Ionospheric Correction and Analysis for Time-series InSAR Based on Reformulating Range Split Spectrum Interferometry
-
摘要:
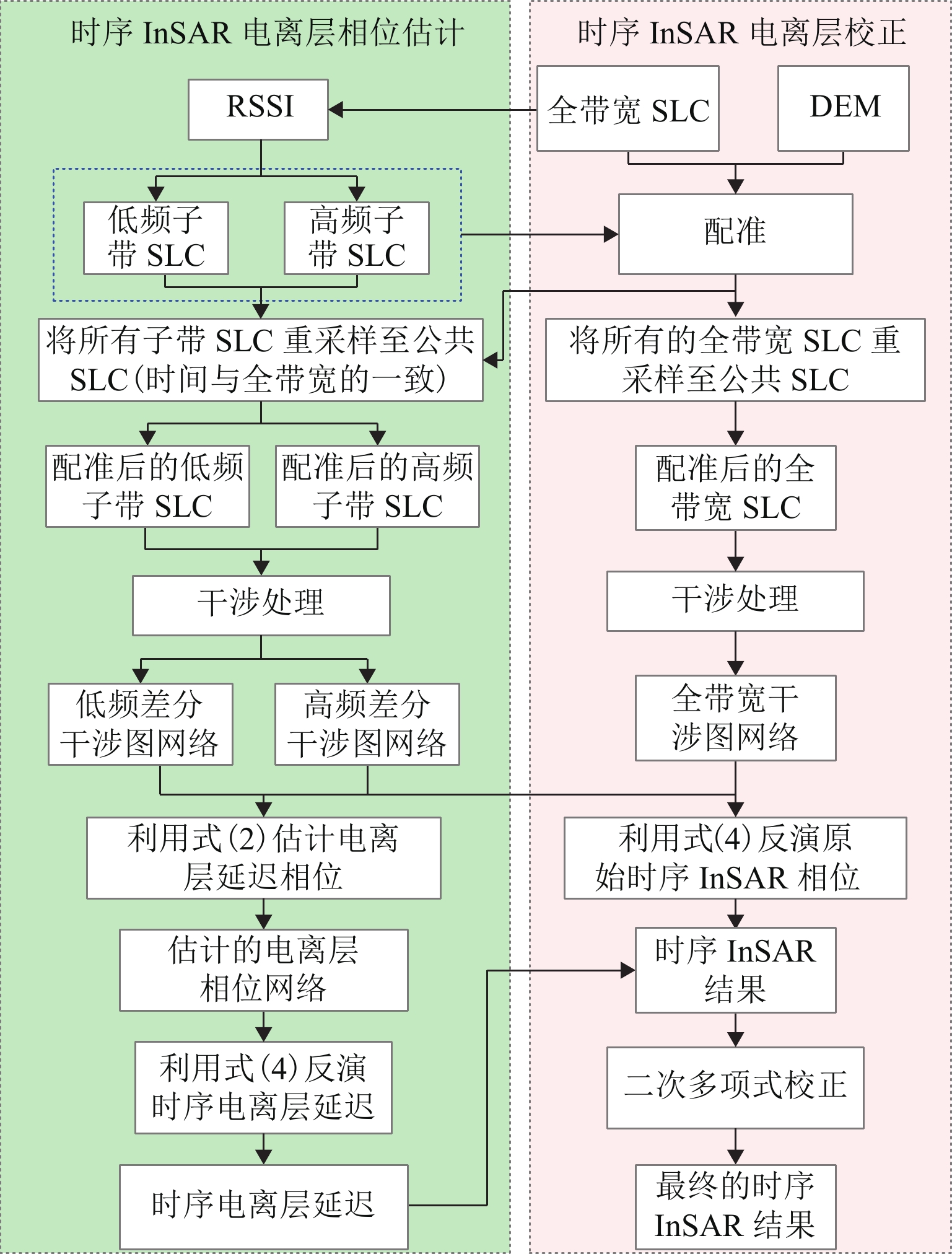
合成孔径雷达干涉技术(InSAR)受电离层延迟影响较大,特别是在低高纬地区,用于时序InSAR解算的干涉对数量大大减少,严重影响了低频合成孔径雷达(SAR)系统的监测精度. 针对该问题,引入重构距离向分谱法(RRSSI),将其扩展为时序InSAR电离层误差估计与校正方法. 为测试方法性能,获取2006年6月至2010年8月间覆盖阿拉斯加Anaktuvuk河区域的ALOS-1 PALSAR数据进行实验. 实验结果表明:本文方法能够有效估计时序InSAR结果中的电离层误差,且对小空间尺度电离层扰动具有较高的敏感性;经提出方法校正后,研究区域的年平均形变速率均值从校正前的1.46 cm/a降至0.49 cm/a,而标准差则从1.16 cm/a降至0.65 cm/a,精度显著提升;选取时序点的累积形变由校正前的大幅波动变得更加平稳,更符合形变规律.
-
关键词:
- 小基线集-InSAR /
- 电离层校正 /
- 距离向分谱法 /
- 时序
Abstract:Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) is greatly affected by ionospheric delay, especially at low and high latitudes, which decreases the number of available interferometric pairs for time-series InSAR and the monitoring accuracy of low-frequency SAR systems. To this end, the reformulating range split spectrum interferometry (RRSSI) was introduced for the ionospheric error estimation and correction in time-series InSAR. The performance of the proposed method was tested by ALOS-1 PALSAR images covering the Anaktuvuk River area in Alaska from June 2006 to August 2010. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively estimate the ionospheric errors of time-series InSAR results and is sensitive to ionospheric disturbances at small spatial scales. After correction, the average annual deformation rate in the study area decreases from 1.46 to 0.49 cm/year, and the standard deviation from 1.16 to 0.65 cm/year, indicating an improvement in monitoring accuracy. Additionally, the cumulative deformation of the selected time-series points becomes more stable than the large fluctuation before correction, which is more consistent with the real deformation.
-
Key words:
- SBAS-InSAR /
- ionospheric correction /
- range split spectrum method /
- time series
-
-
[1] WRIGHT P A, QUEGN S, WHEADON N S, et al. Faraday rotation effects on L-band spaceborne SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2003,41(12):2735-2744. [2] PI X Q. Ionospheric effects on spaceborne synthetic aperture radar and a new capability of imaging the ionosphere from space[J]. Space Weather,2015,13(11):737-741. [3] MEYER F, BAMLER R, JAKOWSKI N, et al. The potential of low-frequency SAR systems for mapping ionospheric TEC distributions[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters,2006,3(4):560-564. [4] MAO W F, LIU G X, WANG X W, et al. An InSAR ionospheric correction method based on variance component estimation with integration of MAI and RSS measurements[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing,2021,14:1423-1433. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3045267 [5] ZHANG B C, DING X L, ZHU W, et al. Mitigating ionospheric artifacts in coseismic interferogram based on offset field derived from ALOS-PALSAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing,2016,9(7):3050-3059. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2533441 [6] KAZUO O C. Recent trend and advance of synthetic aperture radar with selected topics[J]. Remote Sensing,2013,5(2):716-807. [7] ROTT H. Advances in interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) in earth system science[J]. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment,2009,33(6):769-791. doi: 10.1177/0309133309350263 [8] 刘国祥,陈强,罗小军,等. InSAR原理与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019. [9] AOKI Y, FURUYA M, DE ZAN F, et al. L-band synthetic aperture radar: current and future applications to earth sciences[J]. Earth, Planets and Space,2021,73(1):1-4. doi: 10.1186/s40623-020-01323-x [10] RAUCOULES D, DE MICHELE M. Assessing ionospheric influence on L-band SAR data: implications on coseismic displacement measurements of the 2008 Sichuan earthquake[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters,2010,7(2):286-290. [11] JUNG H S, LEE D T, LU Z, et al. Ionospheric correction of SAR interferograms by multiple-aperture interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2013,51(5):3191-3199. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2218660 [12] WEGMULLER U, STROZZI T, WERNER C. Ionospheric path delay estimation using split-beam interferometry[C]//2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Munich: IEEE, 2012: 3631-3634. [13] FREEMAN A F. Calibration of linearly polarized polarimetric SAR data subject to faraday rotation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2004,42(8):1617-1624. [14] ZHU W, JUNG H S, CHEN J Y. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry (InSAR) ionospheric correction based on faraday rotation: two case studies[J]. Applied Sciences,2019,9(18):3871.1-3871.19. [15] GOMBA G, PARIZZI A, DE ZAN F, et al. Toward operational compensation of ionospheric effects in SAR interferograms: the split-spectrum method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2015,54(3):1446-1461. [16] FATTAHI H, SIMONS M, AGRAM P. InSAR time-series estimation of the ionospheric phase delay: an extension of the split range-spectrum technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2017,55(10):5984-5996. [17] GOMBA G, DE ZAN F, PARIZZI A. Ionospheric phase screen and ionospheric azimuth shift estimation combining the split-spectrum and multi-squint methods[C]//Proceedings of EUSAR 2016: 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar. Hamburg: VDE, 2016: 1-4. [18] LIANG C R, LIU Z, FIELDING E J, et al. InSAR time series analysis of L-band wide-swath SAR data acquired by ALOS-2[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2018,56(8):4492-4506. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2821150 [19] LIANG C R, AGRAM P, SIMONS M, et al. Ionospheric correction of InSAR time series analysis of C-band sentinel-1 TOPS data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2019,57(9):6755-6773. [20] WEGMÜLLER U, WERNER C, FREY O, et al. Reformulating the split-spectrum method to facilitate the estimation and compensation of the ionospheric phase in SAR interferograms[J]. Procedia Computer Science,2018,138:318-325. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.045 [21] BERARDINO P, FORNARO G, LANARI R, et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2002,40(11):2375-2383. [22] ZHANG Y, FATTAHI H, AMELUNG F. Small baseline InSAR time series analysis: Unwrapping error correction and noise reduction[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2019,133:104331.1-104331.29. [23] JONES B M, KOLDEN C A, JANDT R, et al. Fire behavior, weather, and burn severity of the 2007 anaktuvuk river tundra fire, north slope, Alaska[J]. Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research,2009,41(3):309-316. doi: 10.1657/1938-4246-41.3.309 [24] LIU L, JAFAROV E E, SCHAEFER K M, et al. InSAR detects increase in surface subsidence caused by an Arctic tundra fire[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2014,41(11):3906-3913. doi: 10.1002/2014GL060533 [25] LIAO H. Ionospheric correction of interferometric sar data with application to the cryospheric sciences[D]. Alaska Fairbanks: University of Alaska Fairbanks, 2018. [26] ZHANG B. Mitigation of ionospheric artifacts in InSAR data for estimating earthquake deformation[D]. Hong Kong: The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, 2020. -




 下载:
下载:






