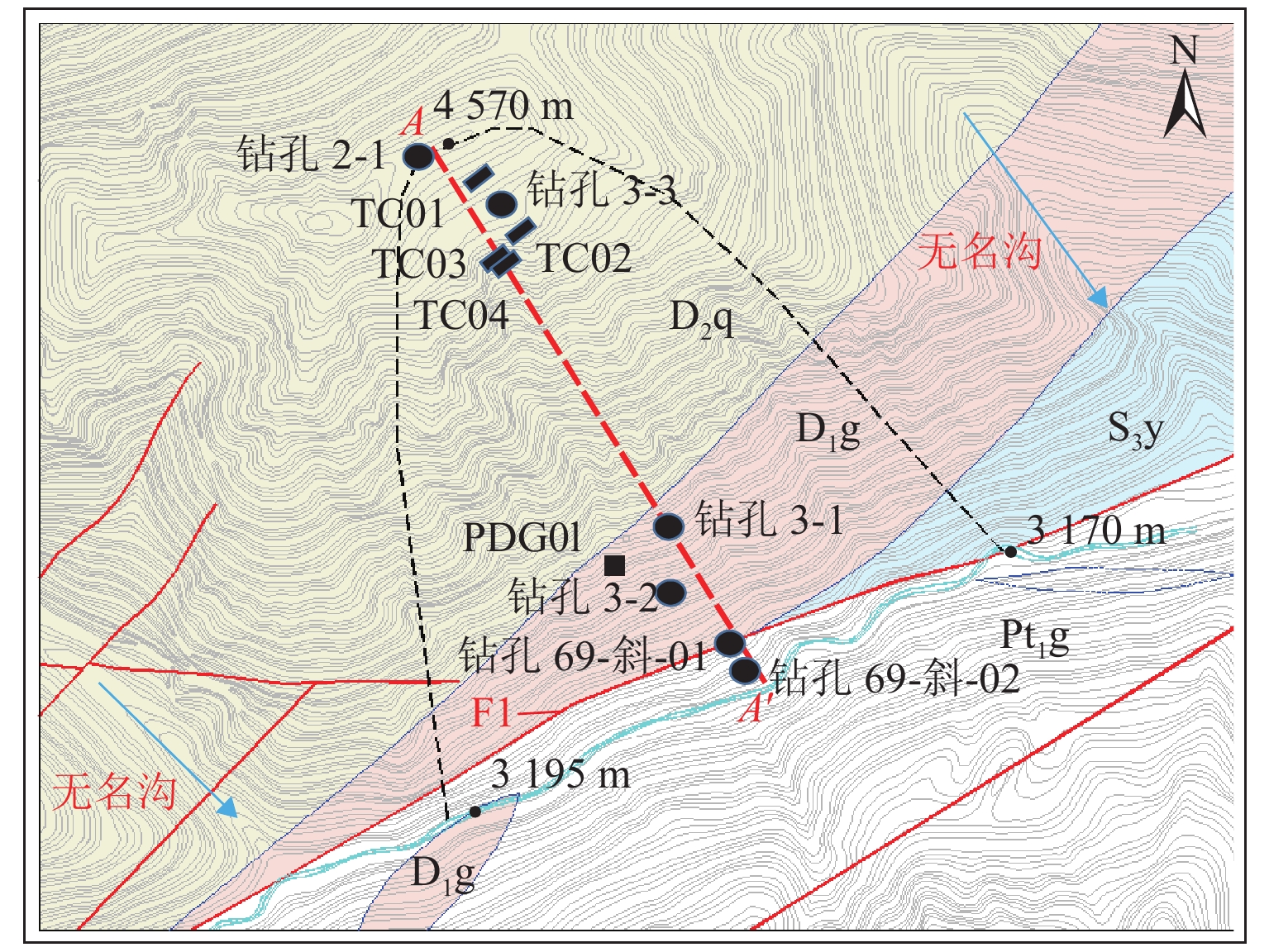
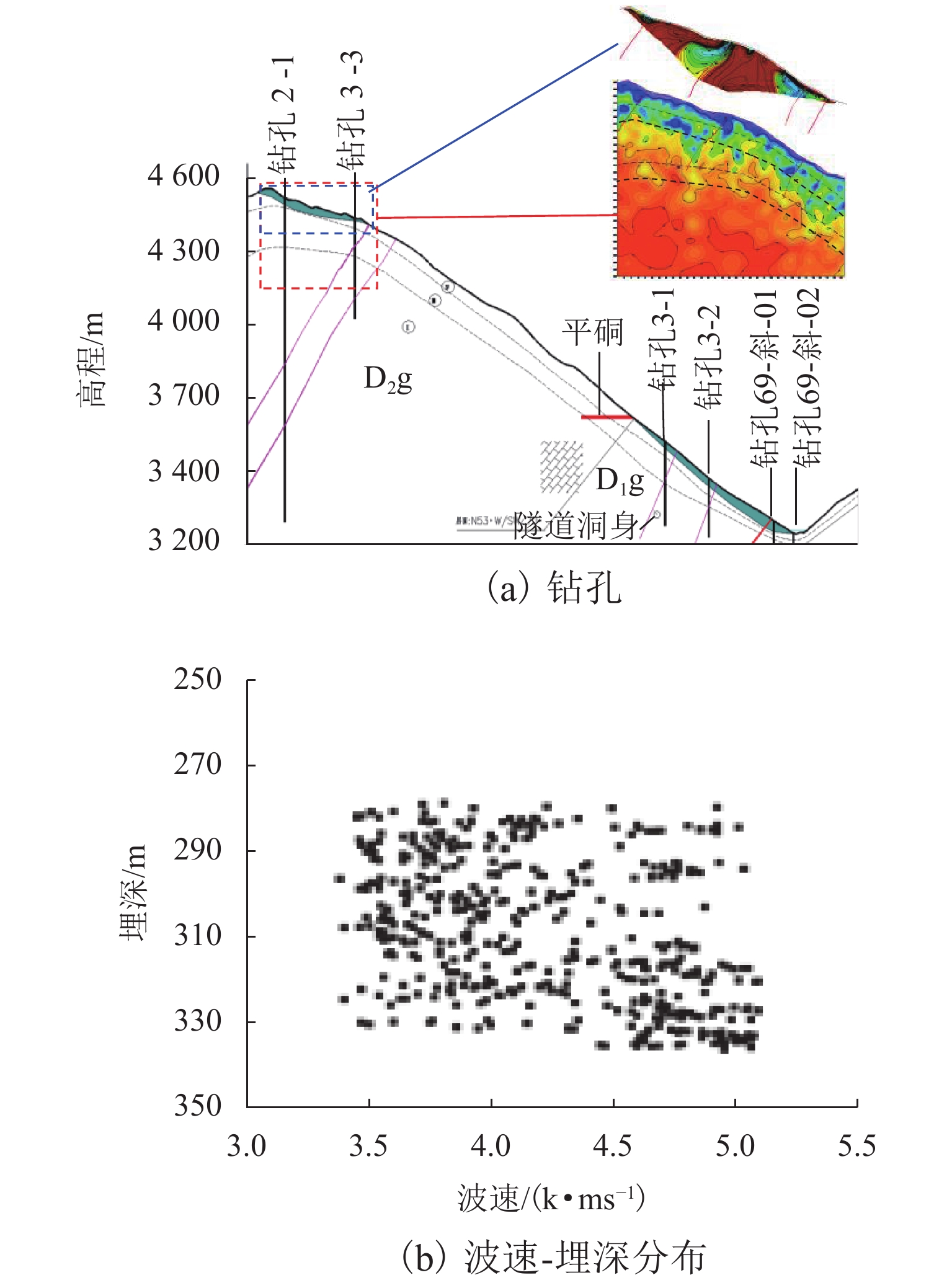
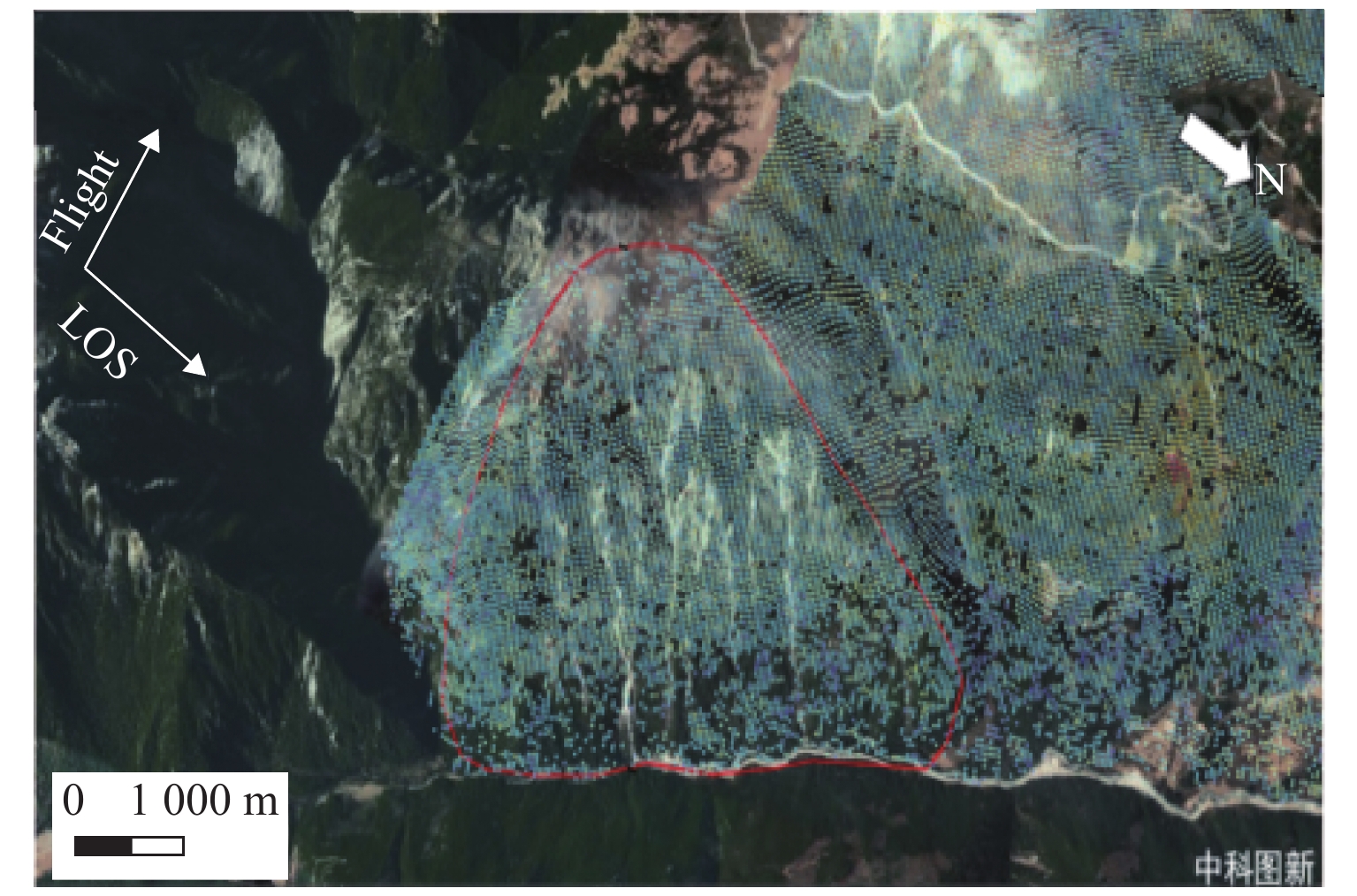
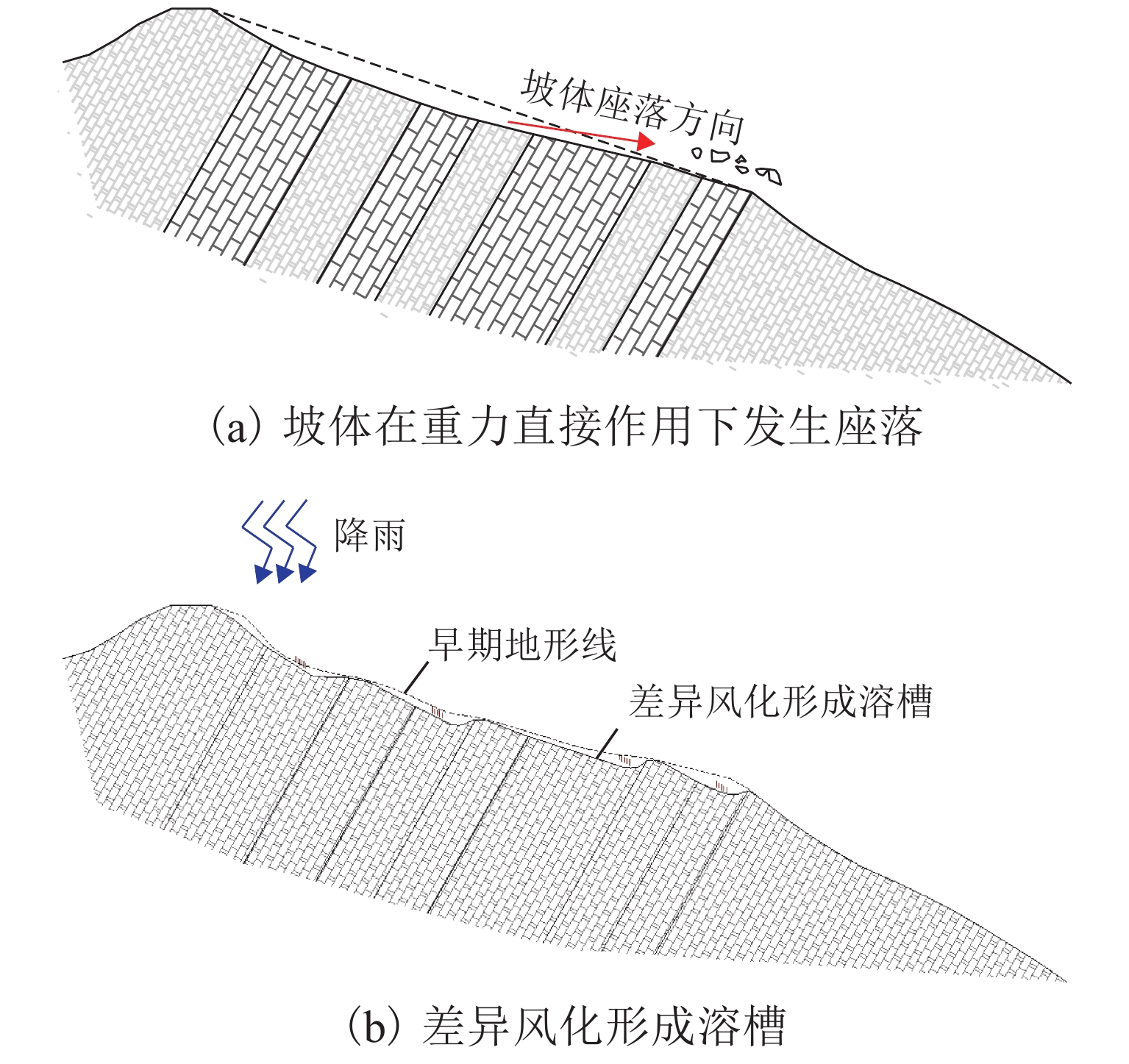
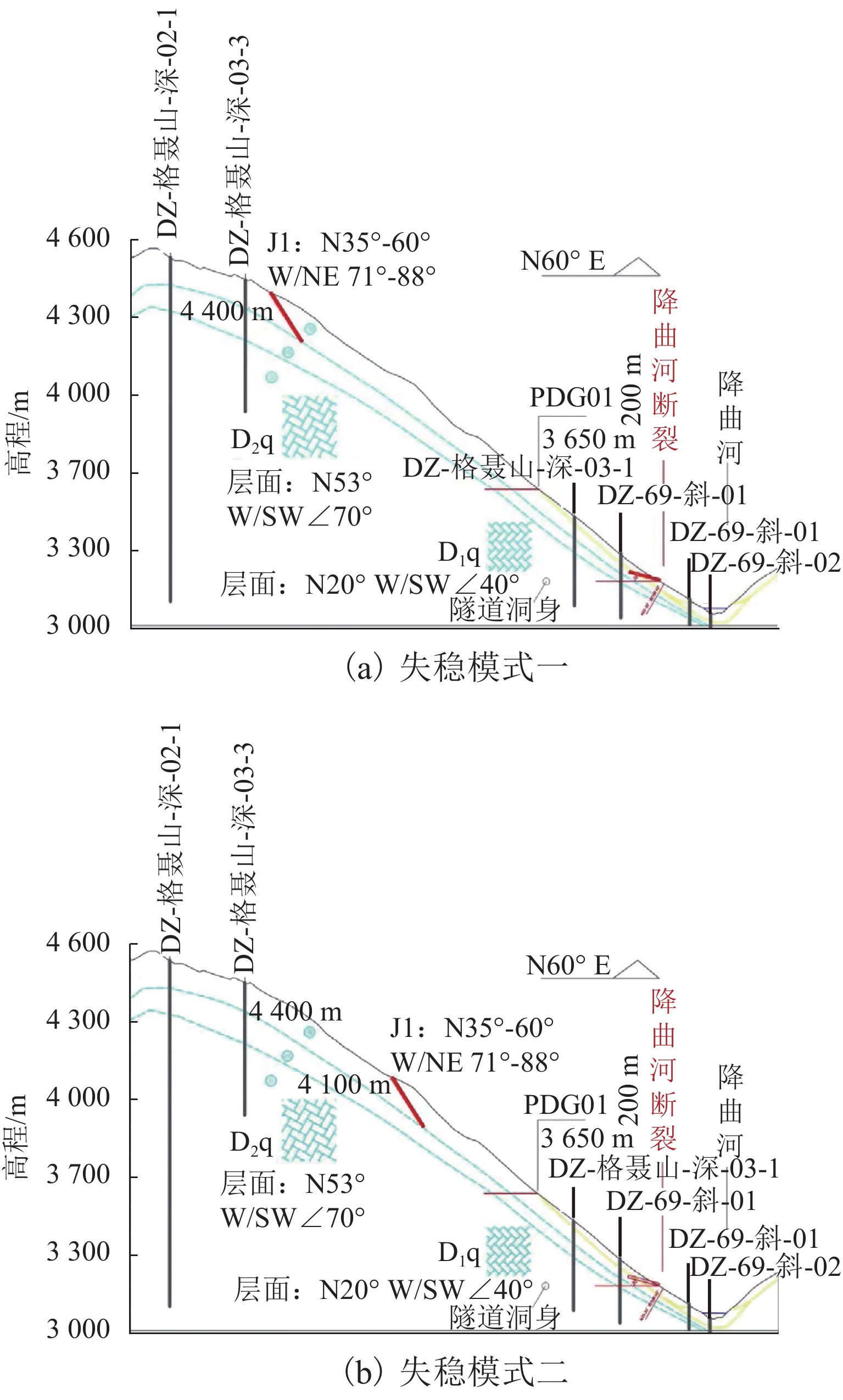
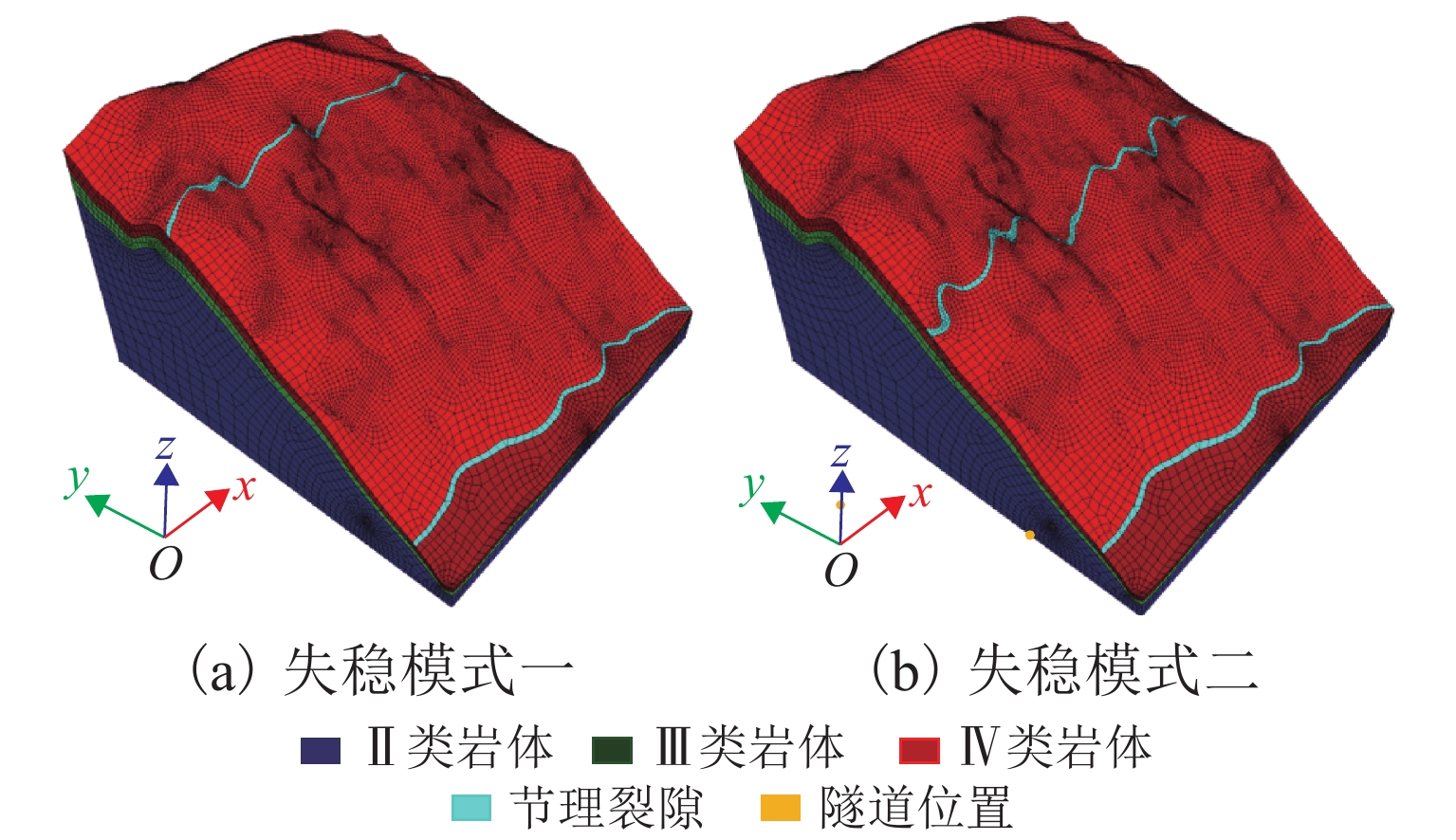
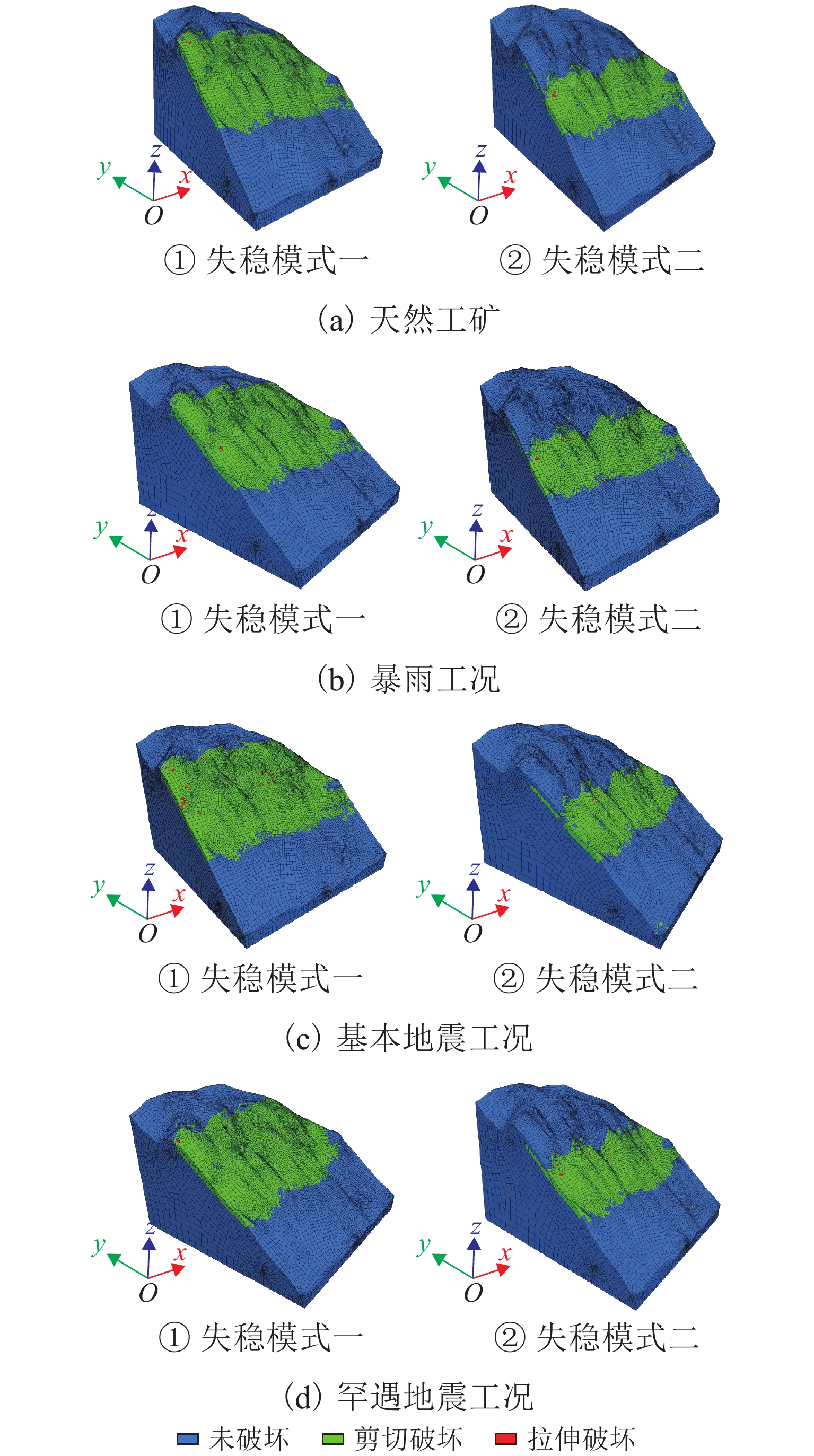
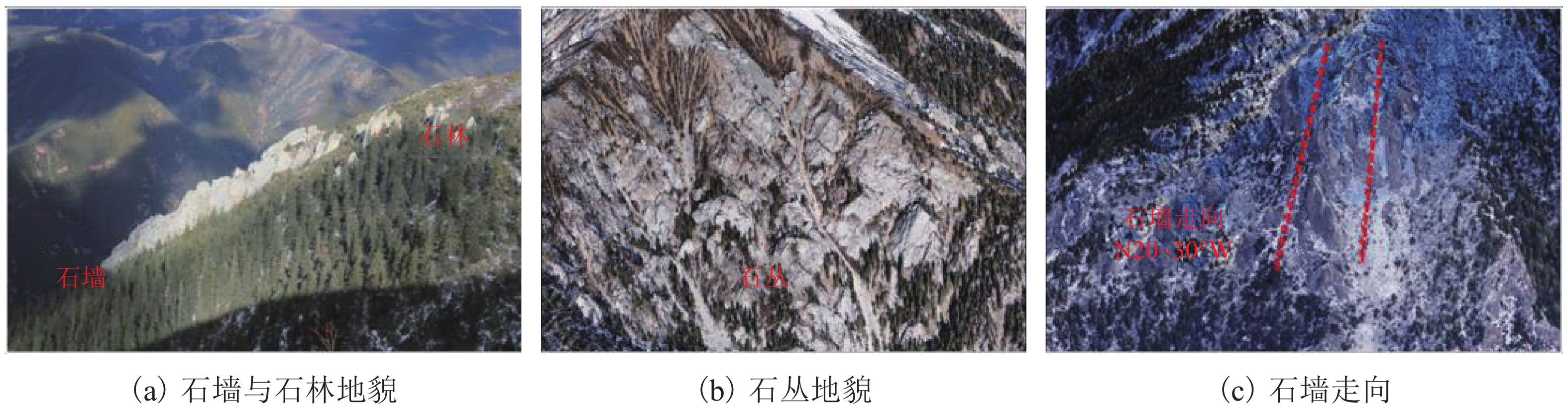
高地震烈度、高地应力、高陡、高寒等复杂孕灾环境下的隧道洞口斜坡,在降雨、强震或人类强烈工程活动影响下,极易发生崩塌、滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害. 为探究复杂孕灾环境下隧道进口斜坡在不同工况条件下的稳定性,以我国西南某加日山隧道为依托,通过无人机摄影、槽探、室内实验及洞探原位测试等“天空地”一体化勘察技术,实现斜坡工程地质信息精细获取,系统揭示斜坡典型破坏特征,讨论斜坡2种破坏成因与演化模式,在此基础上,利用极限平衡法与三维数值模拟方法,量化分析不同工况下的斜坡稳定性. 研究结果表明:加日山隧道进口斜坡在自然工况、暴雨工况、地震工况3种工况下稳定性系数均大于1.15,斜坡整体处于稳定状态,仅后缘表部存在局部变形失稳的可能,成果可为类似隧道的选线规划以及建设运营安全提供理论指导和技术支撑.
Abstract:Influenced by rainfall, strong earthquakes, and intensive engineering activities, the slope at the tunnel entrance may experience collapses, landslides, debris flows, and other geological disasters, especially under the complex conditions of violent earthquakes, high geostress, abrupt slopes, and extremely cold environments. To explore the stability of tunnel entrance slopes under different working conditions in complex disaster-prone environments, the Jiarishan tunnel in southwest China was taken as an example, and a “space-air-ground” integrated investigation technology combining unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) photography, surface trenching, laboratory experiments, field tests, and cave surveys was employed to obtain accurate engineering geological information. Typical failure characteristics of the studied slope were systematically revealed, and the two failure causes and evolution models of the slope were discussed. In addition, the slope stability under different working conditions was qualitatively analyzed using the limit equilibrium method and three-dimensional numerical simulation. The results indicate that the stability factor of the slope at the Jiarishan tunnel entrance is always greater than 1.15 under natural, rainstorm, and earthquake working conditions. Overall, the slope is stable except for the local deformation and instability of the shallow horizon of the posterior margin. This research can provide theoretical guidance and technical support for similar tunnels in terms of siting, construction, and operation safety.
-
Key words:
- disaster-prone environment /
- slope deformation /
- evolution mode /
- stability analysis
-
表 1 斜坡岩体力学参数建议值
Table 1. Suggested mechanical parameters of slope rock masses
岩体质量等级 干密度 ρd (g·cm−3) 变形模量 E0/GPa 泊松比 μ 抗剪断强度 摩擦系数 黏聚力 /MPa Ⅱ 类 2.52~2.58 10~20 0.25~0.29 1.20~1.40 1.50~2.00 Ⅲ 类 2.30~2.50 5~10 0.29~0.33 0.80~1.20 0.70~1.50 Ⅳ 类 2.10~2.40 2~5 0.33~0.37 0.55~0.80 0.30~0.70 表 2 结构面强度试验成果
Table 2. Test results ofstructural surface strength
试验编号 试验位置/m 抗剪断强度 抗剪强度 地质特征 摩擦系数 黏聚力/MPa 摩擦系数 黏聚力/MPa 1-1 PDG01 洞0+150 m 1.09 1.33 0.87 0.20 主要为压碎带弱风化大理岩,但剪切主要沿压碎带及其影响带剪断 1-2 PDG01 洞0+71 m 0.81 1.34 0.70 0.51 弱风化大理岩,碎裂结构,岩级为 Ⅳ 岩体 -
[1] 王振涛. 青藏高原的地质特征与形成演化[J]. 科技导报,2017,35(6): 51-58.WANG Zhentao. Geological features, the formation and the evolution of the Qinghai—Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(6): 51-58. [2] 刘刚,燕云鹏,刘建宇. 青藏高原西部地质灾害分布特征及背景分析[J]. 中国地质调查,2017,4(3): 37-45.LIU Gang, YAN Yunpeng, LIU Jianyu. Analysis of distribution character and background of geological hazards in western Qinghai—Tibet Plateau[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2017, 4(3): 37-45. [3] ZHAO S Y, HE Z L, DENG J H, et al. Giant river-blocking landslide dams with multiple failure sources in the Nu River and the impact on transient landscape evolution in southeastern Tibet[J]. Geomorphology, 2022, 413: 108357.0-108357.16. [4] CUI Y L, DENG J H, HU W Y, et al. 36Cl exposure dating of the Mahu Giant landslide (Sichuan Province, China)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 285: 106039.1-106039.11. [5] 杨帆. 西部山区大型滑坡分类及识别图谱初步研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2017. [6] 陈帆,刘立,陆海空,等. 岩质高陡边坡稳定性分析[J]. 西华大学学报(自然科学版),2010,29(3): 54-55,94.CHEN Fan, LIU Li, LU Haikong, et al. Stability analysis of high and steep rock slope[J]. Journal of Xihua University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 29(3): 54-55,94. [7] 雷远见,王水林. 基于离散元的强度折减法分析岩质边坡稳定性[J]. 岩土力学,2006,27(10): 1693-1698.LEI Yuanjian, WANG Shuilin. Stability analysis of jointed rock slope by strength reduction method based on UDEC[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(10): 1693-1698. [8] 邓建辉,高云建,余志球,等. 堰塞金沙江上游的白格滑坡形成机制与过程分析[J]. 工程科学与技术,2019,51(1): 9-16.DENG Jianhui, GAO Yunjian, YU Zhiqiu, et al. Analysis on the formation mechanism and process of baige landslides damming the upper reach of Jinsha River, China[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2019, 51(1): 9-16. [9] GAO Y J, ZHAO S Y, DENG J H, et al. Flood assessment and early warning of the reoccurrence of river blockage at the Baige landslide[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2021, 31(11): 1694-1712. doi: 10.1007/s11442-021-1918-9 [10] CHEN F, GAO Y J, ZHAO S Y, et al. Kinematic process and mechanism of the two slope failures at Baige Village in the upper reaches of the Jinsha River, China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2021, 80(4): 3475-3493. doi: 10.1007/s10064-021-02146-0 [11] YANG Z K, WEI J B, DENG J H, et al. Mapping outburst floods using a collaborative learning method based on temporally dense optical and SAR data: a case study with the baige landslide dam on the Jinsha River, Tibet[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(11): 2205.1-2205.21. [12] 朱赛楠,殷跃平,王猛,等. 金沙江结合带高位远程滑坡失稳机理及减灾对策研究——以金沙江色拉滑坡为例[J]. 岩土工程学报,2020,43(4): 688-697.ZHU Sainan, YIN Yueping, WANG Meng, et al. Instability mechanism and disaster mitigation measures of long-distance landslide at high location in Jinsha River junction zone: case study of Sela landslide in Jinsha River, Tibet[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 43(4): 688-697. [13] ZHANG S L, YIN Y P, HU X W, et al. Geo-structures and deformation-failure characteristics of rockslide areas near the Baige landslide scar in the Jinsha River tectonic suture zone[J]. Landslides, 2021, 18(11): 3577-3597. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01741-2 [14] 刘文,王猛,朱赛楠,等. 基于光学遥感技术的高山极高山区高位地质灾害链式特征分析——以金沙江上游典型堵江滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5): 29-39.LIU Wen, WANG Meng, ZHU Sainan, et al. An analysis on chain characteristics of highstand geological disasters in high mountains and extremely high mountains based on optical remote sensing technology: a case study of representative large landslides in upper reach of Jinsha River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(5): 29-39. [15] YAO X, LI L J, ZHANG Y S, et al. Types and characteristics of slow-moving slope geo-hazards recognized by TS-InSAR along Xianshuihe active fault in the eastern Tibet Plateau[J]. Natural Hazards, 2017, 88(3): 1727-1740. doi: 10.1007/s11069-017-2943-y [16] 郭长宝,吴瑞安,李雪,等. 川西日扎潜在巨型岩质滑坡发育特征与形成机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(4): 772-783.GUO Changbao, WU Ruian, LI Xue, et al. Developmental characteristics and formation mechanism of the rizha potential giant rock landslide, western Sichuan Province, China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(4): 772-783. [17] 谭明健, 周春梅, 孙东, 等. 软硬互层顺层岩质边坡破坏试验[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 274-281, 324.TAN Mingjian, ZHOU Chunmei, SUN Dong, et al. Failure experiment of soft-hard interlayer bedding rock slope, 2022, 41(2): 274-281, 324. [18] 黄少平,晏鄂川,尹晓萌,等. 不同临空条件的层状反倾岩质边坡倾倒变形几何特征参数影响规律[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(1): 159-165.HUANG Shaoping, YAN Echuan, YIN Xiaomeng, et al. Action law of geometrical characteristic parameters in the anti-dip rock slopes under different free face conditio[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 159-165. [19] 伍保祥. 金沙江上游波罗水电站库区滑坡发育规律及岸坡稳定性风险分析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2008. [20] 帅正阳. 叶巴滩水电站坝区右岸深部变形破裂成因模拟研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2017. [21] 朱吉龙. 溪洛渡库区滑坡地质灾害风险评价研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2019. -





 下载:
下载: